10-K: Annual report pursuant to Section 13 and 15(d)
Published on June 23, 2023
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM
(Mark One)
For the fiscal year ended
or
For the transition period from |
|
to |
|
Commission file number:
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
Québec, |
|
|
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) |
(Address of principal executive offices, including zip code)
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code:
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class |
|
Name of each exchange on which registered |
|
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files).
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer |
☐ |
Accelerated filer |
☐ |
|
|
|
|
☒ |
Smaller reporting company |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Emerging growth company |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. Yes ☐ No ☒
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common shares held by non-affiliates of the registrant, based on the closing sale price of the registrant’s common shares on the last business day of its most recently completed second fiscal quarter, as reported on the Nasdaq Stock Market, was approximately $
Auditor Firm Id:
Former Auditor Firm Id: 85 Auditor Name: KPMG LLP Auditor Location: Montréal, QC, Canada
ACASTI PHARMA INC.
FORM 10-K
For the Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2023
Table of Contents
|
|
|
|
|
Item 1. |
7 |
|
|
Item 1A. |
16 |
|
|
Item 1B. |
36 |
|
|
Item 2. |
36 |
|
|
Item 3. |
36 |
|
|
Item 4. |
36 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 5. |
37 |
|
|
Item 6. |
40 |
|
|
Item 7. |
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operation |
41 |
|
Item 7A. |
51 |
|
|
Item 8. |
51 |
|
|
Item 9. |
Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
51 |
|
Item 9A. |
51 |
|
|
Item 9B. |
51 |
|
|
Item 9C. |
Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 10. |
52 |
|
|
Item 11. |
54 |
|
|
Item 12. |
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Shareholder Matters |
60 |
|
Item 13. |
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions and Director Independence |
61 |
|
Item 14. |
63 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 15. |
65 |
|
|
Item 16. |
65 |
|
|
|
||
SPECIAL NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This annual report contains information that may be forward-looking information within the meaning of Canadian securities laws and forward-looking statements within the meaning of U.S. federal securities laws, both of which we refer to in this annual report as forward-looking information. Forward- looking information can be identified by the use of terms such as “may”, “will”, “should”, “expect”, “plan”, “anticipate”, “believe”, “intend”, “estimate”, “predict”, “potential”, “continue” or other similar expressions concerning matters that are not statements about the present or historical facts. Forward-looking information in this annual report includes, among other things, information or statements about:
Although the forward-looking statements in this annual report are based upon what we believe are reasonable assumptions, you should not place undue reliance on those forward-looking statements since actual results may vary materially from them. Important assumptions made by us when making forward-looking statements include, among other things, assumptions by us that:
In addition, the forward-looking statements in this annual report are subject to a number of known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors many of which are beyond our control, that could cause our actual results and developments to differ materially from those that are disclosed in or implied by the forward-looking statements, including, among others:
All of the forward-looking statements in this annual report are qualified by this cautionary statement. There can be no guarantee that the results or developments that we anticipate will be realized or, even if substantially realized, that they will have the consequences or effects on our business, financial condition, or results of operations that we anticipate. As a result, you should not place undue reliance on the forward-looking statements. Except as required by applicable law, we do not undertake to update or amend any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise. All forward-looking statements are made as of the date of this annual report.
We express all amounts in this annual report in U.S. dollars, except where otherwise indicated. References to “$” and “U.S.$” are to U.S. dollars and references to “C$” or “CAD$” are to Canadian dollars.
Except as otherwise indicated, references in this annual report to “Acasti,” “the Corporation,” “we,” “us” and “our” refer to Acasti Pharma Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries.
PART I
Item 1. Business
Overview
We are focused on developing and commercializing products for rare and orphan diseases that have the potential to improve clinical outcomes by using our novel drug delivery technologies. We seek to apply new proprietary formulations to approved and marketed pharmaceutical compounds to achieve enhanced efficacy, faster onset of action, reduced side effects, more convenient drug delivery and increased patient compliance; all of which could result in improved patient outcomes. The active pharmaceutical ingredients used in the drug candidates under development by Acasti may be already approved in a target indication or could be repurposed for use in new indications.
The existing well understood efficacy and safety profiles of these marketed compounds provides the opportunity for us to utilize the Section 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway under the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act for the development of our reformulated versions of these drugs, and therefore may provide a potentially shorter path to regulatory approval. Under Section 505(b)(2), if sufficient support of a product’s safety and efficacy either through previous FDA experience or sufficiently within the scientific literature can be established, it may eliminate the need to conduct some of the pre-clinical and clinical studies that new drug candidates might otherwise require.
Our therapeutic pipeline consists of three unique clinical stage and multiple pre-clinical stage assets supported by an intellectual property portfolio of more than 40 granted and pending patents in various jurisdictions worldwide. These drug candidates aim to improve clinical outcomes in the treatment of rare and orphan diseases by applying proprietary formulation and drug delivery technologies to existing pharmaceutical compounds to achieve improvements over the current standard of care, or to provide treatment for diseases with no currently approved therapies.
We believe that rare disorders represent an attractive area for drug development, and there remains an opportunity for Acasti to utilize already approved drugs that have established safety profiles and clinical experience to potentially address significant unmet medical needs. A key advantage of pursuing therapies for rare disorders is the potential to receive orphan drug designation (“ODD”) from the FDA. Acasti's three drug candidates currently in clinical development have received ODD status, provided certain conditions are met at NDA approval. ODD provides for seven years of marketing exclusivity in the United States post-launch, provided certain conditions are met, and the potential for faster regulatory review. ODD status can also result in tax credits of up to 50% of clinical development costs conducted in the United States upon market approval and a waiver of the NDA fees, which we estimate can translate into savings of approximately $3.0 million. Developing drugs for rare diseases can often allow for clinical trials that are more manageably scaled and may require a smaller, more targeted commercial infrastructure.
The specific diseases targeted for drug development by Acasti are well understood although these patient populations may remain poorly served by available therapies or in some cases approved therapies do not yet exist. We aim to effectively treat debilitating symptoms that result from these underlying diseases.
Our lead drug candidate:
Other drug candidates:
In April 2023, we announced the strategic decision to prioritize development of GTX-104 with a goal to advance to commercialization, while conserving resources as much as possible to complete development efficiently. We estimate that the deferral of GTX-102 and GTX-101 could be 3 years given the timeline to complete the development and commercial launch of GTX 104. Further development of GTX-102 and GTX-101 will occur at such time as we obtain additional funding or enter into strategic partnerships for license or sale with third parties.
The decision to defer further development has triggered a comprehensive impairment review of our intangible assets in March 2023. Given the extended timeline, we increased the discount rates used to value the assets in order to recognize additional risks related to prioritizing one asset over the others, financing the projects given limited available resources and the need to preserve cash to advance GTX 104 as far as possible, potential competitor advances that could arise over three years, and the general market depression affecting small cap development companies like us and the prohibitively high dilution and expense of available funding in the capital markets. Increasing the discount rates significantly reduced the discounted cash flow values for each of the programs deferred. Accordingly, in the quarter ended March 31, 2023 we booked impairment charges related to GTX 102 and GTX 101 of $22.7M and $6.0M respectively, together with further adjustments made to deferred taxes and goodwill directly related to those assets. The impairment charge overall amounts to $33.5M. Management continues to believe that GTX 102 and GTX 101 will eventually provide significant value for the Company when development resumes and they are launched successfully.
Our management team possesses significant experience in drug formulation and drug delivery research and development, clinical and pharmaceutical development and manufacturing, regulatory affairs, and business development, as well as being well-versed in late-stage drug development and commercialization. Importantly, our team is comprised of industry professionals with deep expertise and knowledge, including a world-renowned practicing neurosurgeon-scientist and respected authority in SAH, as well as product development, chemistry, manufacturing and controls (“CMC”), planning, implementation, management, and execution of global Phase 2 and Phase 3 trials for a drug candidate for SAH.
GTX-104 Overview
Nimodipine was granted FDA approval in 1988, and is the only approved drug that has been clinically shown to improve neurological outcomes in SAH patients. It is only available in the United States as a generic oral capsule and as a branded oral liquid solution called NYMALIZE, which is manufactured and sold by Arbor
7
Pharmaceuticals (acquired in September 2021 by Azurity Pharmaceuticals). Nimodipine has poor water solubility and high permeability characteristics as a result of its high lipophilicity. Additionally, orally administered nimodipine has dose-limiting side-effects such as hypotension, poor absorption and low bioavailability resulting from high first-pass metabolism, and a narrow administration window as food effects lower bioavailability significantly. Due to these issues, blood levels of orally administered nimodipine can be highly variable, making it difficult to manage blood pressure in SAH patients. Nimodipine capsules are also difficult to administer, particularly to unconscious patients or those with impaired ability to swallow. Concomitant use with CYP3A inhibitors is contraindicated (NIMODIPINE Capsule PI).
NIMOTOP is an injectable form of nimodipine that is manufactured by Bayer Healthcare. It is approved in Europe and in other regulated markets (but not in the United States). It has limited utility for SAH patients because of its high organic solvent content, namely 23.7% ethanol and 17% polyethylene glycol 400 (NIMOTOP SmPC).
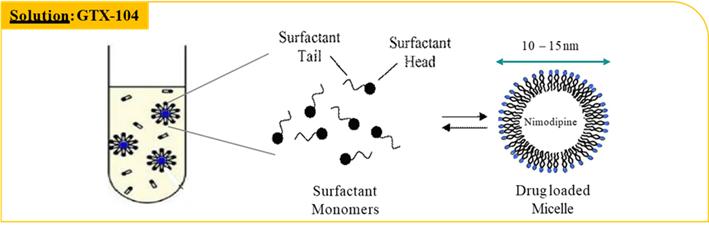
Key potential benefits of GTX-104 include:
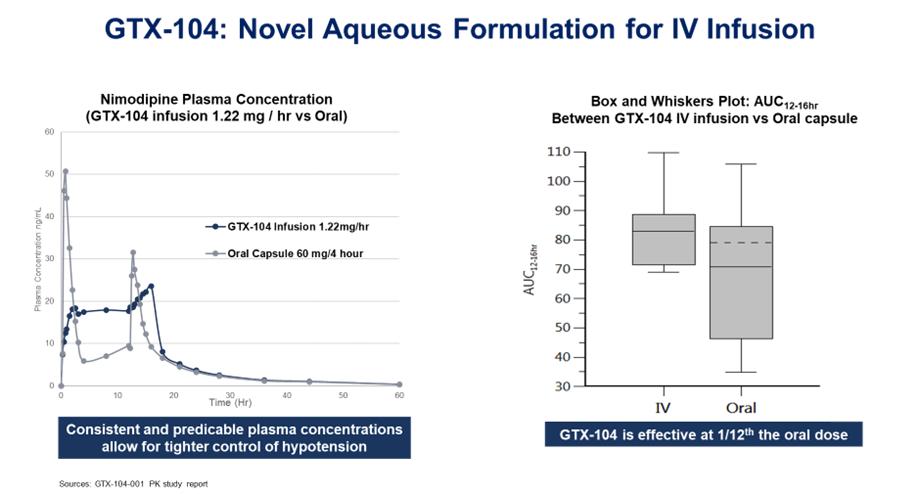
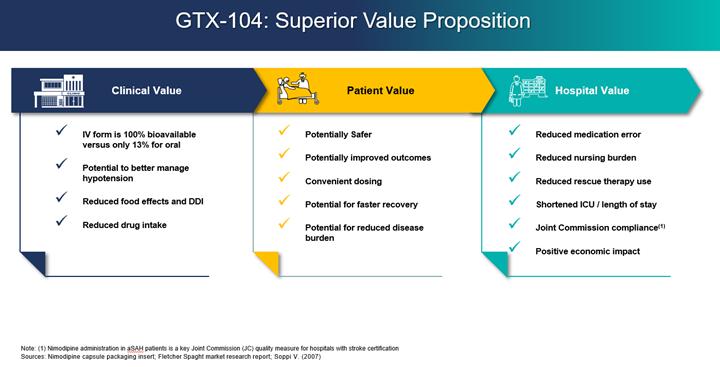
GTX-104 could provide a more convenient mode of administration as compared to generic nimodipine capsules or NYMALIZE GTX-104 is administered as an initial bolus followed by a continuous infusion as compared to oral administration via a nasogastric tube in unconscious patients every two to four hours for both nimodipine capsules and NYMALIZE solution. Therefore, GTX-104 could make a major contribution to patient care by potentially reducing the dosing frequency, and the associated nursing burden. More convenient continuous, and consistent dosing can also reduce the risk of medication errors. In addition, as depicted in the charts below, two PK studies have shown that GTX-104 has the potential to provide improved bioavailability and lower intra-subject variability compared to oral administration. Because of its IV formulation, we also expect GTX-104 to reduce certain drug-drug interactions and food effects.
8
Despite the positive impact it has on recovery, physicians often must discontinue their patients from oral nimodipine, primarily as a result of hypotensive episodes that cannot be controlled by titrating the oral form of drug. Such discontinuation could potentially be avoided by administering GTX-104, which because of its IV administration, may reduce the complexity associated with the need for careful attention to the timing of nimodipine administration at least one hour before or two hours after a meal. Administration of GTX-104 via a peripheral vein is often much more comfortable for the patients compared to administration by central venous access (as is the case for NIMOTOPTM), which can often be a difficult, invasive and more risky procedure. Also, unconscious patients will likely receive more consistent concentrations of nimodipine when delivered via the IV route as compared to oral gavage or a nasogastric tube. More consistent dosing is expected to result in a reduction of vasospasm and a better, more consistent management of hypotension. As summarized in the table below, we also anticipate reduced use of rescue therapies, such as vasopressors, and expensive hospital resources, such as the angiography suite, are possible by more effectively managing blood pressure with GTX-104. Reduced incidences of vasospasm could result in shorter length of stay and better outcomes.
About Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)
SAH is bleeding over the surface of the brain in the subarachnoid space between the brain and the skull, which contains blood vessels that supply the brain. A primary cause of such bleeding is rupture of an aneurysm. The result is a relatively uncommon type of stroke that accounts for about 5% of all strokes and has an incidence of six per 100,000 person years (Becske, 2018).
In contrast to more common types of stroke in elderly individuals, SAH often occurs at a relatively young age, with approximately half the affected patients younger than 60 years old (Becske, 2018). Approximately 10% to 15% of aneurysmal SAH (“aSAH”) patients die before reaching the hospital (Rinkel, 2016), and those who survive the initial hours post hemorrhage are admitted or transferred to tertiary care centers with high risk of complications, including rebleeding and delayed cerebral ischemia (“DCI”). Systemic manifestations affecting cardiovascular, pulmonary, and renal function are common and often complicate management of DCI. Approximately 70% of aSAH patients experience death or a permanent dependence on family members, and half die within one month after the hemorrhage. Of those who survive the initial month, half remain permanently dependent on a caregiver to maintain daily living (Becske, 2018).
We estimate that approximately 50,000 individuals experience aSAH each year in the US based on third-party market research, and that total addressable market for SAH is approximately $300 million in the U.S. There are an estimated 150,000 aSAH patients each year in China and approximately 55,000 patients in the European Union based on annual inpatient admissions and the average length-of-stay.
GTX-104 Recent Activities & Near Term Milestones: Conduct Phase 3 Safety Study
In September 2021, we initiated our pivotal PK bridging trial to evaluate the relative bioavailability of GTX-104 compared to currently marketed oral nimodipine capsules in approximately 50 healthy subjects. The PK trial was the next required step in our proposed 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway for GTX-104.
Final results from this pivotal PK trial were reported on May 18, 2022, and showed that the bioavailability of GTX-104 compared favorably with the oral formulation of nimodipine in all subjects, and no serious adverse events were observed for GTX-104.
All three endpoints indicated that statistically there was no difference in exposures between GTX-104 and oral nimodipine over the defined time periods for both maximum exposure and total exposure. Plasma concentrations obtained following IV administration showed significantly less variability between subjects as compared to oral administration of capsules, since IV administration is not as sensitive to some of the physiological processes that affect oral administration, such as taking the drug with and without meals, variable gastrointestinal transit time, variable drug uptake from the gastrointestinal tract into the systemic circulation, and variable hepatic blood flow and hepatic first pass metabolism. Previous studies have shown these processes significantly affect the oral bioavailability of nimodipine, and therefore cause oral administration to be prone to larger inter- and intra-subject variability.
9
The bioavailability of oral nimodipine capsules observed was only 8% compared to 100% for GTX-104. Consequently, about one-twelfth the amount of nimodipine is delivered with GTX-104 to achieve the same blood levels as with the oral capsules.
No serious adverse events and no adverse events leading to withdrawal were reported during the trial.
Next Steps – Initiate Phase 3 Safety trial for GTX-104
In April 2023, we received a Type C written meeting response and clarifying feedback from the FDA on our proposed Phase 3 safety trial for GTX-104. The FDA provided additional comments on our development plan that, pending submission of the final clinical protocol and FDA approval of same, will allow us to proceed with the initiation of a Phase 3 safety clinical trial in aSAH patients.
The FDA concurred with the suitability of the 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway with the selected Reference Listed Drug NIMOTOP oral capsules (NDA 018869), and that our GTX-104-002 PK trial may have met the criteria for a scientific bridge.
Based on the FDA's proposed Phase 3 trial design, we will target enrollment of aSAH patients (across all grades of severity) in a 1:1 randomized trial with oral nimodipine, to be conducted in an estimated 25-30 sites in the U.S. The FDA confirmed the use of the Hunt and Hess scale to stratify patients based on severity. The primary endpoint is safety, and it will be measured as the percentage of significant adverse events of hypotension related to study drugs in both arms.
We expect the first patient to be enrolled during the second half of 2023. The trial is expected to take approximately18 months to complete from the time the first patient is enrolled, and we expect this safety trial to be the final clinical step required to seek approval under the 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway. Before submitting a NDA, we plan to hold a pre-NDA meeting with the FDA to enhance the likelihood of market approval.
GTX-102 Overview
GTX-102 is a novel, concentrated oral-mucosal spray of betamethasone intended to improve neurological symptoms of Ataxia Telangiectasia (“A-T”) for which there are currently no FDA-approved therapies. GTX-102 is a stable, concentrated oral spray formulation comprised of the gluco-corticosteroid betamethasone that together with other excipients can be sprayed conveniently over the tongue of the A-T patient and is rapidly absorbed.
About Ataxia Telangiectasia
A-T is a rare genetic progressive autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder that affects children, with the hallmark symptoms of cerebellar ataxia and other motor dysfunction, and dilated blood vessels (telangiectasia) that occur in the sclera of the eyes. A-T is caused by mutations in the ataxia telangiectasia gene, which is responsible for modulating cellular response to stress, including breaks in the double strands of DNA.
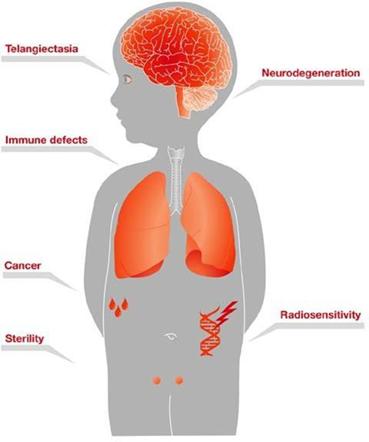
Children with A-T begin to experience balance and coordination problems when they begin to walk (toddler age), and ultimately become wheelchair-bound in their second decade of life. In pre-adolescence (between ages 5 and 8), patients experience oculomotor apraxia, dysarthria, and dysphagia. They also often develop compromised immune systems and are at increased risk of developing respiratory tract infections and cancer (typically lymphomas and leukemia) (U.S. National Cancer Institute A-T, 2015).
A-T is diagnosed through a combination of clinical assessment (especially neurologic and oculomotor deficits), laboratory analysis, and genetic testing. There is no known treatment to slow disease progression, and treatments that are used are strictly aimed at controlling the symptoms (e.g., physical, occupational or speech therapy for neurologic issues), or conditions secondary to the disease (e.g., antibiotics for lung infections, chemotherapy for cancer, etc.) (U.S. National Cancer Institute A-T, 2015). There are no FDA-approved therapeutic options currently available. Patients typically die by age 25 from complications of lung disease or cancer. According to a third-party report we commissioned, A-T affects approximately 4,300 patients per year in the United States and has a potential total addressable market of $150 million, based on the number of treatable patients in the United States.
GTX-102 - R&D and Clinical Studies to Date
We have licensed the data from the multicenter, double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled crossover trial from Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Senese, Siena, Italy, where Dr. Zannolli et. al. studied the effect of oral liquid solution of betamethasone to reduce ataxia symptoms in patients with A-T. This oral liquid solution is not marketed in the United States, and therefore is not available for clinical use; currently, betamethasone is only available in the United States as an injectable or as a
10
topical cream. This license gives us the right to reference the study’s data in its NDA filing. On November 12, 2015, we submitted the data from the Zannolli study to the FDA’s Division of Neurology at a pre-Investigational New Drug (“IND”) meeting and received guidance from the agency on the regulatory requirements to seek approval.
In a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled crossover trial conducted in Italy, Dr. Zannolli et al. studied the effect of an oral liquid solution of betamethasone on the reduction of ataxia symptoms in 13 children (between ages 2 to 8 years) with A-T. The primary outcome measure was the reduction in ataxia symptoms as assessed by the International Cooperative Ataxia Rating Scale (“ICARS”).
In the trial, oral liquid betamethasone reduced the ICARS total score by a median of 13 points in the intent-to-treat population and 16 points in the per-protocol population (the median percent decreases of ataxia symptoms of 28% and 31%, respectively). Adverse events in the trial were minimal, with no compulsory withdrawals and only minor side effects that did not require medical intervention. Clinical trial results in A-T patients administered oral betamethasone indicated that betamethasone significantly reduced ICARS total score relative to placebo (P = 0.01). The median ICARS change score (change in score with betamethasone minus change in score with placebo) was -13 points (95% confidence interval for the difference in medians was -19 to -5.5 points).
Based on the Zannolli data, we believe that our GTX-102 concentrated oral spray has the potential to provide clinical benefits in decreasing A-T symptoms, including assessments of posture and gait disturbance and kinetic, speech and oculomotor functions. In addition, GTX-102 may ease drug administration for patients experiencing A-T given its application of 1-3x/day of 140µL of concentrated betamethasone liquid sprayed onto the tongue using a more convenient metered dose delivery system, as these A-T patients typically have difficulty swallowing (lefton-greif 2000).
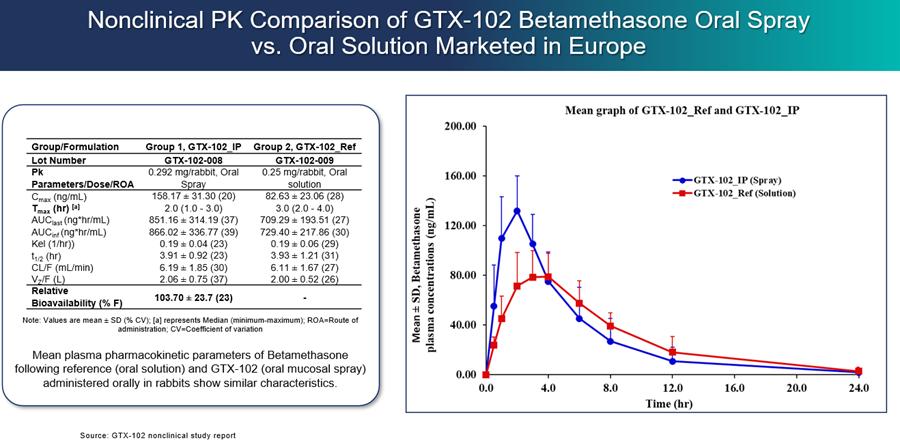
GTX-102 PK Data to Date:
GTX-102 administered as a concentrated oral spray achieves similar blood levels at only 1/70th the volume of an oral solution of betamethasone. This more convenient mode of administration will be important for A-T patients who have difficulties swallowing large volumes of liquids.
GTX-102 Recent Activities:
11
We initiated a PK bridging trial of GTX-102 as compared to the oral liquid solution of betamethasone used in the Zannolli study and against the injectable form of betamethasone that is approved in the U.S. in the third calendar quarter of 2022. The primary objectives of the PK bridging trial were to evaluate the bioavailability, pharmacokinetics and safety of GTX-102. On December 28, 2022, we reported that the topline results of this trial met all primary outcome measures.
Results showed that GTX-102 betamethasone blood concentrations were highly predictable and consistent based on AUC (the area under the concentration time curve up to 72 hours post-dose, extrapolated to infinity) and Cmax (the maximum concentration occurring between 0 hour to 72 hours after study drug administration), indicating good linearity and dose-proportionality. GTX-102 betamethasone blood concentrations were within the same range of exposure as IM betamethasone, based on AUC. This IM formulation will serve as a bridge for GTX-102 in the context of the proposed 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway. GTX-102 betamethasone blood concentrations were also within the same range of exposure as Oral Solution (OS), based on AUC. This OS formulation was used by Zannolli and may serve as a clinical comparator for further clinical development. Furthermore, statistically there was no significant difference (p>0.05) between GTX-102 administered at a fast rate (each spray immediately following the preceding one) vs. a slow rate (1 spray/minute), as indicated by Cmax and AUC. We believe this result is important because being able to use the fast or the slow rate of administration may provide greater flexibility for patients and caregivers. The Cmax of GTX-102 was within the same range of exposure as the OS, but the Cmax for the IM formulation was lower than both GTX-102 and the OS, as well as what has been reported previously for the IM in industry publications. It is important to note that achieving bioequivalence with the IM was not an objective of this trial, nor was it expected. Finally, of the 48 healthy adult subjects, no serious adverse events (AE) were reported, and the most frequent drug-related adverse effect was mild headache (4 cases).
The further development of GTX-102 has been deprioritized in favor of our focus on development of GTX-104. Pending additional dedicated funding for GTX-102 or the signing of a strategic partnership, We will work with our clinical experts and the FDA to determine the best final dosing regimen for GTX-102 to incorporate into our Phase 3 trial design. Based on previous discussions with the FDA, we plan to conduct a confirmatory Phase 3 safety and efficacy trial in A-T patients, and plan to seek guidance from the FDA on the trial design at a Type B meeting. It is also possible that we may out-license or sell our GTX-102 drug candidate.
GTX-101 Overview
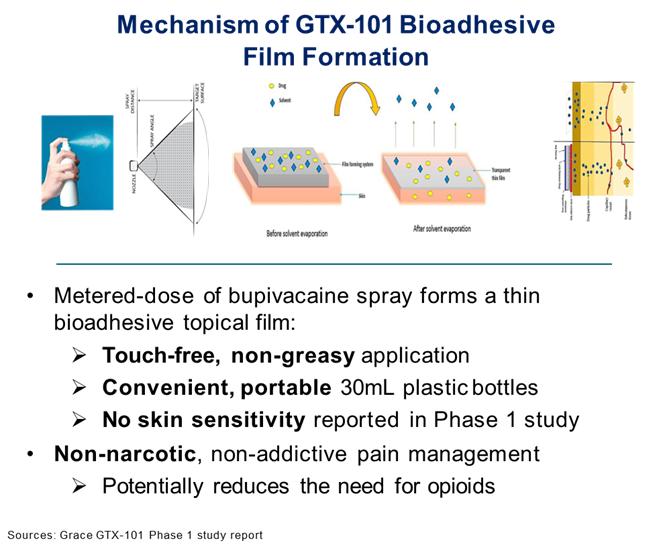
GTX-101 is a non-narcotic, topical bio-adhesive film-forming bupivacaine spray designed to ease the symptoms of patients suffering with postherpetic neuralgia (“PHN”). GTX-101 is administered via a metered-dose of bupivacaine spray and forms a thin bio-adhesive topical film on the surface of the patient’s skin, which enables a touch-free, non-greasy application. It also comes in convenient, portable 30 ml plastic bottles. Unlike oral gabapentin and lidocaine patches, we believe that the biphasic delivery mechanism of GTX-101 has the potential for rapid onset of action and continuous pain relief for up to eight hours. No skin sensitivity was reported in a Phase 1 trial.
About Postherpetic Neuralgia (PHN)
PHN is neuropathic pain due to damage caused by the varicella zoster virus (“VZV”). Infection with VZV causes two distinct clinical conditions. Primary VZV infection causes varicella (i.e., chickenpox), a contagious rash illness that typically occurs among young children. Secondary VZV can reactivate clinically, decades after initial infection, to cause herpes zoster (“HZ”), otherwise known as shingles. Acute HZ arises when dormant virus particles, persisting within an affected sensory ganglion from the earlier, primary infection with VZV become reactivated when cellular immunity to varicella decreases. Viral particles replicate and may spread to the dorsal root, into the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, and through peripheral sensory nerve fibers down to the level of the skin. Viral particles also may circulate in the blood. This reactivation is accompanied by inflammation of the skin, immune response, hemorrhage, and destruction of peripheral and central neurons and their fibers. Following such neural degeneration, distinct types of pathophysiological mechanisms involving both the central and peripheral nervous systems may give rise to the severe nerve pain associated with PHN.
While the rash associated with HZ typically heals within two to four weeks, the pain may persist for months or even years, and this PHN manifestation is the most common and debilitating complication of HZ. There is currently no consensus definition for PHN, but it has been suggested by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (“CDC”) that PHN is best defined as pain lasting at least three months after resolution of the rash.
12
PHN is associated with significant loss of function and reduced quality of life, particularly in the elderly. It has a detrimental effect on all aspects of a patient's quality of life. The nature of PHN pain varies from mild to severe, constant, intermittent, or triggered by trivial stimuli. Approximately half of patients with PHN describe their pain as “horrible” or “excruciating,” ranging in duration from a few minutes to constant on a daily or almost daily basis (Katz, 2004). The pain can disrupt sleep, mood, work, and activities of daily living, adversely impacting the quality of life and leading to social withdrawal and depression. PHN is the number-one cause of intractable, debilitating pain in the elderly, and has been cited as the leading cause of suicide in chronic pain patients over the age of 70 (Hess, 1990).
Current treatment of PHN most often consists of oral gabapentin (first line) and prescription lidocaine patches or antidepressants (second line), and refractory cases may be prescribed opioids to address persistent pain. Gabapentin and opioid abuse have continued to proliferate, and lidocaine patches are suboptimal for many reasons. An independent third-party market research firm we commissioned interviewed more than 250 physicians who regularly treat PHN patients, and found that approximately 40% of patients using lidocaine patches experience insufficient pain relief. Lidocaine patches are difficult to use, fall off, and look unsightly with possible skin sensitivity and irritation. Additionally, lidocaine patches can only be used for 12 hours on and then need to be removed for 12 hours before being reapplied. Prescription lidocaine patches are only approved for PHN, and the market is currently made up of both branded and generic offerings. It is estimated that PHN affects approximately 120,000 patients per year in the United States. According to a third-party report we commissioned, the total addressable market for GTX-101 could be as large as $2.5 billion, consisting of approximately $200 million for PHN pain and $2.3 billion for non-PHN pain indications.
GTX-101 R&D History and Clinical Studies Completed to Date
To date, we have conducted four Phase I trials in healthy volunteers to assess the PK, safety and tolerability of GTX-101 and to determine the plasma levels of bupivacaine HCl administered as a single dose in various concentrations between 30 mg (three sprays) and 2100 mg (twenty sprays).
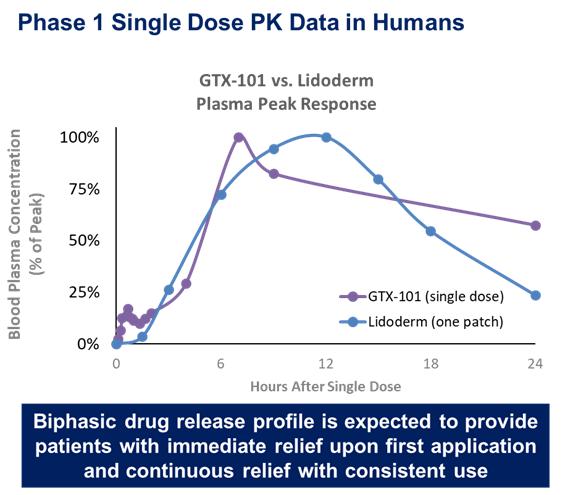
These studies confirmed that bupivacaine delivered as a topical spray (GTX-101) is well absorbed through the skin, as demonstrated in the graph below, while very little is absorbed systemically.
In all four studies, the administration of GTX-101 to healthy volunteers was safe and well tolerated. In addition, no evidence of skin irritation was observed at the application site following the spray administrations. The data below is from two separate trials of GTX-101 and the Lidoderm patch superimposed on each other.
GTX-101 recent activities:
We believe that the PHN pain market will continue to grow, and non-opioid products like GTX-101 that can relieve PHN pain more quickly and in a sustained manner by means of a more efficient delivery system, will be an attractive therapy option for patients and physicians. GTX-101 is administered by spraying our proprietary bupivacaine formulation over the affected area, which we believe has the potential to provide several advantages over currently marketed products such as the lidocaine patch, including faster onset of action, sustained pain relief, possibly lower dosing requirements and improved dosing convenience, all which could lead to increased patient satisfaction and compliance.
The data from the single dose Phase 1 clinical trial for GTX-101 was submitted to the FDA’s Division of Anesthesiology and feedback was received at a pre-IND meeting on April 18, 2018, that informed the design of pre-clinical toxicology studies and a clinical and regulatory pathway to approval under section 505(b)(2). We completed a minipig skin sensitivity study in the second calendar quarter of 2022, and we initiated a single dose PK trial in healthy human volunteers in July 2022. Topline results from this single dose PK trial were reported on December 23, 2022 and the results met all primary outcome measures.
The median Tmax (the time of maximum concentration between 0 hour and 240 hours after study drug administration) of bupivacaine in plasma following GTX-101 single-dose topical applications ranged between 18 to 24 hours depending on dose, while the median Tmax following the subcutaneous injection of 10 mg of bupivacaine was only 23 minutes. This result suggests that bupivacaine delivered by GTX-101 remains in the skin for a long period of time, potentially inducing prolonged analgesic effect in the sprayed area. The exposure to bupivacaine based on Cmax (the maximum concentration occurring at Tmax between 0 hour and 240 hours after study drug administration) and AUC (the area under the concentration time curve, extrapolated to infinity) following GTX-101 topical application as a single-dose increased with increasing dose.
13
The systemic exposure to bupivacaine following a 200mg dose of GTX-101 was approximately 29-fold less than a single subcutaneous dose of 10mg of bupivacaine based on Cmax and approximately 6-fold less than a single subcutaneous dose of 10mg of bupivacaine based on AUC. We predict these lower blood levels will correspond to an increased safety margin for GTX-101 with regards to toxicity risk. Mean half-life (T half) following GTX-101 single-dose topical applications ranged between 24 to 37 hours depending on dose, suggesting a slow elimination and potentially long duration of effect, while mean Tmax following the subcutaneous injection of 10 mg of bupivacaine was only 8 hours.
There were only two adverse events judged as related to the study drug by the investigator for each of GTX-101 and the bupivacaine subcutaneous injection. Following GTX-101 topical application: headache (1 event = 3%) and numbness (1 event = 3%) at the sprayed area following bupivacaine subcutaneous injection: dizziness (1 event = 8%) and nausea (1 event = 8%).
The further development of GTX-101 has been deprioritized in favor of our focus on development of GTX-104. Pending additional dedicated funding for GTX-101 or the signing of a strategic partnership, we plan to follow this successful PK trial with a multiple ascending dose study in 2023. Results from these non-clinical and clinical studies and trials are required before the initiation of our Phase 2 program in PHN patients. It is also possible that we may out-license or sell our GTX-101 drug candidate.
Overall Commercialization Strategy
We plan to retain our worldwide commercialization rights for some of our key drug candidates, while for other drug candidates we may consider collaboration opportunities to maximize market penetration and returns. If we receive regulatory approval, we may look to out license commercialization opportunities or consider outsourcing sales to ensure efficient commercial management. A similar review and approach will be applied to GTX-102. Given that GTX-101 will be targeted to a larger primary care and pain specialist market, if GTX-101 receives regulatory approval, we will likely seek commercial partnerships to fully exploit the market potential of this drug product. As our product candidates advance through the pipeline, our commercial plans may change. Clinical data, the size of the development programs, the size of the target market, the size of a commercial infrastructure and manufacturing needs may all influence our U.S., European Union, and rest-of-world strategies. Currently, we have prioritized the development of GTX-104 and de-emphasized the development of GTX-102 and GTX-101. It is possible that we may out-license or sell GTX-102 and/or GTX-101.
14
Manufacturing and Supply
We currently do not own any manufacturing facilities. The manufacture of our pipeline of drug candidates is highly reliant on complex techniques and personnel aseptic techniques, which present significant challenges and require specialized expertise. Further, these processes undergo a high level of scrutiny by regulatory agencies. Consequently, we utilize a network of third-party CMOs for manufacturing of our drug candidates. All CMOs are monitored and evaluated by us to assess compliance with regulatory requirements.
We work with independent consultants to perform periodic quality audits of our manufacturers to review the manufacturing process for our drug candidates and to provide input on quality issues. All lots of the drug substance and drug product used in clinical supply are manufactured under current good manufacturing practices. We plan to continue to rely upon CMOs to manufacture clinical and commercial quantities once the product is approved. We have development agreements in place with these CMOs and we have personnel with pharmaceutical development and manufacturing experience who are responsible for the relationships with our CMOs.
Intellectual Property Portfolio
We have a strong and multi-layered intellectual property protection strategy, which we believe will create barriers to entry and solidify our position in the market. All of our leading pipeline products have received orphan status designation from the FDA, which could result in 7 years of marketing exclusivity in the United States and 10 years in Europe, provided they receive the final marketing authorizations from the applicable government agencies, and they can meet the conditions for receiving such marketing exclusivity. In addition, we protect our drug candidates through a well-defined patent filing strategy. Our patent estate includes more than 40 granted and pending patents in various global jurisdictions, including 6 U.S. issued patents and 4 filed U.S. patent applications. We believe that our intellectual property portfolio, consisting primarily of composition and method-of-use patents, will protect the market value of our products by extending exclusivity beyond what is granted through the orphan designation. We intend to continue to build our patent portfolio by filing for patent protection on new developments with respect to our product candidates. We expect that these patents will, if and when issued, allow us to list our own patents in the Orange Book: Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence issued by the FDA, to which potential competitors will be required to certify upon submission of their applications referencing our drug products, if approved.
We strive to protect and enhance the proprietary technology, inventions, and improvements that are commercially important to the development of our business, including seeking, maintaining, and defending patent rights, whether developed internally or licensed from third parties. We also rely on trade secrets relating to manufacturing know-how, continuing technological innovation and in-licensing opportunities to develop, strengthen, and maintain our proprietary position. We may also rely on regulatory protections afforded through orphan drug status, data exclusivity, market exclusivity, and patent term extensions, where available.
We are actively seeking U.S. and international patent protection for a variety of technologies and intend to seek patent protection or rely upon trade secret rights to protect other technologies that may be used to discover and validate targets and that may be used to identify and develop novel pharmaceutical products. We seek these protections, in part, through confidentiality and proprietary information agreements.
Individual patents extend for varying periods depending on the date of filing or the date of issuance, and the legal term of patents in the countries in which they are obtained. Generally, utility patents issued for applications filed in the United States are granted a term of 20 years from the earliest effective filing date of a non-provisional patent application. In addition, in certain instances, a patent term can be extended to recapture a portion of the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office delay in issuing the patent as well as a portion of the term effectively lost as a result of the FDA regulatory review period. However, as to the FDA component, the restoration period cannot be longer than 5 years and the total patent term including the restoration period must not exceed 14 years following FDA approval. The duration of foreign patents varies in accordance with provisions of applicable local law, but typically is also 20 years from the earliest effective filing date. The actual protection afforded by a patent may vary on a product-by-product basis from country to country and can depend upon many factors, including the type of patent, the scope of its coverage, the availability of regulatory-related extensions, the availability of legal remedies in a particular country and the validity and enforceability of the patent.
We have several issued U.S. patents and patent applications as well as patents and patent applications in other jurisdictions. Five patents for GTX-104 have been granted in the United States. One patent for GTX-101 has been granted in Europe, China, Mexico, Japan and South Africa. One patent for GTX-102 has been granted in Japan.
Recent Developments
Announcement of centralization of marketplace for shares on the Nasdaq with voluntary delisting from TSX Venture Exchange
On March 13, 2023, we announced that we had applied and received approval for a voluntary delisting of our common shares from the TSX Venture Exchange ("TSXV"). The delisting from the TSXV did not affect the Company's listing on the Nasdaq Capital Market (the "Nasdaq"). The common shares continue to trade on the Nasdaq under the symbol "ACST". Effective as at the close of trading on March 27, 2023, Acasti's common shares were no longer be listed and posted for trading on the TSXV.
Announcement of resignation of a director
On March 30, 2023, we announced that effective immediately, Mr. Jean-Marie (John) Canan had tendered his resignation from the board of directors of the Company.
Announcement of appointment of Prashant Kohli as CEO
On April 4, 2023, we announced the appointment of Prashant Kohli as Acasti's new Chief Executive Officer, succeeding Jan D'Alvise. The parties mutually agreed to part ways, and Ms. D'Alvise stepped down from the board of directors of the Company.
Announcement of intention to proceed with Phase 3 clinical safety study for GTX-104 following FDA feedback
On April 4, 2023 we announced that we received a Type C written meeting response and clarifying feedback from the FDA on our proposed Phase 3 safety study for GTX-104. The FDA provided additional comments on our development plan that, subject to submission of the final clinical protocol and FDA approval of same, will allow us to proceed with the initiation of a Phase 3 safety clinical trial in aneurysmal aSAH patients.
Announcement of successful submission of pivotal GTX-104 Phase 3 safety study protocol with FDA and implementation of strategic realignment plan
On May 8, 2023, we announced the successful submission to the FDA of GTX-104's full protocol of its pivotal Phase 3 safety study and implementation of a strategic realignment plan to maximize shareholder value. The realignment follows a comprehensive strategic review of the Company by Prashant Kohli, its recently appointed CEO, and its board of directors.
15
Key strategies being implemented are:
In connection with the transformation of the operating model, we have moved to appoint the following industry experts to our senior management team:
As a result of this strategic realignment, we are, over time, discontinuing our operations in Canada, and have proceeded to lay off substantially all our workforce, allowing our new management team to rebuild a leaner organization in the United States. All of our finance team will remain in their current role for a transition period until at least the end June 2023.
Corporate Structure
Acasti was incorporated on February 1, 2002 under Part 1A of the Companies Act (Québec) under the name “9113-0310 Québec Inc.” On February 14, 2011, the Business Corporations Act (Québec), or QBCA, came into effect and replaced the Companies Act (Québec). We are now governed by the QBCA. On August 7, 2008, pursuant to a Certificate of Amendment, we changed our name to “Acasti Pharma Inc.”, our share capital description, the provisions regarding the restriction on securities transfers and our borrowing powers. On November 7, 2008, pursuant to a Certificate of Amendment, we changed the provisions regarding our borrowing powers. We became a reporting issuer in the Province of Québec on November 17, 2008. On December 18, 2019, we incorporated a new wholly owned subsidiary named Acasti Innovation AG, or AIAG, under the laws of Switzerland for the purpose of future development of our intellectual property and for global distribution of our products. AIAG currently does not have any operations. On August 27, 2021, Acasti completed its acquisition of Grace Therapeutics Inc. via a merger. Following completion of the merger, Grace became a wholly owned subsidiary of Acasti and was renamed Acasti Pharma U.S. Inc.
Available Information
This annual report on Form 10-K, our quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, our current reports on Form 8-K, and any amendments to these reports are filed, or will be filed, as applicable, with the SEC, and the Canadian Securities Administrators, or CSA. These reports are available free of charge on our website, www.acastipharma.com, as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such reports with or furnish such reports to the SEC and the CSA. Information contained on, or accessible through, our website is not a part of this annual report, and the inclusion of our website address in this document is an inactive textual reference.
Additionally, our filings with the SEC may be accessed through the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov and our filings with the CSA may be accessed through the CSA’s System for Electronic Document Analysis and Retrieval at www.sedar.com.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
Summary of Risk Factors
We are providing the following summary of the risk factors contained in this annual report to enhance the readability and accessibility of our risk factor disclosures. This summary does not address all of the risks that we face. We encourage you to carefully review the full risk factors contained in this annual report on Form 10-K in their entirety for additional information regarding the material factors that make an investment in our securities speculative or risky. The primary categories by which we classify risks include: (i) general risks related to our company; (ii) risks relating to our business; (iii) risks relating to the development, testing and commercialization of our products; (iv) risks relating to our intellectual property; (v) risks relating to our dependence on third parties; and (vi) risks relating to ownership of our common shares. Set forth below within each of these categories is a summary of the principal factors that make an investment in our common shares speculative or risky.
General Risks Related to the Company
16
Risk Factors Relating to our Business
Risks Related to Development, Testing and Commercialization of Our Products
17
Risks Relating to our Intellectual Property
Risks Related to Our Dependence on Third Parties
Risks Related to Tax
Risks Relating to Ownership of our Common Shares
18
Any investment in our common shares involves a high degree of risk. The following risk factors and other information included in this annual report should be carefully considered. If any of these risks actually occur, our business, financial condition, prospects, results of operations or cash flow could be materially and adversely affected, and you could lose all or a part of the value of your investment. Additional risks or uncertainties not currently known to us, or that we deem immaterial, may also negatively affect our business operations.
19
General Risks Related to the Company
We may not achieve our publicly announced milestones on time, or at all.
From time to time, we may publicly announce the timing of certain events that we expect to occur, such as the anticipated timing of results from our clinical trials and the timing of an upcoming NDA filing. These statements are forward-looking and are based on the best estimate of management at the time relating to the occurrence of the events. However, the actual timing of these events may differ from what has been publicly disclosed. The timing of events such as completion of a clinical trial, discovery of a new product candidate, filing of an application to obtain regulatory approval, beginning of commercialization of products, completion of a strategic partnership, or announcement of additional clinical trials for a product candidate may ultimately vary from what is publicly disclosed. These variations in timing may occur as a result of different events, including the nature of the results obtained during a clinical trial or during a research phase, problems with a supplier or a distribution partner or any other event having the effect of delaying the publicly announced timeline. We undertake no obligation to update or revise any forward-looking information, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as otherwise required by law. Any variation in the timing of previously announced milestones could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or operating results and the trading price of our common shares.
We are heavily dependent on the success of our lead drug candidate, GTX-104
Our business and future success are substantially dependent on our ability to successfully and timely develop, obtain regulatory approval for, and commercialize our lead product candidate, GTX-104. Any delay or setback in the development of GTX-104 could adversely affect our business. Our planned development, approval and commercialization of GTX-104 may fail to be completed in a timely manner or at all. As part of our recent strategic realignment plan, we determined to focus primarily on the development of GTX-104, which concentrates the level of our drug development risk on one drug candidate. We cannot provide assurance that we will be able to obtain approval for GTX-104 or any other of our drug candidates from the FDA or any foreign regulatory authority or that we will obtain such approval in a timely manner.
We may not be able to maximize value from our de-prioritized drug candidates, GTX-102 and GTX-101, through either development, out-licensing or sale.
Our GTX-102 and GTX-101 drug candidates are at an earlier development stage than GTX-104 and will require additional time and resources to develop. As part of our recent strategic realignment plan, we determined to focus primarily on the development of GTX-104 and to de-emphasize the development of GTX-102 and GTX-101. While we will continue to seek ways to maximize the value of GTX-102 and GTX-101, including through subsequent development, out-licensing or sale, we may not be successful in doing so.
We may not be able to maintain our operations and advance our research and development and commercialization of our GTX-104 lead drug candidate without additional funding.
We have incurred operating losses and negative cash flows from operations since our inception. To date, we have financed our operations through public offerings and private placements of securities, proceeds from exercises of warrants, rights and options, and receipt of research tax credits and research grant programs. Our cash and cash equivalents and short-term investments were $27.9 million as of March 31, 2023 and $43.7 million as of March 31, 2022.
Our current assets, as of March 31, 2023, are projected to support our current liabilities as at that date when combined with the projected level of our expenses for the next twelve months, including fully funding the completion of our Phase 3 program for GTX-104. We expect that additional time and capital will be required by us to file an NDA to obtain FDA approval for GTX-104 in the United States, to further scale up our manufacturing capabilities, and to complete marketing and other pre-commercialization activities. Consequently, we expect to require additional capital to fund our daily operating needs beyond the next twelve months. Based on the steps we are taking in our strategic realignment plan to focus primarily on the development of GTX-104 and to de-emphasize the development of GTX-102 and GTX-101, we believe that our existing cash and cash equivalents will enable us to fund our operating expenses and capital expenditure requirements beyond the completion of our Phase 3 trials for GTX-104. To fully execute our business plan, we plan to raise the necessary capital primarily through additional securities offerings and multiple sources of non-dilutive capital, such as grants or loans and strategic alliances. If we are unable to raise additional capital in sufficient amounts or on terms acceptable to us, we may have to significantly delay the research and development and commercial launch of our GTX-104. If we determine to continue development of GTX-102 and GTX-101, significant additional funding will be needed. Unexpected negative results in our clinical programs for our lead drug candidate may affect our ability to raise additional capital and/or complete strategic development and/or distribution partnerships to support the commercial launch of our drug candidate. Additional funding from third parties may not be available on acceptable terms or at all to enable us to continue with the research and development and commercialization of our lead drug candidate.
Business disruptions could seriously harm our future revenue and financial condition and increase our costs and expenses.
Our operations, and those of our suppliers, third-party manufacturers and other contractors and consultants could be subject to earthquakes, power shortages, telecommunications failures, water shortages, floods, hurricanes, typhoons, fires, extreme weather conditions, medical pandemics and other natural or man-made disasters or business interruptions, for which we are predominantly self-insured. The occurrence of any of these business disruptions could seriously harm our operations and financial condition and increase our costs and expenses. We rely on third-party manufacturers to manufacture our drug candidate products. Our ability to obtain supplies of drug candidate products could be disrupted if the operations of our manufacturers and suppliers are affected by a man-made or natural disaster or other business interruption.
We may be subject to foreign exchange rate fluctuations.
Our functional currency is the U.S. dollar. However, many of our expenses currently are and/or are expected to be, denominated in foreign currencies, including Canadian dollars. As we previously completed financings in both Canadian and U.S. dollars, both currencies are maintained and used to make required payments in the applicable currency. Though we plan to implement measures designed to reduce our foreign exchange rate exposure, the U.S. dollar/Canadian dollar and U.S. dollar /European euro exchange rates have fluctuated significantly in the recent past and may continue to do so, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial position and results of operations.
If securities or industry analysts do not publish research or publish inaccurate or unfavorable research about our business, our share price and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for our common shares will depend in part on the research and reports that securities or industry analysts publish about us or our business. We currently have limited research coverage by securities and industry analysts. If few or no securities or industry analysts cover our company, the trading price for our common shares could be negatively impacted. If one or more of the analysts who covers us downgrades our common shares or publishes inaccurate or unfavorable research about our
20
business, our share price would likely decline. If one or more of these analysts ceases coverage of us or fails to publish reports on us regularly, demand for our common shares could decrease, which could cause our share price and trading volume to decline.
Risk Factors Relating to our Business
Our future success depends on our ability to retain key executives and to attract, retain and motivate qualified personnel.
We recently appointed several new members to our executive team and are highly dependent on the principal members of our executive team. While members of our executive team have significant industry experience, they have not been with our company for long. Any of our executive officers could leave our employment at any time, as all of our employees are “at will” employees. Also, as part of our strategic realignment, we have significantly reduced the number of our employees while we shift the base of our operations from Canada to the United States. As a result, in the process of shifting the base of our operations to the United States, we will have to recruit employees from the industry employment market in the United States. Recruiting and retaining qualified employees for our business, including scientific and technical personnel, will also be critical to our success. There is currently a shortage of skilled executives and other personnel in our industry, which is likely to continue. As a result, competition for skilled personnel is intense and the turnover rate can be high. As we rebuild our organization in accordance with our strategic realignment, we may not be able to attract and retain personnel on acceptable terms given the competition among numerous pharmaceutical companies for individuals with similar skill sets. In addition, failure to succeed in clinical studies may make it more challenging to recruit and retain qualified personnel. The inability to recruit key executives or the loss of the services of any executive or key employee might impede the progress of our development and commercialization objectives.
We may need to expand our organization, and we may experience difficulties in managing this growth, which could disrupt our operations and our ability to compete.
If our drug development efforts are successful, we expect to expand our employee base to increase our managerial, scientific, engineering, operational, sales, marketing, financial and other resources and to hire more consultants and contractors. Future growth would impose significant additional responsibilities on our management, including the need to identify, recruit, maintain, motivate, and integrate additional employees, consultants and contractors. We may not be able to effectively manage the expansion of our operations, which may result in weaknesses in our infrastructure, give rise to operational mistakes, loss of business opportunities, loss of employees and reduced productivity among remaining employees. Future growth could require significant capital expenditures and may divert financial resources from other projects, such as the development of our existing or future product candidates. Our future financial performance and our ability to sell and commercialize our product candidates, if approved, and compete effectively will depend, in part, on our ability to effectively manage any future growth.
We face potential product liability, and if claims are brought against us, we may incur substantial liability.
The use of our product candidates in clinical trials, and the sale of any drug candidates for which we obtain marketing approval, exposes us to the risk of product liability claims. Product liability claims might be brought against us by consumers, healthcare providers, pharmaceutical companies or others selling or otherwise coming into contact with our product candidates. If we cannot successfully defend against product liability claims, we could incur substantial liability and costs. In addition, regardless of merit or eventual outcome, product liability claims may result in:
Our current product liability insurance coverage may not be sufficient to reimburse us for any expenses or losses we may suffer. Moreover, insurance coverage is becoming increasingly expensive, and, in the future, we may not be able to maintain insurance coverage at a reasonable cost or in sufficient amounts to protect us against losses due to liability. A successful product liability claim or series of claims brought against us could cause our share price to decline and, if judgments exceed our insurance coverage, could adversely affect our results of operations and business.
We rely significantly on information technology and any failure, inadequacy, interruption, or security lapse of that technology, including any cybersecurity incidents, could harm our ability to operate our business effectively.
Despite the implementation of security measures, our internal computer systems, and those of third parties with which we contract are vulnerable to damage from cyber-attacks, computer viruses, unauthorized access, natural disasters, terrorism, war and telecommunication and electrical failures. System failures, accidents or security breaches could cause interruptions in our operations and could result in a material disruption of our drug product development and clinical activities and business operations, in addition to possibly requiring substantial expenditures of resources to remedy. The loss of drug product development or clinical trial data could result in delays in our regulatory approval efforts and significantly increase our costs to recover or reproduce the data. To the extent that any disruption or security breach were to result in a loss of, or damage to, our data or applications, or inappropriate disclosure of confidential or proprietary information, we could incur liability and our development programs, and the development of our product candidates could be delayed.
Risks Related to Development, Testing and Commercialization of Our Products
Even if our drug candidates receive regulatory approval in the United States, we may never obtain regulatory approval or successfully commercialize our products outside of the United States.
Our business plan is highly dependent upon our ability to obtain regulatory approval to market and commercialize our lead drug candidate, GTX-104in the United States. As GTX-104 is currently the focus of our drug development program, the failure to commercialize it would have a material adverse effect on our ability to execute on our business plan and generate revenue. In addition, even if we obtain U.S. regulatory approvals to commercialize GTX-104, we may not be able to do so in other international jurisdictions.
21
We are subject to uncertainty relating to healthcare reform measures and reimbursement policies which, if not favorable to our drug candidates, could hinder or prevent our drug candidates’ commercial success.
Our ability to commercialize our drug candidates successfully will depend in part on the extent to which governmental authorities, private health insurers and other third-party payors establish appropriate coverage and reimbursement levels for our drug candidates and related treatments. As a threshold for coverage and reimbursement, third-party payors generally require that drug products have been approved for marketing by the FDA. Third-party payors are increasingly imposing additional requirements and restrictions on coverage and limiting reimbursement levels for medical products. These restrictions and limitations influence the purchase of healthcare services and products. The cost containment measures that healthcare payors and providers are instituting and the effect of any healthcare reform could significantly reduce our revenues from the sale of any approved drug. We cannot provide any assurances that we will be able to obtain third-party coverage or reimbursement for our drug candidates in whole or in part.
In the United States, there have been a number of legislative and regulatory changes to the healthcare system in ways that could affect our future revenues and profitability and the future revenues and profitability of our potential customers. Under the prescription drug benefit, Medicare beneficiaries can obtain prescription drug coverage from private sector plans that are permitted to limit the number of prescription drugs that are covered in each therapeutic category and class on their formularies. If our products are not widely included on the formularies of these plans, our ability to market our products to the Medicare population could be harmed.
There also have been, and likely will continue to be, legislative and regulatory proposals at the federal and state levels directed at containing or lowering the cost of healthcare. We cannot predict the initiatives that may be adopted in the future. The continuing efforts of the government, insurance companies, managed care organizations and other payors of healthcare costs to contain or reduce costs of healthcare may adversely affect one or more of the following:
Any of these scenarios could harm our ability to market our products and generate revenues. It is also possible that other proposals having a similar effect will be adopted.
Our commercial success depends upon attaining significant market acceptance of our drug candidates and drug products, if approved, among physicians, nurses, pharmacists, patients and the medical community.
Even if we obtain regulatory approval for our drug product candidates, our drug product candidates may not gain market acceptance among physicians, nurses, pharmacists, patients, the medical community or third-party payors, which is critical to commercial success. Market acceptance of our drug candidates and any drug product for which we receive approval depends on a number of factors, including:
If our drug candidates or drug products, if approved, fail to achieve an adequate level of acceptance by physicians, nurses, pharmacists, patients, and the medical community, we will be unable to generate significant revenues, and we may not become or remain profitable.
Guidelines and recommendations published by government agencies can reduce the use of our drug candidates and drug products, if approved and negatively impact our ability to gain market acceptance and market share.
Government agencies promulgate regulations and guidelines applicable to certain drug classes which may include our drug products and product candidates that we are developing. Recommendations of government agencies may relate to such matters as usage, dosage, route of administration and use of concomitant therapies. Regulations or guidelines suggesting the reduced use of certain drug classes which may include our drug products and product candidates that we are developing or the use of competitive or alternative drug products as the standard of care to be followed by patients and healthcare providers could result in decreased use of our drug candidates or negatively impact our ability to gain market acceptance and market share.
If we are unable to establish sales and marketing capabilities or enter into agreements with third parties to market and sell our drug candidates, we may be unable to generate any revenue.
Although we intend to establish a small, focused, specialty sales and marketing organization to promote GTX-104, if approved for marketing in the United States, we currently have no such organization and the cost of establishing and maintaining such an organization may exceed the benefit of doing so. We believe that GTX-102 could also be marketed by a small, focused, specialty sales and marketing organization if and when we decide to resume development of GTX-102. Given the size of its potential market, we anticipate that commercializing GTX-101 would require entering into a strategic partnership with a larger marketing partner, if GTX-101 is approved by the
22
FDA for marketing, and the ability to find any such strategic partnership would be uncertain. If we are unable to establish adequate sales, marketing and distribution capabilities, whether independently or with third parties, we may not be able to generate sufficient product revenue and may not become profitable. We will be competing with many companies that currently have extensive and well-funded marketing and sales operations. Without an internal team or the support of a third-party to perform marketing and sales functions, we may be unable to compete successfully against these more established companies.
If we obtain approval to commercialize any approved drug products outside of the United States, a variety of risks associated with international operations could materially adversely affect our business.
If any of our drug candidates are approved for commercialization, we may enter into agreements with third parties to market these drug products outside the United States. We expect that we will be subject to additional risks related to entering into international business relationships, including:
If we are unable to differentiate our drug candidates from branded reference drugs or existing generic therapies for similar treatments, or if the FDA or other applicable regulatory authorities approve generic products that compete with any of our drug candidates, our ability to successfully commercialize our drug candidates would be adversely affected.
Although we believe that our drug candidates will be clinically differentiated from branded reference drugs and their generic counterparts, if any, it is possible that such differentiation will not impact our market position. If we are unable to achieve significant differentiation for our product candidates against other drugs, the opportunity for our product candidates to achieve premium pricing and be commercialized successfully would be adversely affected.
In addition to existing branded reference drugs and the related generic products, the FDA or other applicable regulatory authorities may approve generic products that compete directly with our drug candidates, if approved. Once an NDA, including a 505(b)(2) application, is approved, the product covered thereby becomes a “listed drug” which can, in turn, be cited by potential competitors in support of approval of an abbreviated new drug application (“ANDA”). The Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, FDA regulations and other applicable regulations and policies provide incentives to manufacturers to create modified, non-infringing versions of a drug to facilitate the approval of an ANDA for generic substitutes. These manufacturers might only be required to conduct a relatively inexpensive study to show that their product has the same active ingredient(s), dosage form, strength, route of administration and conditions of use or labeling as our product candidate and that the generic product is bioequivalent to ours, meaning it is absorbed in the body at the same rate and to the same extent as our drug product. These generic equivalents, which must meet the same quality standards as branded pharmaceuticals, would be significantly less costly than ours to bring to market and companies that produce generic equivalents are generally able to offer their drug products at lower prices. After the introduction of a generic competitor, a significant percentage of the sales of any branded drug product is typically lost to the generic drug product. Accordingly, competition from generic equivalents of our drug candidates would materially adversely impact our ability to successfully commercialize our drug candidates.
We face significant competition from other biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, and our operating results will suffer if we fail to compete effectively.
The biopharmaceutical industry is intensely competitive and subject to rapid and significant technological change. We expect to have competitors both in the United States and internationally, including major multinational pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology companies and universities and other research institutions.
Many of our competitors have substantially greater financial, technical and other resources, such as larger research and development staff and experienced marketing and manufacturing organizations. If our competitors market products that are more effective, safer or less expensive than our drug products, if any, or that reach the market sooner than our drug products, if any, we may enter the market too late in the cycle and may not achieve commercial success. In addition, the biopharmaceutical industry is characterized by rapid technological change. If we fail to stay at the forefront of technological change, we may be unable to compete effectively. Technological advances or drug products developed by our competitors may render our drug products, if any, or drug candidates obsolete, less competitive or not economical.
We could incur substantial costs and disruption to our business and delays in the launch of our drug candidates if our competitors and/or collaborators bring legal actions against us, which could harm our business and operating results.
We cannot predict whether our competitors or potential competitors, may bring legal actions against us based on our research, development, and commercialization activities, as well as any drug candidates or drug products resulting from these activities, claiming, among other things, infringement of their intellectual property rights, breach of contract or other legal theories. If we are forced to defend any such lawsuits, whether they are with or without merit or are ultimately determined in our favor, we may face costly litigation and diversion of technical and management personnel. These lawsuits could hinder our ability to enter the market early with our drug candidates and thereby hinder our ability to influence usage patterns when fewer, if any, of our potential competitors have entered such market, which could adversely impact our potential revenue from such drug candidates. Some of our competitors have substantially greater resources than we do and could be able to sustain the cost of litigation to a greater extent and for longer periods of time than we could. Furthermore, an adverse outcome of a dispute may require us: to pay damages, potentially
23
including treble damages and attorneys’ fees, if we are found to have willfully infringed a party’s patent or other intellectual property rights; to cease making, licensing or using products that are alleged to incorporate or make use of the intellectual property of others; to expend additional development resources to reformulate our products or prevent us from marketing a certain drug; and to enter into potentially unfavorable royalty or license agreements in order to obtain the rights to use necessary technologies. Royalty or licensing agreements, if required, may be unavailable on terms acceptable to us, or at all.
The COVID-19 pandemic, or a similar pandemic, epidemic, or outbreak of an infectious disease, may materially and adversely affect our business and our financial results and could cause a disruption to the development of our drug candidates.
Public health crises such as pandemics or similar outbreaks could adversely impact our business. The coronavirus pandemic is evolving, and has led to the implementation of various responses, including government-imposed quarantines, travel restrictions and other public health safety measures. While to date, the coronavirus pandemic has not had a material adverse effect on our business, any negative impact COVID-19 has to patient enrollment or treatment, or the research and development of our drug candidates could cause costly delays to clinical trial activities, which could adversely affect our ability to obtain regulatory approval for and to commercialize our drug candidates, increase our operating expenses, and have a material adverse effect on our financial results.
Additionally, timely enrollment in planned clinical trials is dependent upon clinical trial sites which could be adversely affected by global health matters, such as pandemics.
We are subject to numerous complex regulatory requirements and failure to comply with these regulations, or the cost of compliance with these regulations, may harm our business.
The research, testing, development, manufacturing, quality control, approval, labeling, packaging, storage, record-keeping, promotion, advertising, marketing, distribution, possession and use of our drug candidates, among other things, are subject to regulation by numerous governmental authorities in the United States and elsewhere. The FDA regulates drugs under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, and implementing regulations. Non-compliance with any applicable regulatory requirements can result in refusal of the governmental authority to approve products for marketing, criminal prosecution and fines, warning letters, product recalls or seizure of products, total or partial suspension of production, prohibitions or limitations on the commercial sale of products or refusal to allow the entering into of federal and state supply contracts. FDA and comparable governmental authorities have the authority to withdraw product approvals that have been previously granted. In addition, the regulatory requirements relating to our drug candidates and drug products, if any, may change from time to time and it is impossible to predict what the impact of any such changes may be.
If the FDA does not conclude that our drug candidates satisfy the requirements for the 505(b)(2) regulatory approval pathway, or if the requirements for approval of any of our drug candidates under Section 505(b)(2) are not as we expect, the approval pathway for our drug candidates will likely take significantly longer, cost significantly more and encounter significantly greater complications and risks than anticipated, and in any case may not be successful.
We intend to seek FDA approval through the 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway for our lead drug candidate GTX-104. The Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984, also known as the Hatch-Waxman Act, added Section 505(b)(2) to the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act (“FDCA”). Section 505(b)(2) permits the filing of an NDA where at least some of the information required for approval comes from studies that were not conducted by or for the applicant.
If the FDA does not allow us to pursue the 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway for GTX-104, we may need to conduct additional clinical trials, provide additional data and information and meet additional standards for regulatory approval. If this were to occur, the time and financial resources required to obtain FDA approval for our drug candidates would likely substantially increase. Moreover, an inability to pursue the 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway could result in new competitive products reaching the market faster than our drug candidates, which could materially adversely impact our competitive position and prospects. Even if we are allowed to pursue the 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway for a drug candidate, we cannot assure you that we will receive the requisite or timely approvals for commercialization of such drug candidate.
In addition, it is possible that our competitors may file citizens’ petitions with the FDA in an attempt to persuade the FDA that our drug candidates, or the clinical studies that support their approval, contain deficiencies. Such actions by our competitors could delay or even prevent the FDA from approving any NDA that we submit under Section 505(b)(2).
Clinical development is a lengthy and expensive process with an uncertain outcome, and results of earlier studies and trials may not be predictive of future trial results. Failure can occur at any stage of clinical development.
Clinical testing, even when utilizing the 505(b)(2) pathway, is expensive and can take many years to complete, and its outcome is inherently uncertain. Failure can occur at any time during the clinical trial process, even with active ingredients that have previously been approved by the FDA as safe and effective. The results of pre-clinical studies and early clinical trials of our drug candidates may not be predictive of the results of later stage clinical trials. A number of companies in the biopharmaceutical industry have suffered significant setbacks in advanced clinical trials due to lack of efficacy or adverse safety profiles, notwithstanding promising results in earlier trials.
Our drug candidates are in various stages of development. Clinical trial failures may occur at any stage and may result from a multitude of factors both within and outside our control, including flaws in formulation, adverse safety or efficacy profile and flaws in trial design, among others. If the trials result in negative or inconclusive results, we or our collaborators may decide, or regulators may require us, to discontinue trials of our drug candidates or conduct additional clinical trials or pre-clinical studies. In addition, data obtained from trials and studies are susceptible to varying interpretations, and regulators may not interpret our data as favorably as we do, which may delay, limit or prevent regulatory approval. For these reasons, our future clinical trials may not be successful.
Delays in clinical trials are common and have many causes, and any delay could result in increased costs to us and could jeopardize or delay our ability to obtain regulatory approval and commence drug product sales. We may also find it difficult to enroll patients in our clinical trials, which could delay or prevent development of our drug candidates.
We may experience delays in clinical trials of our drug candidates. Our planned clinical trials may not begin on time, have an effective design, enroll a sufficient number of patients or be completed on schedule, if at all. Our clinical trials can be delayed for a variety of reasons, including:
24
If initiation or completion of our planned clinical trials is delayed for any of the above reasons or other reasons, our development costs may increase, our regulatory approval process could be delayed and our ability to commercialize and commence sales of our drug candidates could be materially harmed, which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
In addition, identifying and qualifying patients to participate in clinical trials of our drug candidates is critical to our success. The timing of our clinical trials depends on the speed at which we can recruit patients to participate in testing our drug candidates as well as completion of required follow-up periods. We may not be able to identify, recruit and enroll a sufficient number of patients, or those with required or desired characteristics or to complete our clinical trials in a timely manner. Patient enrollment is and completion of the trials are affected by a variety of factors, including:
Our drug products or drug candidates may cause adverse effects or have other properties that could delay or prevent their regulatory approval or limit the scope of any approved label or market acceptance, or result in significant negative consequences following marketing approval, if any.
As with many pharmaceutical and biological products, treatment with our drug products or drug candidates may produce undesirable side effects or adverse reactions or events. Although the nature of our drug products or drug candidates as containing active ingredients that have already been approved means that the side effects arising from the use of the active ingredient or class of drug in our drug products or drug candidates is generally known, our drug products or drug candidates may still cause undesirable side effects, which may harm our business, financial condition and prospects significantly.
Further, if any of our drug products cause serious or unexpected side effects after receiving market approval, a number of potentially significant negative consequences could result, including:
Any of these events could prevent us from achieving or maintaining market acceptance of the affected drug product or drug candidate and could substantially increase the costs of commercializing our drug products and drug candidates.
The regulatory approval processes of the FDA and comparable foreign authorities are lengthy, time consuming and inherently unpredictable, and if we are ultimately unable to obtain regulatory approval for our drug candidates, our business will be substantially harmed.
25
The time required to obtain approval by the FDA and comparable foreign authorities is unpredictable but typically takes many years following the commencement of clinical trials and depends upon numerous factors, including the substantial discretion of the regulatory authorities. In addition, approval policies, regulations or the type and amount of clinical data necessary to gain approval may change during the course of a drug candidate’s clinical development and may vary among jurisdictions. It is possible that none of our existing drug candidates or any drug candidates we may seek to develop will ever obtain regulatory approval in the United States or other jurisdictions.
Our drug candidates could fail to receive regulatory approval for many reasons, including the following:
This lengthy approval process as well as the unpredictability of future clinical trial results may result in us failing to obtain regulatory approval to market our drug candidates, which would harm our business, results of operations and prospects significantly.
We have limited experience using the 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway to submit an NDA or any similar drug approval filing to the FDA, and we cannot be certain that any of our drug candidates will receive regulatory approval. If we do not receive regulatory approvals for our drug candidates, we may not be able to continue our operations. Even if we successfully obtain regulatory approvals to market one or more of our drug candidates, our revenue will be dependent, to a significant extent, upon the size of the markets in the territories for which we gain regulatory approval. If the markets for patients or indications that we are targeting are not as significant as we estimate, we may not generate significant revenue from sales of such drug products, if approved.
An NDA submitted under Section 505(b)(2) subjects us to the risk that we may be subject to a patent infringement lawsuit that would delay or prevent the review or approval of our drug candidate. The FDA and other regulatory agencies actively enforce the laws and regulations prohibiting the promotion of off-label uses.
Our drug candidates will be submitted to the FDA for approval under Section 505(b)(2) of the FDCA. Section 505(b)(2) permits the submission of an NDA where at least some of the information required for approval comes from studies that were not conducted by, or for, the applicant and on which the applicant has not obtained a right of reference. The 505(b)(2) application would enable us to reference published literature and/or the FDA’s previous findings of safety and effectiveness for the branded reference drug. For NDAs submitted under Section 505(b)(2) of the FDCA, the patent certification and related provisions of the Hatch-Waxman Act apply. In accordance with the Hatch-Waxman Act, such NDAs may be required to include certifications, known as paragraph IV certifications, that certify that any patents listed in the Patent and Exclusivity Information Addendum of the FDA’s publication, Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations, commonly known as the Orange Book, with respect to any product referenced in the 505(b)(2) application, are invalid, unenforceable or will not be infringed by the manufacture, use or sale of the product that is the subject of the 505(b)(2) NDA.
Companies that produce branded reference drugs routinely bring litigation against 505(b)(2) applicants that seek regulatory approval to manufacture and market generic and reformulated forms of their branded products. These companies often allege patent infringement or other violations of intellectual property rights as the basis for filing suit against a 505(b)(2) applicant. Likewise, patent holders may bring patent infringement suits against companies that are currently marketing and selling their approved generic or reformulated products. When a drug, such as GTX-104, has orphan drug exclusivity, the FDA may not approve any other application to market the same drug for the same indication for a period of up to seven years, except in limited circumstances, such as a showing of clinical superiority over the drug product with orphan exclusivity. In the United States, pediatric exclusivity adds six months to any existing exclusivity period.
Our drug development strategy relies heavily upon the 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway, which requires us to certify that we do not infringe upon third-party patents covering approved drugs. Such certifications often result in third-party claims of intellectual property infringement, the defense of which will be costly and time consuming, and an unfavorable outcome in any litigation may prevent or delay our development and commercialization efforts which would harm our business.
Litigation or other proceedings to enforce or defend intellectual property rights are often complex in nature, may be very expensive and time-consuming, may divert our management’s attention from other aspects of our business and may result in unfavorable outcomes that could adversely impact our ability to launch and market our drug candidates, or to prevent third parties from competing with our drug products and drug candidates.
In particular, our commercial success depends in large part on our avoiding infringement of the patents and proprietary rights of third parties for existing approved drug products. Because we intend to utilize the 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway for the approval of our drug products and drug candidates, we rely in whole or in part on studies conducted by third parties related to those approved drug products.
Because patent applications can take many years to issue, there may be currently pending or subsequently filed patent applications which may later result in issued patents that may be infringed by our drug products or drug candidates. If any third-party patents were held by a court of competent jurisdiction to cover aspects of our drug candidates, including the formulation, method of use, any method or process involved in the manufacture of any of our drug candidates, any molecules or intermediates formed during such manufacturing process or any other attribute of the final product itself, the holders of any such patents may be able to block our ability to commercialize our drug candidates unless we obtain a license under the applicable patents, or until such patents expire. In either case, such a license may not be available on commercially reasonable terms or at all.
26
Parties making claims against us may request and/or obtain injunctive or other equitable relief, which could effectively block our ability to further develop and commercialize one or more of our drug candidates on a temporary or permanent basis. Defense of these claims, regardless of their merit, would involve substantial litigation expense and would be a substantial diversion of employee resources from our business. In the event of a successful claim of infringement against us, we may have to pay substantial damages, including treble damages and attorneys’ fees for willful infringement, obtain one or more licenses from third parties, pay royalties or redesign our infringing products or manufacturing processes, which may be impossible or require substantial time and monetary expenditure. We cannot predict whether any such license would be available at all or whether it would be available on commercially reasonable terms. Furthermore, even in the absence of litigation, we may need to obtain licenses from third parties to advance our research, manufacture clinical trial supplies or allow commercialization of our drug candidates. We may fail to obtain any of these licenses at a reasonable cost or on reasonable terms, if at all. In that event, we would be unable to further develop and commercialize one or more of our drug candidates, which could harm our business significantly. We cannot provide any assurances that third-party patents do not exist which might be enforced against our products, resulting in either an injunction prohibiting our sales, or, with respect to our sales, an obligation on our part to pay royalties and/or other forms of compensation to third parties.
Our business is subject to extensive regulatory requirements and our drug candidates that obtain regulatory approval will be subject to ongoing and continued regulatory review, which may result in significant expense and limit our ability to commercialize such products.
Even after a drug product is approved, we will remain subject to ongoing FDA and other regulatory requirements governing the labeling, packaging, storage, distribution, safety surveillance, advertising, promotion, import, export, record-keeping and reporting of safety and other post-market information. The holder of an approved NDA is obligated to monitor and report adverse events, and any failure of a drug product to meet the specifications in the NDA. The holder of an approved NDA must also submit new or supplemental applications and obtain FDA approval for certain changes to the approved drug product, product labeling or manufacturing process. Advertising and promotional materials must comply with FDA laws and regulations and are subject to FDA review, in addition to other potentially applicable federal and state laws. In addition, the FDA may impose significant restrictions on the approved indicated uses for which the drug product may be marketed or on the conditions of approval. For example, a product’s approval may contain requirements for potentially costly post-approval studies and surveillance to monitor the safety and efficacy of the drug product, or the imposition of a REMS program.
In addition, the FDA’s regulations, policies, or guidance may change and new or additional statutes or government regulations in the United States and other jurisdictions may be enacted that could prevent or delay regulatory approval of our drug product candidates or further restrict or regulate post-approval activities. We cannot predict the likelihood, nature or extent of adverse government regulation that may arise from pending or future legislation or administrative action, either in the United States or abroad. If we are not able to achieve and maintain regulatory compliance, we may not be permitted to market our drug products and/or drug candidates, which would adversely affect our ability to generate revenue and achieve or maintain profitability.
Our employees, independent contractors, principal investigators, consultants, commercial partners and vendors may engage in misconduct or other improper activities, including non-compliance with regulatory standards and requirements.
We are exposed to the risk that our employees, independent contractors, principal investigators, consultants, commercial partners, and vendors may engage in fraudulent conduct or other illegal activity. Misconduct by these parties could include intentional, reckless and/or negligent conduct that violates (1) the laws of the FDA and similar foreign regulatory bodies, including those laws requiring the reporting of true, complete, and accurate information to such regulatory bodies; (2) healthcare fraud and abuse laws of the United States and similar foreign fraudulent misconduct laws; and (3) laws requiring the reporting of financial information or data accurately. Specifically, the promotion, sales and marketing of health care items and services, as well as certain business arrangements in the healthcare industry are subject to extensive laws designed to prevent misconduct, including fraud, kickbacks, self-dealing and other abusive practices. These laws may restrict or prohibit a wide range of pricing, discounting, marketing, structuring and commission(s), certain customer incentive programs and other business arrangements generally. Activities subject to these laws also involve the improper use of information obtained in the course of patient recruitment for clinical trials. It is not always possible to identify and deter employee and other third-party misconduct. The precautions we take to detect and prevent inappropriate conduct may not be effective in controlling unknown or unmanaged risks or losses or in protecting us from governmental investigations or other actions or lawsuits stemming from a failure to comply with these laws. If any such actions are instituted against us, and we are not successful in defending ourselves, those actions could have a significant impact on our business, including the imposition of civil, criminal and administrative penalties, damages, monetary fines, possible exclusion from participation in Medicare, Medicaid and other federal healthcare programs, contractual damages, reputational harm, diminished profits and future earnings, and curtailment of our operations, any of which could adversely affect our ability to operate our business and our results of operations.
Any relationships with healthcare professionals, principal investigators, consultants, customers (actual and potential) and third-party payors are and will continue to be subject, directly or indirectly, to federal and state healthcare fraud and abuse laws, false claims laws, marketing expenditure tracking and disclosure, or sunshine laws, government price reporting and health information privacy and security laws. If we are unable to comply, or have not fully complied, with such laws, we could face penalties, including, without limitation, civil, criminal, and administrative penalties, damages, monetary fines, disgorgement, possible exclusion from participation in Medicare, Medicaid and other federal healthcare programs, contractual damages, reputational harm, diminished profits and future earnings and curtailment or restructuring of our operations.
Our business operations and activities may be directly or indirectly, subject to various federal, state, and local fraud and abuse laws, including, without limitation, the federal Anti-Kickback Statute and the federal False Claims Act. These laws may impact, among other things, our current activities with principal investigators and research subjects, as well as proposed and future sales, marketing, and education programs. In addition, we may be subject to patient privacy regulation by the federal government, state governments and foreign jurisdictions in which we conduct our business. The laws that may affect our ability to operate include, but are not limited to:
27
In addition, any sales of our drug products or drug candidates, if and once commercialized outside the United States will also likely subject us to foreign equivalents of the healthcare laws mentioned above, among other foreign laws.
If our operations are found to be in violation of any of the laws described above or any other governmental regulations that apply to us, we may be subject to, without limitation, civil, criminal and administrative penalties, damages, monetary fines, disgorgement, possible exclusion from participation in Medicare, Medicaid and other federal healthcare programs, contractual damages, reputational harm, diminished profits and future earnings and curtailment or restructuring of our operations, any of which could adversely affect our ability to operate.
We are required to obtain regulatory approval for each of our drug candidates in each jurisdiction in which we intend to market such products, and the inability to obtain such approvals would limit our ability to realize their full market potential.
In order to market drug products outside of the United States, we must comply with numerous and varying regulatory requirements of other countries regarding safety and efficacy. Clinical trials conducted in one country may not be accepted by regulatory authorities in other countries, and regulatory approval in one country does not mean that regulatory approval will be obtained in any other country. However, the failure to obtain regulatory approval in one jurisdiction may adversely impact our ability to obtain regulatory approval in another jurisdiction. Approval processes vary among countries and can involve additional product testing and validation and additional administrative review periods. Seeking foreign regulatory approval could result in difficulties and costs for us and require additional non-clinical studies or clinical trials which could be costly and time consuming. Regulatory requirements can vary widely from country to country and could delay or prevent the introduction of our drug products in those countries. If we fail to comply with regulatory requirements in international markets or to obtain and maintain required approvals, or if regulatory approval in international markets is delayed, our target market will be reduced and our ability to realize the full market potential of our drug products will be harmed.
Risks Relating to Our Intellectual Property
If we are sued for infringing intellectual property rights of third parties, it will be costly and time consuming, and an unfavorable outcome in that litigation would have a material adverse effect on our business.
Our commercial success also depends upon our ability and the ability of our future collaborators to develop, manufacture, market and sell our drug candidates and to use our proprietary technologies without infringing the proprietary rights of third parties. Numerous U.S. and foreign issued patents and pending patent applications, which are owned by third parties, exist in the fields in which we are developing drug candidates. Because patent applications can take many years to issue, there may be currently pending applications, which may later result in issued patents that our product candidates or proprietary technologies may infringe. Similarly, there may be issued patents relevant to our drug candidates of which we are not aware.
There is a substantial amount of litigation involving patent and other intellectual property rights in the biotechnology and biopharmaceutical industries generally. In particular, the generic drug industry is characterized by frequent litigation between generic drug companies and branded drug companies. If a third-party claims that we infringe its intellectual property rights, we may face a number of issues, including, but not limited to:
28
We have not conducted an extensive search of patents issued to third parties, and no assurance can be given that third-party patents containing claims covering our drug candidates, technology or methods do not exist, have not been filed, or could not be filed or issued. Because of the number of patents issued and patent applications filed in our technical areas or fields, we believe there is a significant risk that third parties may allege they have patent rights encompassing our products, technology, or methods. Other drug candidates that we may in-license or acquire could be subject to similar risks and uncertainties.
We may be subject to claims that our employees, consultants, or independent contractors have wrongfully used or disclosed alleged confidential information or trade secrets of their other clients or former employers to us.
As is common in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industry, certain of our employees were formerly employed by other biotechnology or pharmaceutical companies, including our competitors or potential competitors. Moreover, we engage the services of consultants to assist us in the development of our drug candidates, many of whom were previously employed at or may have previously been or are currently providing consulting services to, other biotechnology or pharmaceutical companies, including our competitors or potential competitors. We may be subject to claims that these employees and consultants or we have inadvertently or otherwise used or disclosed trade secrets or other proprietary information of their former employers or their former or current customers. Litigation may be necessary to defend against these claims. Even if we are successful in defending against these claims, litigation could result in substantial costs and be a distraction to management. Any such litigation would be protracted, expensive, and potentially subject to an unfavorable outcome.
Our success depends in part upon our ability to protect our intellectual property for our branded products and drug candidates.
Our commercial success with respect to our drug products and drug candidates, depends on obtaining and maintaining patent protection in the United States and in other countries and trade secret protection for our drug candidates, proprietary technologies and their uses. Our ability to protect our drug products from unauthorized or infringing use by third parties depends in substantial part on our ability to obtain and maintain valid and enforceable patents.
Due to evolving legal standards relating to patentability, validity and enforceability of patents covering pharmaceutical inventions and the scope of claims made under these patents, our ability to maintain, obtain and enforce patents is uncertain and involves complex legal and factual questions. The patent positions of pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies can be highly uncertain and involve complex legal and factual questions for which important legal principles remain unresolved. Changes in either the patent laws or in the interpretations of patent laws in the United States and other countries may diminish the value and the scope of our intellectual property. Accordingly, we cannot predict the breadth of claims that may be allowed or enforced in our patents or in third-party patents.
The degree of future protection for our proprietary rights is uncertain. Only limited protection may be available and may not adequately protect our rights or permit us to gain or keep our competitive advantage. For example:
Proprietary trade secrets and unpatented know-how are also very important to our business. Although we have taken steps to protect our trade secrets and unpatented know-how, including entering into confidentiality agreements with third parties, and confidential information and inventions agreements with certain of our employees, consultants, and advisors, third parties may still obtain this information, or we may be unable to protect our rights. Enforcing a claim that a third-party illegally obtained and is using our trade secrets or unpatented know-how is expensive and time consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. In addition, courts outside the United States may be less willing to protect trade secret information. Moreover, our competitors may independently develop equivalent knowledge, methods, and know-how, and we would not be able to prevent their use.
If we fail to comply with our obligations in the agreements under which we license rights to technology from third parties, or if the license agreements are terminated for other reasons, we could lose license rights that are important to our business.
We may be a party to a number of technology licenses that are important to our business and expect to enter into additional licenses in the future. Our existing license agreements impose, and we expect that future license agreements will impose, on us, various development, regulatory and/or commercial diligence obligations, payment of milestones and/or royalties and other obligations. Under these agreements, we must rely on our licensor to comply with their obligations under the primary license agreements under which such third-party obtained rights in the applicable intellectual property, where we may have no relationship with the original licensor of such rights. If our licensors fail to comply with their obligations under these upstream license agreements, the original third-party licensor may have the right to terminate the original license, which may terminate our sublicense. If this were to occur, we would no longer have rights to the applicable intellectual property unless we are able to secure our own direct license with the owner of the relevant rights, which we may not be able to do at a reasonable cost or on reasonable terms, which may impact our ability to continue to develop and commercialize our drug candidates and companion diagnostic incorporating the relevant intellectual property. If we fail to comply with our obligations under our license agreements, or we are subject to a bankruptcy or insolvency, the licensor may have the right to terminate the license. In the event that any of our important technology licenses were to be terminated by the licensor, we would likely cease further development of the related program or be required to spend significant time and resources to modify the program to not use the rights under the terminated license.
We may be subject to claims that our employees, consultants, or independent contractors have wrongfully used or disclosed confidential information of third parties.
We employ individuals who were previously employed at other biotechnology or pharmaceutical companies. We may be subject to claims that we or our employees, consultants or independent contractors have inadvertently or otherwise used or disclosed confidential information of our employees’ former employers or other third parties. We may also be subject to claims that former employers or other third parties have an ownership interest in our patents. Litigation may be necessary to defend
29
against these claims. There is no guarantee of success in defending these claims, and if we are successful, litigation could result in substantial cost and be a distraction to our management and other employees.
We may be subject to claims challenging the inventorship or ownership of our patents and other intellectual property.
We may also be subject to claims that former employees, collaborators or other third parties have an ownership interest in our patents or other intellectual property. We may be subject to ownership disputes in the future arising, for example, from conflicting obligations of consultants or others who are involved in developing our drug candidates and companion diagnostic. Litigation may be necessary to defend against these and other claims challenging inventorship or ownership. If we fail in defending any such claims, in addition to paying monetary damages, we may lose valuable intellectual property rights, such as exclusive ownership of, or right to use, valuable intellectual property. Such an outcome could have a material adverse effect on our business. Even if we are successful in defending against such claims, litigation could result in substantial costs and be a distraction to management and other employees.
Intellectual property rights do not necessarily address all potential threats to our competitive advantage.
The degree of future protection afforded by our intellectual property rights is uncertain because intellectual property rights have limitations and may not adequately protect our business or permit us to maintain our competitive advantage. The following examples are illustrative:
Should any of these events occur, they could significantly harm our business, results of operations and prospects.
Changes in patent law could diminish the value of patents in general, thereby impairing our ability to protect any of our other future drug candidates.
Numerous recent changes to the patent laws and proposed changes to the rules of the various patent offices around the world may have a significant impact on our ability to protect our technology and enforce our intellectual property rights. These changes may lead to increasing uncertainty with regard to the scope and value of our issued patents and to our ability to obtain patents in the future.
Once granted, patents may remain open to opposition, re-examination, post-grant review, inter partes review, nullification derivation and opposition proceedings in court or before patent offices or similar proceedings for a given period after allowance or grant, during which time third parties can raise objections against the initial grant. In the course of any such proceedings, which may continue for a protracted period of time, the patent owner may be compelled to limit the scope of the allowed or granted claims attacked or may lose the allowed or granted claims altogether. Depending on decisions by authorities in various jurisdictions, the laws and regulations governing patents could change in unpredictable ways that may weaken our and our licensors’ ability to obtain new patents or to enforce existing patents we and our licensors or partners may obtain in the future.
We may not be able to protect our intellectual property rights throughout the world.
Many companies have encountered significant problems in protecting and defending intellectual property rights in foreign jurisdictions. The legal systems of some countries, particularly certain developing countries, do not favor the enforcement of patents, trade secrets and other intellectual property protection, which could make it difficult for us to stop the infringement of our patents or marketing of competing products in violation of our proprietary rights generally. Proceedings to enforce our patent rights in foreign jurisdictions could result in substantial costs and divert our efforts and attention from other aspects of our business, could put our patents at risk of being invalidated or interpreted narrowly and our patent applications at risk of not issuing and could provoke third parties to assert claims against us. We may not prevail in any lawsuits that we initiate, and the damages or other remedies awarded, if any, may not be commercially meaningful. Accordingly, our efforts to enforce our intellectual property rights around the world may be inadequate to obtain a significant commercial advantage from the intellectual property that we develop or license.
If our estimates or judgments relating to our critical accounting policies for intangible assets prove to be incorrect, further impairment charges could result.
We carry a significant amount of intangible assets on our consolidated balance sheet, associated with acquired in process research and development. In the ordinary course of business, circumstances may arise, including manifestation of any of the risks identified in this section, that could result in further recognition that the carrying values of our assets may not be recovered from future operations. Under such circumstances, it is possible we may be required to further impair our asset values to the extent that their remaining value after any such impairment can be recovered by our business going forward. Intangible assets with an indefinite useful life are subject to an impairment review at least annually.
30
Risks Related to Our Dependence on Third Parties
We do not have internal manufacturing capabilities, and if we fail to develop and maintain supply relationships with various third-party manufacturers, we may be unable to develop or commercialize our drug candidates.
Our ability to develop and commercialize our drug candidates depends, in part, on our ability to outsource their manufacturing at a competitive cost, in accordance with regulatory requirements and in sufficient quantities for clinical testing and eventual commercialization. All of our manufacturing is outsourced to third parties, and we do not plan to build manufacturing capabilities.
Our contract manufacturers may encounter manufacturing failures that could delay the clinical development or regulatory approval of our drug candidates, or their commercial production, if approved.
Any performance failure on the part of any of our manufacturers could delay the clinical development or regulatory approval of our drug candidates. Our manufacturers may encounter difficulties involving, among other things, production yields, regulatory compliance, quality control and quality assurance, as well as shortages of qualified personnel. Approval of our drug candidates could be delayed, limited, or denied if the FDA does not approve and maintain the approval of our contract manufacturer’s processes or facilities. Moreover, our contract manufacturers may encounter difficulties that have a negative impact on our operations and business. Our manufacturers may encounter difficulties with the manufacturing processes required to manufacture commercial quantities of our drug candidates or the quantities needed for our pre-clinical studies or clinical trials. Such difficulties could result in delays in our pre-clinical studies, clinical trials, and regulatory submissions, in the commercialization of our drug candidates. Further, development of large-scale manufacturing processes may require additional validation studies, which the FDA must review and approve. If any of our manufacturers fail to deliver the required commercial quantities or quantities needed for our pre-clinical studies and clinical trials on a timely basis and upon terms that we find acceptable, we may be unable to meet demand for any of our drug candidates that are approved and could lose potential revenue.
Certain changes in the manufacturing process or procedure, including a change in the location where the drug candidate is manufactured or a change of a third-party manufacturer, generally require prior FDA, or foreign regulatory authority, review and/or approval of the manufacturing process and procedures in accordance with cGMP. We may need to conduct additional pre-clinical studies and clinical trials to support approval of such changes. This review may be costly and time-consuming and could delay or prevent the launch of a drug candidate.
We rely on third parties to conduct our pre-clinical studies and clinical trials. If these third parties do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or meet expected deadlines, we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval for or commercialize our drug candidates and our business could be substantially harmed.
We have relied upon and plan to continue to rely upon third-party CROs to monitor and manage data for our pre-clinical and clinical programs. We rely on these parties for execution of our pre-clinical studies and clinical trials, and control only certain aspects of their activities. Nevertheless, we are responsible for ensuring that each of our trials is conducted in accordance with the applicable protocol, legal, regulatory, and scientific standards and our reliance on the CROs does not relieve us of our regulatory responsibilities. We and our CROs are required to comply with FDA laws and regulations regarding current good clinical practice (“GCP”), which are also required by the Competent Authorities of the Member States of the European Economic Area and comparable foreign regulatory authorities in the form of International Conference on Harmonization, guidelines for all of our drug candidates in clinical development. Regulatory authorities enforce GCP through periodic inspections of trial sponsors, principal investigators, and trial sites. If we or any of our CROs fail to comply with applicable GCP, the clinical data generated in our clinical trials may be deemed unreliable and the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may require us to perform additional clinical trials before approving our marketing applications. We cannot assure you that upon inspection by a given regulatory authority, such regulatory authority will determine that any of our clinical trials comply with GCP regulations. In addition, our clinical trials must be conducted with product produced under cGMP regulations. While we have agreements governing activities of our CROs, we have limited influence over their actual performance. In addition, portions of the clinical trials for our drug candidates are expected to be conducted outside of the United States, which will make it more difficult for us to monitor CROs and perform visits of our clinical trial sites and will force us to rely heavily on CROs to ensure the proper and timely conduct of our clinical trials and compliance with applicable regulations, including GCP. Failure to comply with applicable regulations in the conduct of the clinical trials for our drug candidates may require us to repeat clinical trials, which would delay the regulatory approval process.
We rely on third parties to manufacture commercial and clinical supplies of our drug candidates, and we intend to rely on third parties to manufacture commercial supplies of any approved drug products. The commercialization of any of our drug products could be stopped, delayed, or made less profitable if those third parties fail to provide us with sufficient quantities of active pharmaceutical ingredients, excipients, or drug products, or fail to do so at acceptable quality levels or prices or fail to maintain or achieve satisfactory regulatory compliance.
We do not own any manufacturing facilities, and we do not currently, and do not expect in the future, to independently conduct any aspects of our product manufacturing and testing, or other activities related to the clinical development and commercialization of our drug candidates. We currently rely, and expect to continue to rely, on third parties with respect to these items, and control only certain aspects of their activities.
Any of these third parties may terminate their engagements with us at any time. If we need to enter into alternative arrangements, it could delay our drug candidate development and commercialization activities. Our reliance on these third parties reduces our control over these activities but does not relieve us of our responsibility to ensure compliance with all required legal, regulatory, and scientific standards and any applicable trial protocols. If these third parties do not successfully carry out their contractual duties, meet expected deadlines or conduct our studies in accordance with regulatory requirements or our stated study plans and protocols, we will not be able to complete, or may be delayed in completing, clinical trials required to support future regulatory submissions and approval of our drug candidates.
More generally, manufacturers of pharmaceutical products often encounter difficulties in production, particularly in scaling up and validating initial production. These problems include difficulties with production costs and yields, quality control, including stability of the product, quality assurance testing, shortages of qualified personnel, as well as compliance with strictly enforced federal, state, and foreign regulations. Additionally, our manufacturers may experience manufacturing difficulties due to resource constraints or as a result of labor disputes or unstable political environments. If our manufacturers were to encounter any of these difficulties, or otherwise fail to comply with their contractual obligations, our ability to make product candidates available for clinical trials and development purposes or to commercialize any of our product candidates in the United States would be jeopardized. Any delay or interruption in our ability to meet commercial demand may result in the loss of potential revenues and could adversely affect our ability to gain market acceptance for approved products. In addition, any delay or interruption in the supply of clinical trial supplies could delay the completion of clinical trials, increase the costs associated with maintaining clinical trial programs and, depending upon the period of delay, require us to commence new clinical trials at additional expense or terminate clinical trials completely. Additionally, if supply from one approved manufacturer is interrupted, there could be a significant disruption in commercial supply. Regulatory agencies may also require additional studies if a new manufacturer is relied upon for commercial production. Switching manufacturers may involve substantial costs and is likely to result in a delay in our desired clinical and commercial timelines.
31
The design, development, manufacture, supply, and distribution of our drug candidates is highly regulated and technically complex.
All entities involved in the preparation of therapeutics for clinical trials or commercial sale, including our existing contract manufacturers for our drug candidates, are subject to extensive regulation. Components of a finished therapeutic product approved for commercial sale or used in late-stage clinical trials must be manufactured in accordance with cGMP and equivalent foreign standards. These regulations govern manufacturing processes and procedures (including record-keeping) and the implementation and operation of quality systems to control and assure the quality of investigational products and products approved for sale. Poor control of production processes can lead to the introduction of adventitious agents or other contaminants, or to inadvertent changes in the properties or stability of our drug candidates that may not be detectable in final product testing. The development, manufacture, supply, and distribution of our drug candidates is highly regulated and technically complex. We, along with our third-party providers, must comply with all applicable regulatory requirements of the FDA and foreign authorities.
Regulatory authorities also may, at any time following approval of a drug product for sale, audit our manufacturing facilities or those of our third-party contractors. If any such inspection or audit identifies a failure to comply with applicable regulations or if a violation of our product specifications or applicable regulations occurs independent of such an inspection or audit, we or the relevant regulatory authority may require remedial measures that may be costly and/or time-consuming for us or a third-party to implement and that may include the temporary or permanent suspension of a clinical trial or commercial sales or the temporary or permanent closure of a facility. Any such remedial measures imposed upon us or third parties with whom we contract could materially harm our business. If we or any of our third-party manufacturers fail to maintain regulatory compliance, the FDA can impose regulatory sanctions including, among other things, refusal to approve a pending application for a new drug product or biological product or revocation of a pre-existing approval. As a result, our business, financial condition, and results of operations may be materially harmed.
We may not be successful in establishing development and commercialization collaborations which could adversely affect, and potentially prohibit, our ability to develop our drug candidates.
Because developing pharmaceutical products, conducting clinical trials, obtaining regulatory approval, establishing manufacturing capabilities and marketing approved products are expensive, we are exploring collaborations with third parties outside of the United States that have more resources and experience. In situations where we enter into a development and commercial collaboration arrangement for a drug candidate, we may also seek to establish additional collaborations for development and commercialization in territories outside of those addressed by the first collaboration arrangement for such drug candidate. There are a limited number of potential partners, and we expect to face competition in seeking appropriate partners. If we are unable to enter into any development and commercial collaborations and/or sales and marketing arrangements on acceptable terms, if at all, we may be unable to successfully develop and seek regulatory approval for our drug candidates and/or effectively market and sell future approved drug products, if any, in all of the territories outside of the United States where it may otherwise be valuable to do so.
We may not be successful in maintaining development and commercialization collaborations, and any partner may not devote sufficient resources to the development or commercialization of our drug candidates or may otherwise fail in development or commercialization efforts, which could adversely affect our ability to develop certain of our drug candidates and our financial condition and operating results.
Even if we are able to establish collaboration arrangements, any such collaboration may not ultimately be successful, which could have a negative impact on our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects. If we partner with a third-party for development and commercialization of a drug candidate, we can expect to relinquish some or all of the control over the future success of that drug candidate to the third-party. It is possible that a partner may not devote sufficient resources to the development or commercialization of our drug candidate or may otherwise fail in development or commercialization efforts, in which event the development and commercialization of such drug candidate could be delayed or terminated, and our business could be substantially harmed. In addition, the terms of any collaboration or other arrangement that we establish may not prove to be favorable to us or may not be perceived as favorable, which may negatively impact the trading price of our common shares. In some cases, we may be responsible for continuing development of a product candidate or research program under a collaboration, and the payment we receive from our partner may be insufficient to cover the cost of this development. Moreover, collaborations and sales and marketing arrangements are complex and time consuming to negotiate, document and implement, and they may require substantial resources to maintain.
We are subject to a number of additional risks associated with our dependence on collaborations with third parties, the occurrence of which could cause our collaboration arrangements to fail. Conflicts may arise between us and our partners, such as conflicts concerning the interpretation of clinical data, the achievement of milestones, the interpretation of financial provisions or the ownership of intellectual property developed during the collaboration. If any such conflicts arise, a partner could act in its own self-interest, which may be adverse to our interests. Any such disagreement between us and a partner could result in one or more of the following, each of which could delay or prevent the development or commercialization of our drug candidates and harm our business:
Risks Related to Tax
There is a significant risk that we may be classified as a PFIC for U.S. federal income tax purposes.
Current or potential investors in our common shares who are U.S. Holders (as defined below) should be aware that, based on our most recent financial statements and projections and given uncertainty regarding the composition of our future income and assets, there is a significant risk that we may have been classified as a "passive foreign investment company" or "PFIC" for the 2022 taxable year and may be classified as a PFIC for our current taxable year and possibly subsequent years. Each current or potential investor who is a U.S. Holder should consult his, her or its own tax advisor regarding the U.S. federal, state and local, and non-U.S. tax consequences of the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of our common shares, the U.S. federal tax consequences of the PFIC rules, and the availability of any election that may be available to the holder to mitigate adverse U.S. federal income tax consequences of holding shares of a PFIC.
The rules governing PFICs can have adverse tax effects on U.S. shareholders, which effects may be mitigated by making certain elections for U.S. federal income tax purposes, which elections may or may not be available. If we are a PFIC in any year, a U.S. shareholder in such year will be required to file an annual information return with the IRS on IRS Form 8621 regarding distributions received on their common shares, any gain realized on disposition of such common shares and any other information required by such form. Additionally, if we are classified as a PFIC in any taxable year with respect to which a U.S. shareholder owns common shares, we generally will continue to be treated as a PFIC with respect to such U.S. shareholder in all succeeding taxable years, regardless of whether we continue to meet the tests described above, unless the U.S. shareholder makes a “deemed sale election.”
32
We may not be able to use our net operating loss carry forwards to offset future taxable income for Canadian or U.S. federal income tax purposes.
At March 31, 2023, Acasti Pharma U.S. had net operating loss carry forwards (“NOLs”) for U.S. federal income tax purposes of approximately $14.4 million, which have no expiry.
Acasti Pharma U.S. underwent an “ownership change” within the meaning of Section 382 of the Code as a result of the merger, and therefore Acasti Pharma U.S. may become subject to an annual limit on the amount of NOLs that may be used to offset future taxable income of Acasti Pharma U.S. for U.S. federal income tax purposes. Such annual limit is generally equal to the product of (i) the total value of the loss company’s (in this case, Acasti Pharma U.S.) outstanding equity immediately prior to an “ownership change” (subject to certain adjustments); and (ii) the applicable federal long-term tax-exempt interest rate for the month that includes the “ownership change”.
At March 31, 2023, we had NOLs for Canadian federal income tax purposes of approximately $130.1 million, which expire at various dates through 2043. The extent to which we can utilize any or all of our NOLs will depend on many factors, including the jurisdiction applicable to any of our future taxable revenue. In connection with our planned shift of our operations to the United States, we may not be able to justify the allocation of revenue to Canada sufficient to recover the tax benefits arising from NOLs and other tax credits.
Our ability to use NOLs will also depend on the amount of taxable income generated in future periods. The NOLs may expire before we can generate sufficient taxable income to use the NOLs.
The IRS may not agree that we should be treated as a foreign corporation for U.S. federal tax purposes.
Although we are incorporated in Quebec, Canada, the IRS may assert that we should be treated as a U.S. corporation (and, therefore, a U.S. tax resident) for U.S. federal tax purposes pursuant to Section 7874 of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the "Code"). For U.S. federal tax purposes, a corporation generally is considered a tax resident in the jurisdiction of its organization or incorporation. Because we are an entity incorporated in Canada, we would generally be classified as a foreign corporation (and, therefore, not a U.S. tax resident) for U.S. federal tax purposes. Section 7874 of the Code provides an exception under which a foreign corporation may, in certain circumstances, be treated as a U.S. corporation for U.S. federal tax purposes.
Under Section 7874, if (1) former Grace Therapeutics shareholders owned (within the meaning of Section 7874) 80% or more (by vote or value) of our ordinary shares after the merger by reason of holding Grace Therapeutics common stock (such ownership percentage, the "Section 7874 ownership percentage"), and (2) our "expanded affiliated group" did not have "substantial business activities" in Canada ("the substantial business activities test"), we will be treated as a U.S. corporation for U.S. federal tax purposes. If the Section 7874 ownership percentage of the former Grace Therapeutics shareholders after the merger was less than 80% but greater than or equal to 60%, and the substantial business activities test was not met, we and our U.S. affiliates may, in some circumstances, be subject to certain adverse U.S. federal income tax provisions (which, among other things, could limit their ability to utilize certain U.S. tax attributes such as NOLs to offset U.S. taxable income or gain resulting from certain transactions). The application of these rules could result in significant additional U.S. tax liability and limit our ability to restructure or access cash earned by certain of our non-U.S. subsidiaries, in each case, without incurring substantial U.S. tax liabilities.
Based on the terms of the merger, the rules for determining share ownership under Section 7874 and certain factual assumptions, we believe that former Grace Therapeutics shareholders owned (within the meaning of Section 7874) less than 60% (by both vote and value) of our ordinary shares after the merger by reason of holding shares of Grace common stock. Therefore, under current law, we believe that we should not be treated as a U.S. corporation for U.S. federal tax purposes and that Section 7874 should otherwise not apply to us or our affiliates as a result of the merger with Grace Therapeutics .
Risks Relating to Our Common Shares
We do not expect to pay any cash dividends for the foreseeable future.
The continued operation and expansion of our business will require substantial funding. Accordingly, we do not anticipate that we will pay any cash dividends on our common shares for the foreseeable future. Any determination to pay dividends in the future will be at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend upon our results of operations, financial condition, contractual restrictions, restrictions imposed by applicable law and other factors our board of directors deems relevant.
The price of our common shares may be volatile.
Market prices for securities of pharmaceutical companies can fluctuate significantly. Factors such as the announcement to the public or in various scientific or industry forums of technological innovations; new commercial products; patents or exclusive rights obtained by us or others; disputes or other developments relating to proprietary rights, including patents, litigation matters and our ability to obtain patent protection for our technologies; the commencement, enrollment or announcement of results of clinical trials we conduct, or changes in the development status of our drug candidates; results or delays of pre-clinical and clinical studies by us or others; any delay in our regulatory filings for our drug candidates and any adverse development or perceived adverse development with respect to the applicable regulatory authority’s review of such filings; a change of regulations; additions or departures of key scientific or management personnel; overall performance of the equity markets; general political and economic conditions; publications; failure to meet the estimates and projections of the investment community or that we may otherwise provide to the public; research reports or positive or negative recommendations or withdrawal of research coverage by securities analysts; actual or anticipated variations in quarterly operating results; announcements of significant acquisitions, strategic partnerships, joint ventures or capital commitments by us or our competitors; public concerns over the risks of pharmaceutical products and dietary supplements; unanticipated serious safety concerns related to the use of our drug candidates or drug products; our access to financial resources, future sales of securities by us or our shareholders; and many other factors, many of which are beyond our control, could have considerable effects on the price of our common shares. The price of our common shares has fluctuated significantly in the past and there can be no assurance that the market price of our common shares will not experience significant fluctuations in the future.
In addition, securities of pharmaceutical companies often experience extreme price and volume fluctuations that are unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of those companies. Broad market and industry factors may negatively affect the market price of our common shares, regardless of our actual operating performance. In the past, securities class action litigation has often been instituted against pharmaceutical companies following periods of volatility in the market price of their securities. This type of litigation, if instituted against us, could result in substantial costs and a diversion of management’s attention and resources, which would harm our business, operating results or financial condition.
Raising additional capital may cause dilution to our existing shareholders, restrict our operations, or require us to relinquish rights to our technologies or drug candidates.
33
We will need to raise additional capital in the future in order to fully execute on our business plan. We may seek additional capital through a combination of public and private equity offerings, debt financings, and non-dilutive strategic partnerships and alliances and licensing arrangements. To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, the ownership interests of our shareholders will be diluted, and the terms may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect the rights of our shareholders. We have in place an “at-the-market” sales agreement where we may issue and sell from time-to-time common shares having an aggregate offering price of up to $75,000,000, but due to our market capitalization, under applicable SEC rules, the availability of our access to this program is currently significantly limited. The incurrence of indebtedness by us would result in increased fixed payment obligations and could involve certain restrictive covenants, such as limitations on our ability to incur additional debt, limitations on our ability to acquire or license intellectual property rights and other operating restrictions that could adversely impact our ability to conduct our business. If we raise additional funds through strategic partnerships and alliances and licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish valuable rights to our technologies or drug candidates, or grant licenses on terms unfavorable to us.
The market price of our common shares could decline if our operating results fall below the expectations of investors or fluctuate.
Our net losses and expenses may fluctuate significantly and any failure to meet financial or clinical expectations may disappoint securities analysts or investors and result in a decline in the price of our common shares. Our net losses and expenses have fluctuated in the past and are likely to do so in the future. The market price of our common shares has fluctuated significantly in the past and may continue to do so. Some of the factors that could cause the market price for our common shares to fluctuate include the following:
If our quarterly operating results fall below the expectations of investors or securities analysts, the market price of our common shares could decline substantially. Furthermore, any quarterly fluctuations in our operating results may, in turn, cause the market price of our common shares to fluctuate substantially. We believe that quarterly comparisons of our financial results for a company at our stage of operation are not necessarily meaningful and should not be relied upon as an indication of our future performance.
There can be no assurance that an active market for our common shares will be sustained.
There can be no assurance that an active market for our common shares will be sustained. Holders of common shares may be unable to sell their investments on satisfactory terms. As a result of any risk factor discussed herein, the market price of our common shares at any given point in time may not accurately reflect our long-term value. Furthermore, responding to these risk factors could result in substantial costs and divert management’s attention and resources. Substantial and potentially permanent declines in the value of our common shares may adversely affect the liquidity of the market for our common shares.
Other factors unrelated to our performance that may have an effect on the price and liquidity of our common shares include positive or negative industry or competitor news; extent of analyst coverage; lessening in trading volume and general market interest in our common shares; the size of our public float; our access to funding; and any event resulting in a delisting of our common shares.
If we fail to meet applicable listing requirements, the Nasdaq Stock Market may delist our common shares from trading, in which case the liquidity and market price of our common shares could decline.
Our common shares are currently listed on the Nasdaq Stock Market, but we cannot assure you that our securities will continue to be listed on the Nasdaq Stock Market in the future. On July 27, 2022, we received written notification from the Nasdaq Listing Qualifications Department for failing to maintain a minimum bid price of $1.00
34
per common share for the last 30 consecutive business days, as required by Nasdaq Listing Rule 5550(a)(2) - bid price (the “Minimum Bid Price Rule”). The Nasdaq notification had no immediate effect on the listing of our common shares, and we had 180 calendar days, or until January 23, 2023, to regain compliance.
On January 24, 2023, we received notification from Nasdaq that we are eligible for an additional 180 calendar days, or until July 24, 2023, to regain compliance with the Minimum Bid Price Rule. We were granted the second extension because we meet the continued listing requirements for the market value of publicly held shares and all other initial listing standards for Nasdaq Capital Market, except for the bid price requirement. If at any time over this additional 180 calendar day period the bid price of our common shares closes at $1.00 per share or more for at least a minimum of ten consecutive business days, Nasdaq will provide written confirmation of compliance and the matter will be closed.
We intend to monitor the closing bid price of our common shares and, if necessary, evaluate all available options to resolve the deficiency and regain compliance with the Minimum Bid Price Rule.
If we fail to comply with listing standards and the Nasdaq Stock Market delists our common shares, we and our shareholders could face significant material adverse consequences, including:
We may pursue opportunities or transactions that adversely affect our business and financial condition.
Our management, in the ordinary course of our business, regularly explores potential strategic opportunities and transactions. These opportunities and transactions may include strategic joint venture relationships, significant debt or equity investments in us by third parties, the acquisition or disposition of material assets, the licensing, acquisition or disposition of material intellectual property, the development of new drug candidates, the sale of our common shares and other similar opportunities and transactions. The public announcement of any of these or similar strategic opportunities or transactions might have a significant effect on the price of our common shares. Our policy is to not publicly disclose the pursuit of a potential strategic opportunity or transaction unless we are required to do so by applicable law, including applicable securities laws relating to periodic disclosure obligations. There can be no assurance that investors who buy or sell common shares are doing so at a time when we are not pursuing a particular strategic opportunity or transaction that, when announced, would have a significant effect on the price of our common shares.
In addition, any such future corporate development may be accompanied by certain risks, including exposure to unknown liabilities of the strategic opportunities and transactions, higher than anticipated transaction costs and expenses, the difficulty and expense of integrating operations and personnel of any acquired companies, disruption of our ongoing business, diversion of management’s time and attention, and possible dilution to shareholders. We may not be able to successfully overcome these risks and other problems associated with any future acquisitions and this may adversely affect our business and financial condition.
We are a Québec incorporated company headquartered in Canada, and U.S. investors may be unable to enforce certain judgments against us.
We are a company existing under the Business Corporations Act (Québec). Some of our directors and officers are residents of Canada, and certain of our assets are located outside the United States. As a result, it may be difficult to effect service within the United States upon us or upon some of our directors and officers. Execution by U.S. courts of any judgment obtained against us or any of our directors or officers in U.S. courts may be limited to assets located in the United States. It may also be difficult for holders of our securities who reside in the United States to realize in the United States upon judgments of U.S. courts predicated upon civil liability of us and our directors and executive officers under the U.S. federal securities laws. There may be doubt as to the enforceability in Canada against non-U.S. entities or their controlling persons, directors and officers who are not residents of the United States, in original actions or in actions for enforcement of judgments of U.S. courts, of liabilities predicated solely upon U.S. federal or state securities laws.
35
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
Not applicable.
Item 2. Properties
Our head office and operations are located at 3009 boul. de la Concorde East, Suite 102, Laval, Québec, Canada H7E 2B5 and our research and development and quality control laboratories are located at Espace Lab, 2650 Maximilien-Chagnon, Sherbrooke, Québec, Canada, J1E 0M8. We currently lease our office and laboratory space.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
In the ordinary course of business, we are at times subject to various legal proceedings and disputes. We assess our liabilities and contingencies in connection with outstanding legal proceedings utilizing the latest information available. Where it is probable that we will incur a loss and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated, we record a liability in our consolidated financial statements. These legal reserves may be increased or decreased to reflect any relevant developments on a quarterly basis. Where a loss is not probable or the amount of loss is not estimable, we do not accrue legal reserves. While the outcome of legal proceedings is inherently uncertain, based on information currently available and available insurance coverage, our management believes that it has established appropriate legal reserves. Any incremental liabilities arising from pending legal proceedings are not expected to have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations, or cash flows. However, it is possible that the ultimate resolution of these matters, if unfavorable, may be material to our financial position, results of operations, or cash flows. We are not currently a party to any legal proceedings that, in the opinion of management, are likely to have a material adverse effect on our business.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
36
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Shareholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities Market Information
Our common shares are traded on The Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbol “ACST.”
Holders
As of June 23, 2023, there were 40 holders of record of our common shares. The actual number of our shareholders is greater than this number of record holders because most of our shareholders are beneficial owners whose shares are held in street name by brokers and other nominees.
Dividends
We do not anticipate paying any cash dividend on our common shares in the foreseeable future. We presently intend to retain any future earnings to finance the expansion and growth of our business. Any future determination to pay dividends will be at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend on our financial condition, results of operations, capital requirements and other factors the board of directors deems relevant. In addition, the terms of any future debt or credit facility may preclude us from paying dividends.
Taxation
The following is a summary of certain U.S. federal income tax considerations arising from and relating to the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of our common shares to a U.S. Holder (as defined below) as capital assets.
This summary provides only general information and does not purport to be a complete analysis or listing of all potential U.S. federal income tax consequences that may apply to a U.S. Holder as a result of the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of our common shares. In addition, this summary does not take into account the individual facts and circumstances of any particular U.S. Holder that may affect the U.S. federal income tax consequences applicable to that U.S. Holder. Accordingly, this summary is not intended to be, and should not be construed as, legal or U.S. federal income tax advice with respect to any U.S. Holder. Each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding the U.S. federal, state and local, and non-U.S. tax consequences arising from or relating to the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of our common shares.
No legal opinion from U.S. legal counsel or ruling from the IRS, has been requested, or will be obtained, regarding the U.S. federal income tax consequences to U.S. Holders of the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of our common shares. This summary is not binding on the IRS, and the IRS is not precluded from taking a position that is different from, and contrary to, the positions taken in this summary. In addition, because the authorities on which this summary is based are subject to various interpretations, the IRS and the U.S. courts could disagree with one or more of the positions taken in this summary.
Scope of this Disclosure
Authorities
This summary is based on the Code, U.S. Treasury Regulations promulgated thereunder (whether final, temporary or proposed), published IRS rulings, judicial decisions, published administrative positions of the IRS, and the Convention between Canada and the United States of America with Respect to Taxes on Income and on Capital, signed September 26, 1980, as amended (the Canada-U.S. Tax Treaty), in each case, as in effect as of the date of this report. Any of the authorities on which this summary is based could be changed in a material and adverse manner at any time, and any such change could be applied on a retroactive basis. Unless otherwise discussed, this summary does not discuss the potential effects, whether adverse or beneficial, of any proposed legislation.
U.S. Holders
For purposes of this summary, a “U.S. Holder” is a beneficial owner of common shares that, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, is (a) an individual who is a citizen or resident of the United States, (b) a corporation, or other entity classified as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes, that is created or organized in or under the laws of the U.S., any state in the United States or the District of Columbia, (c) an estate if the income of such estate is subject to U.S. federal income tax regardless of the source of such income, or (d) a trust if (i) such trust has validly elected to be treated as a U.S. person for U.S. federal income tax purposes or (ii) a U.S. court is able to exercise primary supervision over the administration of such trust and one or more U.S. persons have the authority to control all substantial decisions of such trust.
U.S. Holders Subject to Special U.S. Federal Income Tax Rules Not Addressed
This summary does not address the U.S. federal income tax consequences applicable to U.S. Holders that are subject to special provisions under the Code, including, but not limited to, the following U.S. Holders: (a) U.S. Holders that are tax-exempt organizations, qualified retirement plans, individual retirement accounts, or other tax deferred accounts; (b) U.S. Holders that are financial institutions, insurance companies, real estate investment trusts, or regulated investment companies; (c) U.S. Holders that are dealers in securities or currencies or U.S. Holders that are traders in securities that elect to apply a mark-to-market accounting method; (d) U.S. Holders that have a “functional currency” other than the U.S. dollar; (e) U.S. Holders subject to the alternative minimum tax provisions of the Code; (f) U.S. Holders that own common shares as part of a straddle, hedging transaction, conversion transaction, integrated transaction, constructive sale, or other arrangement involving more than one position; (g) U.S. Holders that acquired common shares through the exercise of employee stock options or otherwise as compensation for services; (h) U.S. Holders that hold common shares other than as a capital asset within the meaning of Section 1221 of the Code; (i) U.S. Holders that beneficially own (directly, indirectly or by attribution) 10% or more of our equity securities (by vote or value); and (j) U.S. expatriates. U.S. Holders that are subject to special provisions under the Code, including U.S. Holders described above, should consult their own tax advisor regarding the U.S. federal, U.S. federal alternative minimum, U.S. federal estate and gift, U.S. state and local, and non-U.S. tax consequences arising from and relating to the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of the common shares.
If an entity or arrangement that is classified as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes holds common shares, the U.S. federal income tax consequences to that partnership and the partners of that partnership generally will depend on the activities of the partnership and the status of the partners. Partners of entities that are classified as partnerships for U.S. federal income tax purposes should consult their own tax advisors regarding the U.S. federal income tax consequences arising from and relating to the acquisition, ownership and disposition of the common shares.
Tax Consequences Other than U.S. Federal Income Tax Consequences Not Addressed
This summary does not address the U.S. estate and gift, alternative minimum, state, local or non-U.S. tax consequences to U.S. Holders of the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of our common shares. Each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding the U.S. estate and gift, alternative minimum, state, local and non-U.S. tax consequences arising from and relating to the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of our common shares.
37
U.S. Federal Income Tax Considerations of the Acquisition, Ownership, and Disposition of Common Shares
Distributions on Common Shares
Subject to the discussion under “—Passive Foreign Investment Company Rules” below, a U.S. Holder that receives a distribution, including a constructive distribution or a taxable stock distribution, with respect to the common shares generally will be required to include the amount of that distribution in gross income as a dividend (without reduction for any Canadian income tax withheld from such distribution) to the extent of our current or accumulated “earnings and profits” (as computed for U.S. federal income tax purposes). To the extent that a distribution exceeds our current and accumulated “earnings and profits”, the excess amount will be treated (a) first, as a tax-free return of capital to the extent of a U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in the common shares with respect to which the distribution is made (resulting in a corresponding reduction in the tax basis of those common shares) and, (b) thereafter, as gain from the sale or exchange of those common shares (see the more detailed discussion at “—Disposition of Common Shares” below). We do not intend to calculate our current or accumulated earnings and profits for U.S. federal income tax purposes and, therefore, will not be able to provide U.S. Holders with that information. U.S. Holders should therefore assume that any distribution by us with respect to our common shares will constitute a dividend. However, U.S. Holders should consult their own tax advisors regarding whether distributions from us should be treated as dividends for U.S. federal income tax purposes. Dividends paid on our common shares generally will not be eligible for the “dividends received deduction” allowed to corporations under the Code with respect to dividends received from U.S. corporations.
A dividend paid by us generally will be taxed at the preferential tax rates applicable to long-term capital gains if, among other requirements, (a) we are a “qualified foreign corporation” (as defined below), (b) the U.S. Holder receiving the dividend is an individual, estate, or trust, and (c) the dividend is paid on common shares that have been held by the U.S. Holder for at least 61 days during the 121-day period beginning 60 days before the “ex-dividend date” (i.e., the first date that a purchaser of the common shares will not be entitled to receive the dividend).
For purposes of the rules described in the preceding paragraph, we generally will be a “qualified foreign corporation”, or a QFC, if (a) we are eligible for the benefits of the Canada-U.S. Tax Treaty, or (b) our common shares are readily tradable on an established securities market in the United States, within the meaning provided in the Code. However, even if we satisfy one or more of the requirements, we will not be treated as a QFC if we are classified as a PFIC (as discussed below) for the taxable year during which we pay the applicable dividend or for the preceding taxable year. The dividend rules are complex, and each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding the application of those rules to them in their particular circumstances. Even if we satisfy one or more of the requirements, as noted below. Thus, there can be no assurance that we will qualify as a QFC.
Disposition of Common Shares
Subject to the discussion under “—Passive Foreign Investment Company Rules” below, a U.S. Holder will recognize gain or loss on the sale or other taxable disposition of common shares (that is treated as a sale or exchange for U.S. federal income tax purposes) equal to the difference, if any, between (a) the U.S. dollar value of the amount realized on the date of the sale or disposition and (b) the U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis (determined in U.S. dollars) in the common shares sold or otherwise disposed of. Any such gain or loss generally will be capital gain or loss, which will be long-term capital gain or loss if the common shares are held for more than one year. A U.S. Holder's initial tax basis in the common shares generally will equal the U.S. dollar cost of such common shares. Each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor as to the tax treatment of dispositions of common shares in exchange for Canadian dollars.
Preferential tax rates apply to long-term capital gains of a U.S. Holder that is an individual, estate, or trust. There are currently no preferential tax rates for long-term capital gains of a U.S. Holder that is a corporation. Deductions for capital losses are subject to complex limitations.
Passive Foreign Investment Company Rules
If we are or become a PFIC, the preceding sections of this summary may not describe the U.S. federal income tax consequences to U.S. Holders of the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of our common shares.
Passive Foreign Investment Company Status.
Special, generally unfavorable, rules apply to the ownership and disposition of the stock of a PFIC. For U.S. federal income tax purposes, a non-U.S. corporation is classified as a PFIC if:
Passive income generally includes the following types of income:
In determining whether we are a PFIC, we will be required to take into account a pro rata portion of the income and assets of each corporation in which we own, directly or indirectly, at least 25% by value.
As described above, PFIC status of a non-U.S. corporation depends on the relative values of certain categories of assets and the relative amount of certain kinds of income for a taxable year. Therefore, our status as a PFIC for any given taxable year depends upon the financial results for such year and upon relative valuations, which are subject to change and beyond our ability to predict or control. Based on our most recent financial statements and projections and given uncertainty regarding the composition of our future income and assets, there is a significant risk that we may have been classified as a PFIC for the taxable year that ended on March 31, 2023 and may be classified as a PFIC for our current taxable year and possibly subsequent years. However, PFIC status is fundamentally factual in nature, depends on the application of complex U.S. federal income tax rules (which are subject to differing interpretations), generally cannot be determined until the close of the taxable year in question and is determined annually. Accordingly, there can be no assurance that we will not be a PFIC in our current taxable year or subsequent years. The PFIC rules are complex, and each U.S. Holder should consult its tax advisor regarding the application of the PFIC rules to us.
38
Default PFIC Rules Under Section 1291 of the Code.
Generally, if we are or have been treated as a PFIC for any taxable year during a U.S. Holder’s holding period of common shares, subject to the special rules described below applicable to a U.S. Holder who makes a Mark-to-Market Election or a QEF Election (each as defined below), any “excess distribution” with respect to the common shares would be allocated ratably over the U.S. Holder’s holding period. The amounts allocated to the taxable year of the excess distribution and to any year before we became a PFIC would be taxed as ordinary income. The amount allocated to each other taxable year would be subject to tax at the highest rate in effect for individuals or corporations in that taxable year, as appropriate, and an interest charge would be imposed on the amount allocated to that taxable year. Distributions made in respect of common shares during a taxable year will be excess distributions to the extent they exceed 125% of the average of the annual distributions on common shares received by the U.S. Holder during the preceding three taxable years or the U.S. Holder’s holding period, whichever is shorter. In addition, dividends generally will not be qualified dividend income if we are a PFIC in the taxable year of payment or the preceding year.
Generally, if we are treated as a PFIC for any taxable year during which a U.S. Holder owns common shares, any gain on the disposition of the common shares would be treated as an excess distribution and would be allocated ratably over the U.S. Holder’s holding period and subject to taxation in the same manner as described in the preceding paragraph and would not be eligible for the preferential long-term capital gains rate.
Certain elections (including the Mark-to-Market Election and the QEF Election, as defined and discussed below) may sometimes be used to mitigate the adverse impact of the PFIC rules on U.S. Holders, but these elections may accelerate the recognition of taxable income and have other adverse consequences.
Each current or prospective U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding potential status of us as a PFIC, the possible effect of the PFIC rules to such holder in his, her or its particular circumstances, information reporting required if we were treated as a PFIC and the availability of any election that may be available to the U.S. holder to mitigate adverse U.S. federal income tax consequences of holding shares in a PFIC.
QEF Election.
A U.S. Holder of common shares in a PFIC generally would not be subject to the PFIC rules discussed above if the U.S. Holder had made a timely and effective election (a “QEF Election”) to treat us as a “qualified electing fund” (a “QEF”). Instead, such U.S. Holder would be subject to U.S. federal income tax on its pro rata share of our (i) net capital gain, which would be taxed as long-term capital gain to such U.S. Holder, and (ii) ordinary earnings, which would be taxed as ordinary income to such U.S. Holder, in each case regardless of whether such amounts are actually distributed to such U.S. Holder. However, a U.S. Holder that makes a QEF Election may, subject to certain limitations, elect to defer payment of current U.S. federal income tax on such amounts, subject to an interest charge. If such U.S. Holder is not a corporation, any such interest paid will be treated as “personal interest,” which is not deductible.
A U.S. Holder that makes a timely and effective QEF Election generally (a) may receive a tax-free distribution from us to the extent that such distribution represents our “earnings and profits” that were previously included in income by such U.S. Holder because of such QEF Election and (b) will adjust such U.S. Holder’s tax basis in the common shares to reflect the amount included in income or allowed as a tax-free distribution because of such QEF Election. In addition, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, a U.S. Holder that makes a timely QEF Election generally will recognize capital gain or loss on the sale or other taxable disposition of the common shares.
A QEF Election will be treated as “timely” if such QEF Election is made for the first taxable year in the U.S. Holder’s holding period for the common shares in which we are a PFIC. A U.S. Holder may make a timely QEF Election by filing the appropriate QEF Election documents at the time such U.S. Holder files a U.S. federal income tax return for such first year. If a U.S. Holder makes a QEF Election after the first taxable year in the U.S. Holder’s holding period for the common shares in which we are a PFIC, then, in addition to filing the QEF Election documents, a U.S. Holder may elect to recognize gain (which will be taxed under the rules discussed under “—Default PFIC Rules Under Section 1291 of the Code”) as if the common shares were sold on the qualification date. The “qualification date” is the first day of the first taxable year in which we are a QEF with respect to such U.S. Holder. The election to recognize such gain can only be made if such U.S. Holder’s holding period for the common shares includes the qualification date. By electing to recognize such gain, such U.S. Holder will be deemed to have made a timely QEF Election. In addition, under very limited circumstances, it is possible that a U.S. Holder might make a retroactive QEF Election if such U.S. Holder failed to file the QEF Election documents in a timely manner. If a U.S. Holder fails to make a QEF Election for the first taxable year in the U.S. Holder’s holding period for the common shares in which we are a PFIC and does not elect to recognize gain as if the common shares were sold on the qualification date, such holder will not be treated as having made a “timely” QEF Election and will continue to be subject to the special adverse taxation rules discussed above under “—Default PFIC Rules Under Section 1291 of the Code”.
A QEF Election will apply to the taxable year for which such QEF Election is made and to all subsequent taxable years, unless such QEF Election is invalidated or terminated or the IRS consents to revocation of such QEF Election. If a U.S. Holder makes a QEF Election and, in a subsequent taxable year, we cease to be a PFIC, the QEF Election will remain in effect (although it will not be applicable) during those taxable years in which we are not a PFIC. Accordingly, if we become a PFIC in another subsequent taxable year, the QEF Election will be effective, and the U.S. Holder will be subject to the rules described above during any such subsequent taxable year in which we qualify as a PFIC.
A U.S. Holder cannot make and maintain a valid QEF Election unless we provide certain U.S. tax information necessary to make such an election. On an annual basis, we intend to use commercially reasonable efforts to make available to U.S. Holders, upon their written request (a) timely information as to our status as a PFIC, and (b) for each year in which we are a PFIC, information and documentation that a U.S. Holder making a QEF Election with respect to us is required to obtain for U.S. federal income tax purposes. Each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding the availability of, and procedure for making, a QEF Election with respect to us.
Mark-to-Market Election.
A U.S. Holder of common shares in a PFIC would not be subject to the PFIC rules discussed above under “—Default PFIC Rules Under Section 1291 of the Code” if the U.S. Holder had made a timely and effective election to mark the PFIC common shares to market (a “Mark-to-Market Election”).
A U.S. Holder may make a Mark-to-Market Election with respect to the common shares only if such shares are marketable stock. Such shares generally will be “marketable stock” if they are regularly traded on a “qualified exchange,” which is defined as (a) a national securities exchange that is registered with the SEC, (b) the national market system established pursuant to section 11A of the Exchange Act, or (c) a non-U.S. securities exchange that is regulated or supervised by a governmental authority of the country in which the market is located, provided that (i) such non-U.S. exchange has trading volume, listing, financial disclosure, surveillance, and other requirements, and the laws of the country in which such non-U.S. exchange is located, together with the rules of such non-U.S. exchange, ensure that such requirements are actually enforced and (ii) the rules of such non-U.S. exchange ensure active trading of listed stocks. Our common shares will generally be treated as “regularly traded” in any calendar year in which more than a de minimis quantity of common shares is traded on a qualified exchange for at least 15 days during each calendar quarter. Each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor with respect to the availability of a Mark-to-Market Election with respect to the common shares.
In general, a U.S. Holder that makes a timely Mark-to-Market Election with respect to the common shares will include in ordinary income, for each taxable year in which we are a PFIC, an amount equal to the excess, if any, of (a) the fair market value of the common shares as of the close of such taxable year over (b) such U.S. Holder’s tax basis in such shares. A U.S. Holder that makes a Mark-to-Market Election will be allowed a deduction in an amount equal to the lesser of (a) the excess, if any, of (i) such U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in the common shares over (ii) the fair market value of such shares as of the close of such taxable year or (b) the excess, if any, of
39
(i) the amount included in ordinary income because of such Mark-to-Market Election for prior taxable years over (ii) the amount allowed as a deduction because of such Mark-to-Market Election for prior taxable years. If a U.S. Holder makes a Mark-to-Market Election after the first taxable year in which we are a PFIC and such U.S. Holder has not made a timely QEF Election with respect to us, the PFIC rules described above under “—Default PFIC Rules Under Section 1291 of the Code” will apply to certain dispositions of, and distributions on, the common shares, and the U.S. Holder’s mark-to-market income for the year of the election. If we were to cease being a PFIC, a U.S. Holder that marked its common shares to market would not include mark-to-market gain or loss with respect to its common shares for any taxable year that we were not a PFIC.
A U.S. Holder that makes a Mark-to-Market Election generally will also adjust such U.S. Holder’s tax basis in his common shares to reflect the amount included in gross income or allowed as a deduction because of such Mark-to-Market Election. In addition, upon a sale or other taxable disposition of the common shares subject to a Mark-to-Market Election, any gain or loss on such disposition will be ordinary income or loss (to the extent that such loss does not to exceed the excess, if any, of (a) the amount included in ordinary income because of such Mark-to-Market Election for prior taxable years over (b) the amount allowed as a deduction because of such Mark-to-Market Election for prior taxable years). A Mark-to-Market Election applies to the taxable year in which such Mark-to-Market Election is made and to each subsequent taxable year unless the common shares cease to be “marketable stock” or the IRS consents to revocation of such election. Each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding the availability of, and procedure for making, a Mark-to-Market Election with respect to the common shares.
Reporting.
If we were to be treated as a PFIC in any taxable year, a U.S. Holder will generally be required to file an annual report with the IRS containing such information as the U.S. Treasury Department may require.
Each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding our potential status as a PFIC, the possible effect of the PFIC rules to such holder and information reporting required if we were a PFIC, as well as the availability of any election that may be available to the holder to mitigate adverse U.S. federal income tax consequences of holding shares in a PFIC.
Receipt of Foreign Currency
The amount of a distribution paid in Canadian dollars or Canadian dollar proceeds received on the sale or other taxable disposition of common shares will generally be equal to the U.S. dollar value of the currency on the date of receipt. If any Canadian dollars received with respect to the common shares are later converted into U.S. dollars, U.S. Holders may realize foreign currency gain or loss on the conversion. Any gain or loss generally will be treated as ordinary income or loss and generally will be from sources within the United States for U.S. foreign tax credit purposes. Each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor concerning the possibility of foreign currency gain or loss if any such currency is not converted into U.S. dollars on the date of receipt.
Foreign Tax Credit
Subject to certain limitations, a U.S. Holder who pays (whether directly or through withholding) Canadian or other non-U.S. income tax with respect to the common shares may be entitled, at the election of the U.S. Holder, to receive either a deduction or a credit for Canadian or other non-U.S. income tax paid. Dividends paid on common shares generally will constitute income from sources outside the United States. Any gain from the sale or other taxable disposition of the common shares by a U.S. Holder generally will constitute U.S. source income. The foreign tax credit rules (including the limitations with respect thereto) are complex, and each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding the foreign tax credit rules, having regard to such holder’s particular circumstances.
Information Reporting; Backup Withholding
Generally, information reporting and backup withholding will apply to distributions on, and the payment of proceeds from the sale or other taxable disposition of, the common shares unless (i) the U.S. Holder is a corporation or other exempt entity, or (ii) in the case of backup withholding, the U.S. Holder provides a correct taxpayer identification number, certifies that the U.S. Holder is not subject to backup withholding and otherwise complies with the applicable requirements of the backup withholding rules.
Backup withholding is not an additional tax. Any amount withheld generally will be creditable against a U.S. Holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability or refundable to the extent that it exceeds such liability provided the required information is provided to the IRS in a timely manner.
In addition, certain categories of U.S. Holders must file information returns with respect to their investment in a non-U.S. corporation. For example, certain U.S. Holders must file IRS Form 8938 with respect to certain “specified foreign financial assets” (such as the common shares) with an aggregate value in excess of US$50,000 (and, in some circumstances, a higher threshold). Failure to do so could result in substantial penalties and in the extension of the statute of limitations with respect to such holder’s U.S. federal income tax returns. Each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding application of the information reporting and backup withholding rules to it in connection with an investment in our common shares.
Medicare Contribution Tax
U.S. Holders that are individuals, estates or certain trusts generally will be subject to a 3.8% Medicare contribution tax on, among other things, dividends on, and capital gains from the sale or other taxable disposition of, common shares, subject to certain limitations and exceptions. Each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding possible application of this additional tax to income earned in connection with an investment in our common shares.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
None.
Issuer Repurchases of Equity Securities
None.
Item 6. Reserved
Not applicable.
40
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operation
The following discussion should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and notes thereto found elsewhere in this annual report. This annual report contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the U.S. Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These statements are subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results and events to differ materially from those expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. For a detailed discussion of these risks and uncertainties, see Item 1A, “Risk Factors” of this annual report. We caution readers not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements, which reflect management’s analysis only as of the date of this annual report. We undertake no obligation to update forward-looking statements which reflect events or circumstances occurring after the date of this annual report, unless required by applicable securities laws.
Introduction
This management’s discussion and analysis, or MD&A, is presented in order to provide the reader with an overview of the financial results and changes to our financial position as at March 31, 2023 and for the twelve-month period then ended. This MD&A explains the material variations in our operations, financial position and cash flows for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022.
Market data and certain industry data and forecasts included in this MD&A were obtained from internal corporation surveys, market research, and publicly available information, reports of governmental agencies and industry publications and surveys. We have relied upon industry publications as our primary sources for third-party industry data and forecasts. Industry surveys, publications and forecasts generally state that the information they contain has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable, but that the accuracy and completeness of that information is not guaranteed. We have not independently verified any of the data from third-party sources or the underlying economic assumptions they made. Similarly, internal surveys, industry forecasts and market research, which we believe to be reliable based upon our management’s knowledge of our industry, have not been independently verified. Our estimates involve risks and uncertainties, including assumptions that may prove not to be accurate, and these estimates and certain industry data are subject to change based on various factors, including those discussed under Item 1.A “Risk Factors” in this annual report. While we believe our internal business, research is reliable and the market definitions we use in this MD&A are appropriate, neither our business research nor the definitions we use have been verified by any independent source.
This MD&A, approved by the board of directors on June 23, 2023, should be read in conjunction with our audited consolidated financial statements for the year ended March 31, 2023, and 2022. Our audited financial statements were prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board in the United States, or GAAP. All amounts appearing in this MD&A for the period-by-period discussions are in thousands of U.S. dollars, except share and per share amounts or unless otherwise indicated.
Our assets as at March 31, 2023, include cash and cash equivalents and short-term investments totalling $27.9 million and intangible assets and goodwill totalling $49.2 million. Our current liabilities total $3.4 million as at March 31, 2023 and are comprised primarily of amounts due to or accrued for creditors.
Comparative Financial Information for the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022
|
|
Year ended |
|
|||||||||
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, |
|
|
Increase (Decrease) |
|
|||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Net loss |
|
|
(42,429 |
) |
|
|
(9,819 |
) |
|
|
32,610 |
|
Basic and diluted loss per share |
|
|
(0.95 |
) |
|
|
(0.27 |
) |
|
|
0.68 |
|
Total assets |
|
|
79,123 |
|
|
|
128,620 |
|
|
|
(49,497 |
) |
Working capital1 |
|
|
25,879 |
|
|
|
42,021 |
|
|
|
(16,142 |
) |
Total non-current liabilities |
|
|
7,757 |
|
|
|
17,090 |
|
|
|
(9,333 |
) |
Total shareholders’ equity |
|
|
67,955 |
|
|
|
108,270 |
|
|
|
(40,315 |
) |
Results of Operations
Comparison of the year ended March 31, 2023, and 2022
The following table summarizes our results of operations for the year ended March 31, 2023 and 2022:
|
|
Year ended |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
March 31, |
|
|
March 31, |
|
|
Increase (Decrease) |
|
|||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Operating expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Research and development expenses, net of government assistance |
|
|
9,972 |
|
|
|
5,559 |
|
|
|
4,413 |
|
General and administrative expenses |
|
|
7,614 |
|
|
|
9,263 |
|
|
|
(1,649 |
) |
Sales and marketing expenses |
|
|
661 |
|
|
|
518 |
|
|
|
143 |
|
Impairment of Intangible assets |
|
|
28,682 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
28,682 |
|
Impairment of Goodwill |
|
|
4,826 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
4,826 |
|
Impairment of Assets held for sale |
|
|
400 |
|
|
|
249 |
|
|
|
151 |
|
Loss from operating activities |
|
|
(52,155 |
) |
|
|
(15,589 |
) |
|
|
36,566 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Financial income |
|
|
184 |
|
|
|
5,122 |
|
|
|
(4,938 |
) |
Income tax recovery |
|
|
9,542 |
|
|
|
648 |
|
|
|
8,894 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Net loss |
|
|
(42,429 |
) |
|
|
(9,819 |
) |
|
|
32,610 |
|
41
Net Loss
The net loss of $42,429 or $0.95 loss per share for the year ended March 31, 2023, increased by $32,610 from the net loss of $9,819 or $0.27 loss per share for the year ended March 31, 2022.
Research and development expenses
Research and development expenses consist primarily of:
We record research and development expenses as incurred.
Our research and development during the year ended March 31, 2023 was focused primarily on our clinical development programs GTX 104, GTX 102, and GTX 101 drug candidates. Research and development expenses during the year ended March 31, 2022, related to the completion of our TRILOGY Phase 3 clinical program for our former drug candidate CaPre, as well as the initiation and progression of development work related to GTX 104, GTX 102 and GTX 101.
The following table summarizes our research and development expenses:
Research and development expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Year ended |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, |
|
|
Increase (Decrease) |
|
|||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Third-party contract research expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Clinical development programs: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
GTX 104 |
|
|
838 |
|
|
|
1,796 |
|
|
|
(958 |
) |
GTX 102 |
|
|
1,779 |
|
|
|
61 |
|
|
|
1,718 |
|
GTX 101 |
|
|
2,612 |
|
|
|
538 |
|
|
|
2,074 |
|
Other third-party contract research expenses |
|
|
605 |
|
|
|
724 |
|
|
|
(119 |
) |
Professional fees |
|
|
1,600 |
|
|
|
317 |
|
|
|
1,283 |
|
Other research and development costs |
|
|
270 |
|
|
|
236 |
|
|
|
34 |
|
Government grants & tax credits |
|
|
(165 |
) |
|
|
(577 |
) |
|
|
412 |
|
Total third-party research and development expenses1 |
|
|
7,539 |
|
|
|
3,095 |
|
|
|
4,444 |
|
Salaries and benefits |
|
|
1,742 |
|
|
|
2,017 |
|
|
|
(275 |
) |
Stock-based compensation |
|
|
591 |
|
|
|
447 |
|
|
|
144 |
|
Depreciation and write off of equipment |
|
|
100 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
100 |
|
Total |
|
|
9,972 |
|
|
|
5,559 |
|
|
|
4,413 |
|
42
1Total third-party research and development expenses is calculated before salaries and benefits, depreciation, write-off of equipment and stock-based compensation. Because there is no standard method endorsed by GAAP, the results may not be comparable to similar measurements presented by other public companies.
Total third-party research and development expenses before salaries and benefits, depreciation, amortization and stock-based compensation expenses for the year ended March 31, 2023, totalled $7,539 compared to $3,095 for the year ended March 31, 2022. This resulted in an increase of $4,444 related mostly to the continued work of clinical development programs for GTX-104, GTX-102 and GTX-101.
Third-party contract research expenses related to GTX-104 amounted to $838 for the year ended March 31, 2023, compared to $1,796 for the year ended March 31, 2022. This resulted in a $958 decrease as our PK bridging for GTX-104 study wound down. third-party contract research expenses related to GTX-102 were $1,779 for the year ended March 31, 2023, compared to $61 for the year ended March 31, 2022. This resulted in a $1,718 increase due to the initiation of the PK bridging study for GTX-102 and for clinical trial materials. third-party contract research expenses related to GTX 101 amounted to $2,612 for the year ended March 31, 2023, compared to $538 for the year ended March 31, 2022. This resulted in a $2,074 increase and was mostly related to the planning and initiation of the Phase 1 single dose trial. The program related increases for GTX 104, GTX 102 and GTX 101 were offset by a decrease of $119, related to other third-party contract research expenses for non-clinical outside services. Professional fees of $1,600 for the year ended March 31, 2023, compared to $317 for the year ended March 31, 2022, amounted to an increase of $1,283. This is due to increased specialized clinical and regulatory consultants supporting our clinical programs for GTX-104, GTX-102 and GTX-101. Total third-party research and development expenses were reduced by $165 due to government credits eligible research activities related to our clinical programs GTX 104, GTX 102 and GTX 101.
Salaries and benefits decreased by $275 to $1,742 for the year ended March 31, 2023, from $2,017 for the year ended March 31, 2022. The decrease relates to a reduced accrual of our employee incentive bonus program.
General and administrative expenses
General and administrative expenses consist primarily of salaries and benefits, including share-based compensation, related to our executive, finance, legal, and support functions. Other general and administrative expenses include professional fees for auditing, tax, consulting, rent and utilities, insurance and patent-related services.
General and administrative expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Year ended |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, |
|
|
Increase (Decrease) |
|
|||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Salaries and benefits |
|
|
2,362 |
|
|
|
1,745 |
|
|
|
617 |
|
Professional fees |
|
|
2,013 |
|
|
|
5,199 |
|
|
|
(3,186 |
) |
Other |
|
|
2,053 |
|
|
|
1,477 |
|
|
|
576 |
|
General and administrative expense before stock-based compensation and depreciation 1 |
|
|
6,428 |
|
|
|
8,421 |
|
|
|
(1,993 |
) |
Stock-based compensation |
|
|
1,123 |
|
|
|
842 |
|
|
|
281 |
|
Depreciation |
|
|
63 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
63 |
|
Total |
|
|
7,614 |
|
|
|
9,263 |
|
|
|
(1,649 |
) |
1 General and administrative sub-total expenses is calculated before stock-based compensation and depreciation. Because there is no standard method endorsed by GAAP, the results may not be comparable to similar measurements presented by other public companies.
General and administrative expenses totaled $6,428 before stock-based compensation and depreciation expense for the year ended March 31, 2023, a decrease of $1,993, from $8,421 for the year ended March 31, 2022. The decrease was primarily a result of decreased legal, tax, accounting and other professional fees related to the Grace Therapeutics merger for the year ended March 31, 2022.
Salaries and benefits increased by $617 to $2,362 for the year ended March 31, 2023, from $1,745 for the year ended March 31, 2022. The increase relates to severance amounts accrued in relation to the former CEO. The decrease in professional fees were partially offset by an increase in other expenses. Other expenses increased by $576 to $2,053 for the year ended March 31, 2023, from $1,477 for the year ended March 31, 2022. This increase was related to increased expenses for accounting software upgrades, and IP legal costs to support and maintain our patents relating to TX-104, GTX-102 and GTX-101.
Sales and marketing
Sales and marketing expenses consist primarily of salaries and benefits, including share-based compensation, related to our commercial functions.
Sales and marketing expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Year ended |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, |
|
|
Increase (Decrease) |
|
|||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Salaries and benefits |
|
|
428 |
|
|
|
271 |
|
|
|
157 |
|
Professional fees |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
83 |
|
|
|
(83 |
) |
Other |
|
|
136 |
|
|
|
116 |
|
|
|
20 |
|
Sales and Marketing expenses before stock-based compensation1 |
|
|
564 |
|
|
|
470 |
|
|
|
94 |
|
Stock-based compensation |
|
|
97 |
|
|
|
48 |
|
|
|
49 |
|
Total |
|
|
661 |
|
|
|
518 |
|
|
|
143 |
|
1 Sales and marketing sub-total expenses is calculated before stock-based compensation. Because there is no standard method endorsed by GAAP, the results may not be comparable to similar measurements presented by other public companies.
Sales and marketing expenses before stock-based compensation expense were $564 for the year ended March 31, 2023, compared to $470 for the year ended March 31, 2022. The increase of $94 was mostly due to an increase in salaries associated with added personnel.
Aggregate stock-based compensation expense increased by $474 to $1,811, for the year ended March 31, 2023, as compared to $1,337 for the year ended March 31, 2022.
43
This increase was due to the timing of the stock options granted during the year ended March 31, 2023 and year ended March 31, 2022.
Aggregate depreciation and amortization expense increased by $124 for the year ended March 31, 2023, to $124 as compared to nil for the year ended March 31, 2022. This increase is due to the impact of certain equipment being reclassified from held for sale to held for use during the year ended March 31, 2023, resulting in additional depreciation being recognized.
Impairment
In April 2023, we announced the strategic decision to prioritize development of GTX-104 with a goal to advance to commercialization, while conserving resources as much as possible to complete development efficiently. We estimate that the deferral could be 3 years given the timeline to complete the development and commercial launch of GTX 104. Further development of GTX-102 and GTX-101 will occur at such time as we obtain additional funding or enter into strategic partnerships.
The decision to defer further development has triggered a comprehensive impairment review of our intangible assets in March 2023. Given the extended timeline, we increased the discount rates used to value the assets in order to recognize additional risks related to prioritizing one asset over the others, financing the projects given limited available resources and the need to preserve cash to advance GTX 104 as far as possible, potential competitor advances that could arise over three years, and the general market depression affecting small cap development companies like us and the prohibitively high dilution and expense of available funding in the capital markets. Increasing the discount rates significantly reduced the discounted cash flow values for each of the programs deferred.
Accordingly, an impairment of intangible assets of $28,682 resulted in the year ended March 31, 2023, compared to nil for the year ended March 31, 2022. In addition, an impairment of $4,826 of goodwill resulted in the year ended March 31, 2023, compared to nil for the year ended March 31, 2022.
Income tax recovery
The impairment of $28,682 of the intangible assets resulted in an income tax recovery of $8,633 of the related deferred tax liability.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Share Capital Structure
Our authorized share capital consists of an unlimited number of Class A, Class B, Class C, Class D and Class E shares, each without par value. Issued and outstanding fully paid shares, stock options, restricted shares units and warrants, were as follows for the periods ended (all amounts in the table below give effect to the 1-for-8 share consolidation we completed on August 31, 2021):
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, |
|
||
|
|
Number |
|
|
Number |
|
||
Class A shares, voting, participating and without par value |
|
|
44,612,831 |
|
|
|
44,288,183 |
|
Stock options granted and outstanding |
|
|
4,445,492 |
|
|
|
2,989,381 |
|
May 2018 Canadian public offering of warrants exercisable at CAD$10.48 until May 9, 2023 |
|
|
824,218 |
|
|
|
824,218 |
|
December 2017 U.S. public offering of warrants exercisable at US$10.08 until December 19, 2022 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
884,120 |
|
December 2017 U.S. public offering broker warrants exercisable at US$10.10 until December 27, 2022 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
32,390 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total fully diluted shares |
|
|
49,882,541 |
|
|
|
49,018,292 |
|
Cash Flows and Financial Condition between the years ended March 31, 2023 and March 31, 2022
Summary
As at March 31, 2023, cash and cash equivalents totalled $27,875, a net decrease of $2,464 compared to cash and cash equivalents totalling $30,339 at March 31, 2022.
Net cash used in operating activities
During the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022, our operating activities used cash of $15,913 and $17,234, respectively resulting in a decrease of $1,321. Cash used in operating activities during 2023 primarily related to our net loss of $42,429, adjusted for non-cash items such as stock-based compensation of $1,811, impairments of $33,908, income tax recovery of $9,542 and changes in our operating assets and liabilities of $181. Cash used in operating activities during 2022 primarily related to our net loss of $9,819, adjusted for non-cash items such as change in fair value of warrant liabilities of $5,197, unrealized foreign exchange gain of $370 and changes in our operating assets and liabilities of $2,786.
Investing activities
For the year ended March 31, 2023 our investing activities generated cash of $13,153 compared to cash used of $3,522 for the year ended March 31, 2022. The increase in cash generated was a function of an increase in proceeds from maturity of short-term investments included in 2022.
Financing activities
During the year ended March 31, 2023 we received net proceeds of approximately $304 from our at the market (ATM) program. During the year ended March 31, 2022, we did not have financing activities and used existing cash balances for operations purposes.
ATM Program
On June 29, 2020, we entered into an amended and restated sales agreement (the “Sales Agreement”) with B. Riley, Oppenheimer & Co. Inc. and H.C. Wainwright & Co., LLC (collectively, the “Agents”). Under the terms of the Sales Agreement, which has a three-year term, we may issue and sell from time-to-time common shares having an aggregate offering price of up to $75,000,000 through the Agents. Subject to the terms and conditions of the Sales
44
Agreement, the Agents will use their commercially reasonable efforts to sell the common shares from time to time, based upon our instructions. We have no obligation to sell any of the common shares and may at any time suspend sales under the Sales Agreement. We and the Agents may terminate the Sales Agreement in accordance with its terms. Under the terms of the Sales Agreement, we have provided the Agents with customary indemnification rights and the Agents will be entitled to compensation at a commission rate equal to 3.0% of the gross proceeds from each sale of the common shares.
On November 10, 2021, we filed a prospectus supplement relating to our ATM program, expiring July 7, 2023, to restore available capacity to $75,000,000, with B. Riley, Oppenheimer & Co. Inc. and H.C. Wainwright & Co., LLC continuing to act as Agents. Under the terms of the Sales Agreement and the prospectus supplement, we may issue and sell from time-to-time common shares having an aggregate offering price of up to $75,000,000 through the Agents; however, our use of the shelf registration statement on Form S-3 will be limited for so long as we are subject to General Instruction I.B.6 of Form S-3, which limits the amounts that we may sell under the registration statement and in accordance with the Sales Agreement. The common shares will be distributed at market prices prevailing at the time of the sale and, as a result, prices may vary between purchasers and during the period of distribution. The volume and timing of sales under the ATM program, if any, will be determined at the sole discretion of our board of directors and management.
During the year ended March 31, 2023, 324,648 common shares were sold under the ATM program for total gross proceeds of approximately $314. The common shares were sold at the prevailing market prices, which resulted in an average price of approximately $0.95 per share. During the year ended March 31, 2022, no common shares were sold under the ATM program.
Financial Position
The following table details the significant changes to the consolidated balance sheet as at March 31, 2023, compared to the prior fiscal year end at March 31, 2022:
Accounts |
|
Increase |
|
|
Comments |
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
(2,464 |
) |
|
See cash flow statement |
Investments |
|
|
(13,307 |
) |
|
Decrease in cash available to invest |
Receivables |
|
|
254 |
|
|
Timing of reimbursement of sales taxes |
Assets held for sale |
|
|
(352 |
) |
|
Impairment of RKO and production equipment |
Prepaid expenses |
|
|
(122 |
) |
|
Renewal of insurance contract and other prepaid expenses (advances to US vendors) offset by impairment of prepaid RKO |
Right of use asset |
|
|
148 |
|
|
Adjustment to the net present value of lease contract for Sherbrooke |
Equipment |
|
|
(146 |
) |
|
Depreciation expense, write off of assets |
Intangible assets |
|
|
(28,682 |
) |
|
Related to Impairment |
Goodwill |
|
|
(4,826 |
) |
|
Related to Impairment |
Trade and other payables |
|
|
180 |
|
|
Timing of payments net of accruals |
Lease liability |
|
|
190 |
|
|
Future obligations offset by payment of lease liability |
Derivative warrant liabilities |
|
|
(10 |
) |
|
Change in fair value of derivative warrants |
Deferred tax liability |
|
|
(9,542 |
) |
|
Related to Impairment of intangibles |
See the statement of changes in equity in our financial statements for details of changes to the equity accounts since March 31, 2022.
Treasury Operations
Our treasury policy is to invest cash that is not required immediately into instruments with an investment strategy based on capital preservation. Cash equivalents and marketable securities are primarily in guaranteed investment certificates, term deposits and high-interest savings accounts, which are issued and held with Canadian chartered banks, highly rated promissory notes issued by government bodies and commercial paper. We hold cash denominated in both U.S. and Canadian dollars. Funds received in U.S. dollars from equity financing's are invested as per our treasury policy in U.S. dollar investments and converted to Canadian dollars as appropriate to fulfill operational requirements and funding.
Acquisition of Grace Therapeutics
On August 27, 2021, we completed the Grace Therapeutics merger. In connection with the share-for-share noncash transaction, Grace Therapeutics was merged with a new wholly owned subsidiary of Acasti and became a subsidiary of Acasti. As a result, we acquired Grace Therapeutics entire therapeutic pipeline consisting of three unique clinical stage and multiple pre-clinical stage assets supported by an intellectual property portfolio consisting of various granted and pending patents in various jurisdictions worldwide. Under the terms of the acquisition, each issued and outstanding share of Grace Therapeutics common stock was automatically converted into the right to receive Acasti common shares equal to the equity exchange ratio set forth in the merger agreement.
Consideration for Acquisition
A total of 18,241,233 common shares of Acasti were issued to Grace Therapeutics stockholders as consideration for the acquisition.
|
|
|
|
|
Total common shares issued |
|
|
18,241,233 |
|
Acasti share price (closing share price on August 27, 2021) |
|
$ |
3.3344 |
|
Fair value of common shares issued |
|
$ |
60,824 |
|
Our acquisition of Grace Therapeutics has been accounted for as a business combination using the acquisition method of accounting. This acquisition method requires, among other things, that assets acquired, and liabilities assumed in a business combination be recognized at their fair values as of the acquisition date. The valuation of assets acquired, and liabilities assumed was finalized during the fourth quarter of the year ended March 31, 2022.
Measurement period adjustments to the preliminary purchase price allocation during 2022 included (i) an increase to intangible assets of $4,602; (ii) an increase to goodwill of $12,964; (iii) an increase to deferred tax liability of $17,536; and (iv) other individually insignificant adjustments to identifiable net assets of $30. The adjustments primarily resulted from the completion of the valuation of the intangible assets based on facts and circumstances that existed as of the acquisition date and
did not result from intervening events subsequent to such date.
45
The following table summarizes the final fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the acquisition date:
|
|
$ |
|
|
Assets acquired and liabilities assumed |
|
|
|
|
Cash and equivalents |
|
|
90 |
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
74 |
|
Intangible assets – in-process research and development |
|
|
69,810 |
|
Goodwill |
|
|
12,964 |
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
|
(4,578 |
) |
Deferred tax liability |
|
|
(17,536 |
) |
Total assets acquired and liabilities assumed |
|
|
60,824 |
|
Intangible assets of $69,810 relate to the value of IPR&D of Grace Therapeutics therapeutic pipeline, consisting of three unique clinical stage programs/assets supported by intellectual property. We estimated the fair value of the IPR&D intangible assets using a multi-period excess earnings method. The significant assumptions used in the valuation are the discount rate, the probability of clinical success of research and development programs, obtaining regulatory approval and forecasted net sales. Goodwill of $12,964 was calculated as the excess of the consideration transferred over the net assets recognized and represents the future economic benefits arising from the other assets acquired that could not be individually identified and separately recognized. A deferred tax liability of $17,536 related to the identified intangible assets resulted.
Acquisition-related expenses, which were comprised primarily of regulatory, financial advisory and legal fees, totaled $3.2 million for the year ended March 31, 2022 and were included in general and administrative expenses in the consolidated statements of loss and comprehensive loss. The net loss during the year ended March 31, 2022 attributed to Grace in the consolidated statement of income (loss), since the date of acquisition is $1,505.
Assets Held for Sale
In January 2020 and August 2020, we released Phase 3 TRILOGY clinical trial results for our former lead drug candidate, CaPre. The TRILOGY trials did not meet the primary endpoint which resulted in our board of directors deciding not to proceed with a filing of an NDA with the FDA. With the completion of the TRILOGY trials beginning in the second half of fiscal 2021, we committed to a plan and were actively marketing for the sale Other assets and Production Equipment which met the criteria for classification of assets held for sale:
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, 2022 |
|
||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Reclassed as explained below |
|
||
Other assets (a) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
195 |
|
Production equipment (b) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
157 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
352 |
|
a. Other Assets
Other assets represent krill oil ("RKO") held by the Corporation that was expected to be used in the conduct of R&D activities and commercial inventory scale up related to the development and commercialization of the CaPre drug. Given that the development of CaPre will no longer be pursued, the Corporation expected to sell this reserve. The other asset is being recorded at the fair value less costs to sell, which has resulted in an impairment loss of $195 (2022 - $249). Management’s estimate of the fair value of the RKO less cost -to sell, is based on current market conditions for the age of the RKO and the inability to sell it. These projections are based on Level 3 inputs of the fair value hierarchy and reflect management’s best estimate of market participants’ pricing of the assets as well as the general condition of the asset. The total impairment loss recognized, includes amounts paid for RKO in advance, but not yet received and was recorded previously as a prepaid.
b. Production equipment
March 31, 2022 |
|
Cost, net of previous impairment |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Net book |
|
|||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Production equipment |
|
|
1,179 |
|
|
|
(1,022 |
) |
|
|
157 |
|
|
|
|
1,179 |
|
|
|
(1,022 |
) |
|
|
157 |
|
Similarly, to the Other assets, the announcement of the outcomes of the TRILOGY clinical trials resulted in an impairment trigger for the production equipment. The impairment loss is based on management’s estimate of the fair value of the equipment less cost -to sell, which is based primarily on estimated market conditions for selling used equipment and the inability to sell. These projections are based on Level 3 inputs of the fair value hierarchy and reflect the Corporations best estimate of market participants’ pricing of the assets as well as the general condition of the assets. This resulted in an impairment loss of $157.
In June 2022, we reclassed the following assets from assets held for sale as they no longer met the criteria of such classification.
|
|
Cost, net of |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Net |
|
|||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Furniture and office equipment |
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
(5 |
) |
|
|
12 |
|
Computer equipment |
|
|
94 |
|
|
|
(6 |
) |
|
|
88 |
|
Laboratory equipment |
|
|
585 |
|
|
|
(435 |
) |
|
|
150 |
|
|
|
|
696 |
|
|
|
(446 |
) |
|
|
250 |
|
46
Furthermore, depreciation expense of $94 was recognized related to the period from the date that the assets were classified as held for sale until June 30, 2022. The reclassification from held for sale to equipment was reflected on the comparative balance sheet.
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
Our contractual obligations and commitments include trade payables, operating lease obligations, CMO and CRO agreements, and the RKO supply agreement.
Research and development contracts and contract research organizations agreements
We utilize contract manufacturing organizations, for the development and production of clinical materials and contract research organizations to perform services related to our clinical trials. Pursuant to the agreements with these contract manufacturing organizations and contract research organizations, we have either the right to terminate the agreements without penalties or under certain penalty conditions.
RKO supply agreement
On October 25, 2019, we signed a supply agreement with Aker Biomarine Antartic. (“Aker”) to purchase raw krill oil product for a committed volume of commercial starting material for CaPre for a total fixed value of $3.1 million. As at March 31, 2023, the remaining balance of the commitment with Aker amounts to $2.8 million. During the second calendar quarter of 2022, Aker informed the Company that Aker believed it had satisfied the terms of the supply agreement as to their ability to deliver the remaining balance of krill oil product, and that the Company was therefore required to accept the remaining product commitment and to pay Aker the $2.8 million balance. We disagree with Aker’s position and believe that Aker is not entitled to further payment under the supply agreement. Accordingly, no liability has been recorded. The dispute was unresolved as of March 31, 2023 and remains unresolved. There is uncertainty as to whether the Company will be required to make further payment to Aker in connection with the dispute. Additionally, in the event the Company is required to accept delivery from Aker of the remaining balance of krill oil product under the supply agreement, there is uncertainty as to whether the Company can recover value from the product, which may result in the Company incurring a loss on the supply agreement in the near term.
Use of Estimates and Measurement of Uncertainty
The preparation of our financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, income, and expenses. Actual results may differ from these estimates.
Estimates are based on management’s best knowledge of current events and actions that management may undertake in the future. Estimates and underlying assumptions are reviewed on an ongoing basis. Revisions to accounting estimates are recognized in the period in which the estimates are revised and in any future periods affected.
Estimates and assumptions include the measurement of derivative warrant liabilities, stock-based compensation, assets held for sale, valuation of intangible acquired from Grace Therapeutics, goodwill and the RKO supply agreement. Estimates and assumptions are also involved in measuring the accrual of services rendered with respect to research and development expenditures at each reporting date and determining which research and development expenses qualify for research and development tax credits and in what amounts. We recognize the tax credits once we have reasonable assurance that they will be realized. Recorded tax credits are subject to review and approval by tax authorities and, therefore, could be different from the amounts recorded. Estimates and assumptions are also utilized in the assessment of impairment of equipment, and intangibles.
Critical Accounting Policies
Valuation of Intangible Assets and Goodwill
In a business combination, the fair value of IPR&D acquired is capitalized and accounted for as indefinite-lived intangible assets, and not amortized until the underlying project receives regulatory approval, at which point the intangible assets will be accounted for as definite-lived intangible assets or discontinued. If discontinued, the intangible assets will be written off. R&D costs incurred after the acquisition are expensed as incurred.
Our IPR&D and Goodwill was $49.3 million as of March 31, 2023, which represents 62% of total assets. Goodwill and indefinite-lived assets are not amortized but are subject to an impairment review annually and more frequently when indicators of impairment exist. An impairment of goodwill could occur if the carrying amount of a reporting unit exceeds the fair value of that reporting unit. An impairment of indefinite-lived intangible assets would occur if the fair value of the intangible asset is less than the carrying value.
The nature of the assumptions in the intangible asset's impairment tests are considered critical due to a high level of subjectivity and judgment necessary to account for highly uncertain matters, and the impact of the assumptions on our financial condition and our operating performance could be material.
We test goodwill for impairment by first assessing qualitative factors to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value is less than its carrying amount. If we conclude it is more likely than not that fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, a quantitative impairment test is performed. We test indefinite lived intangible assets for impairment by first assessing qualitative factors to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value is less than its carrying amount. Events that could result in an impairment, or trigger an interim impairment assessment, include the decision to discontinue the development of a drug, the receipt of additional clinical or nonclinical data regarding our drug candidates or a potentially competitive drug candidates, changes in the clinical development program for a drug candidate, or new information regarding potential sales for the drug candidates and increases in our weighted average cost of capital.
Individual IPR&D projects and goodwill is tested for impairment on an annual basis in the fourth quarter, and in between annual tests if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of each technology or our reporting unit below its carrying value. We identified the strategic realignment plan announced on April 4, 2023 to prioritize resources to GTX-104, from GTX-101 and GTX-102 triggered a comprehensive impairment review of our intangible assets and have considered these facts in our annual impairment test. Deferral of development for GTX 101 and 102 has extended the cash runway from existing resources and
47
has also reduced the values in the discounted cashflow due to the deferral. The result of the impairment assessment resulted in the following activity between March 31, 2022 and March 31, 2023:
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
||||
|
|
GTX 104 |
|
GTX 102 |
|
GTX 101 |
|
Total |
|
||||
Intangible assets – in-process research and development |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Balance, beginning of the year |
|
|
27,595 |
|
|
31,908 |
|
|
10,307 |
|
|
69,810 |
|
Impairment |
|
|
— |
|
|
(22,712 |
) |
|
(5,970 |
) |
|
(28,682 |
) |
Balance, end of the year |
|
|
27,595 |
|
|
9,196 |
|
|
4,337 |
|
|
41,128 |
|
The impairment of $28,682 of the identified intangible assets resulted in a recovery of $8,633 of the related deferred tax liability.
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
|
|
Balance, beginning of the year |
|
|
12,964 |
|
Impairment |
|
|
(4,826 |
) |
Balance, end of the year |
|
|
8,138 |
|
The estimated fair values of our intangible assets were determined using the multi-period excess earnings method, which is a valuation methodology that provides an estimate of the fair value of an asset based on market participant expectations of the cash flows an asset would generate over its remaining useful life. The projected discounted cash flow models used to estimate the fair value of assets of our IPR&D reflect significant assumptions and are Level 3 unobservable data regarding the estimates a market participant would make in order to evaluate a drug development asset, including the following:
The projected discounted cash flow model used to estimate the fair value of our reporting unit and intangible assets as of March 31, 2023 includes a significant assumption related to each project's probability of clinical success, which is reflected in the cash flows.
Based on our fair value assessment, an impairment loss of GTX 104 would result if the probability of success assumption decreased more than approximately 6.2% for each year, all other assumptions remaining constant. Furthermore, a reasonably possible change of -1% in the probability of success assumption would decrease the fair value of GTX 101 and GTX 102 by $331K and $305K, respectively.
The projected discounted cash flow model used to estimate the fair value of our reporting unit and the intangibles as of March 31, 2023 includes a significant assumption related to each project's projected net sales levels, which is reflected in the cash flows. Based on our fair value assessment, an impairment loss for GTX 104 would result if the net sales assumptions decreased more than approximately 11.8%, for each year, all other assumptions remaining constant. Furthermore, a reasonably possible change of -1% in the net sales assumptions would decrease the fair value of GTX 101 and GTX 102 by $119K and $233K, respectively. We believe that the net sales assumptions developed were applied with a conservative framework such as the exclusion of addressable markets outside the United States, which markets we expect to provide revenue upside if and when GTX-101, GTX-102 and GTX-104 are approved by the FDA.
The following table depicts as at the impairment assessment, the discount rate used in the fair value model and the discount rate in which an impairment loss would occur for GTX 104.
Discount assumption |
|
GTX 104 |
|
|
|
Discount rate used in fair value model |
|
22.8% |
Discount rate that results in an impairment |
|
≤24.1% |
Furthermore, a reasonably possible change of 1% in the discount rate assumption would change the fair value of GTX 101 and GTX 102 by $1.6M and $2.0M, respectively. During the year ended March 31, 2022, a discount rate of 19.2% was used in each of the programs as at the date of the acquisition.
The valuation of our IPR&D has significant measurement uncertainty given the risks and uncertainties associated with the timely and successful completion of the development and commercialization of drug candidates. We engaged a third-party valuation firm to assist us with the valuation of the IPR&D and goodwill. Assumptions are difficult to make accurately and were mainly derived from life science studies, industry data, and peer company information that our management believes represent
48
appropriate comparable data. Estimates of value are required to be discounted to account for risks related to the inherent uncertainties of the overall development and commercialization processes.
The summation of our Goodwill and IPR&D fair values, as indicated by our discounted cash flow calculations, were compared to our consolidated fair value, as indicated by our market capitalization, to evaluate the reasonableness of our calculations. Our determination of a reasonable control premium that an investor would pay, over and above market capitalization for a control position, included a number of factors:
The impairment assessment is sensitive to changes in forecasted cash flows, our selected discount rates as well as the implied control premiums. Changes to our assumptions, in particular changes in technological feasibility or changes in the regulatory approval process could materially affect the estimation of the fair value and could result in impairment charges in future quarters.
Measurement of Assets Held for Sale and RKO Supply Agreement
Assets that are classified as held for sale are measured at the lower of their carrying amount or fair value less expected selling costs (“estimated selling price”) with a loss recognized to the extent that the carrying amount exceeds the estimated selling price. The classification is applicable at the date upon which the sale of assets is probable, and the assets are available for immediate sale in their present condition. Assets, once classified as held for sale, are not subject to depreciation or amortization and both the assets and any liabilities directly associated with the assets held for sale are classified as current in our consolidated balance sheets. Subsequent changes to the estimated selling price of assets held for sale are recorded as gains or losses to the consolidated statements of income wherein the recognition of subsequent gains is limited to the cumulative loss previously recognized.
In addition, there is judgment and potential for loss regarding the recognition and measurement of our RKO supply agreement with Aker to purchase RKO product for a committed volume of commercial starting material for CaPre for a total fixed value of $3.1 million, which is described in more detail in note 21 of our financial statements found elsewhere in this annual report.
Financial Instruments
Credit Risk
Credit risk is the risk of a loss if a customer or counter party to a financial asset fails to meet its contractual obligations. We have credit risk relating to cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities, which we manage by dealing only with highly rated Canadian institutions. The carrying amount of financial assets, as disclosed in the statements of financial position, represents our credit exposure at the reporting date.
Currency Risk
We are exposed to the financial risk related to the fluctuation of foreign exchange rates and the degrees of volatility of those rates. Foreign currency risk is limited to the portion of our business transactions denominated in currencies other than our functional currency. On April 1, 2022, our functional currency was changed from the Canadian dollar to the US dollar. This change is reflected prospectively in our financial statements. Fluctuations related to foreign exchange rates could cause unforeseen fluctuations in our operating results. Since April 1, 2022, a portion of our expenses, salaries is incurred in Canadian dollars and research contracts in Euros, for which no financial hedging is in place. There is a financial risk related to the fluctuation in the value of the Canadian dollar and the Euro in relation to the U.S. dollar. In order to minimize the financial risk related to the fluctuation in the value of the Canadian dollar in relation to the U.S. dollar, certain funds continue to be invested as cash and cash equivalents and short-term investments in the Canadian dollar.
The following table provides an indication of our significant foreign exchange currency exposures from functional currency at the following dates:
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, 2022 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
CAD |
|
|
Euro |
|
|
US |
|
|
Euro |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
2,132 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
35,079 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Investments |
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
14,872 |
|
|
|
— |
|
Trade and other payables |
|
|
(1,219 |
) |
|
|
(32 |
) |
|
|
(2,130 |
) |
|
|
(79 |
) |
|
|
|
928 |
|
|
|
(32 |
) |
|
|
47,821 |
|
|
|
(79 |
) |
The following exchange rates are those applicable to the following periods and dates:
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, 2022 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
Average |
|
|
Reporting |
|
|
Average |
|
|
Reporting |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
US$ per CAD$ (2022 - CAD per US$) |
|
|
0.7400 |
|
|
|
0.7398 |
|
|
|
1.2536 |
|
|
|
1.2505 |
|
US$ per Euro (2022- CAD per Euro) |
|
|
1.0415 |
|
|
|
1.0839 |
|
|
|
1.4569 |
|
|
|
1.3836 |
|
Based on our foreign currency exposures noted above, varying the above foreign exchange rates to reflect a 5% strengthening of the Canadian dollar and Euro would have an increase (decrease) in net loss as follows, assuming that all other variables remain constant:
49
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, |
|
||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Increase (decrease) in net loss |
|
|
34 |
|
|
|
3,129 |
|
An assumed 5% weakening of the foreign currencies would have an equal but opposite effect on the basis that all other variables remained constant.
Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk is the risk that the fair value or future cash flows of a financial instrument will fluctuate because of changes in market rates. Our exposure to interest rate risk as at March 31, 2023 and March 31, 2022 was as follows:
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
Short-term fixed interest rate |
Investments |
|
Short-term fixed interest rate |
Our capacity to reinvest the short-term amounts with equivalent return will be impacted by variations in short-term fixed interest rates available on the market. Management believes the risk we will realize a loss as a result of the decline in the fair value of our short-term investments is limited because these investments have short-term maturities and are held to maturity.
Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk is the risk that we will not be able to meet our financial obligations as they fall due. We manage liquidity risk through the management of our capital structure and financial leverage. We also manage liquidity risk by continuously monitoring actual and projected cash flows. The board of directors reviews and approves our operating budgets and reviews material transactions outside the normal course of business.
Our contractual obligations related to financial instruments and other obligations and liquidity resources are presented in the liquidity and capital resources of this MD&A.
We have incurred operating losses and negative cash flows from operations in each year since our inception. We expect to incur significant expenses and continued operating losses for the foreseeable future. We expect our expenses will increase substantially in connection with our ongoing activities, particularly as we advance clinical development for our drug candidates in our pipeline; continue to engage contract manufacturing organizations to manufacture our clinical study materials and to ultimately develop large-scale manufacturing capabilities in preparation for commercial launch; seek regulatory approval for our drug candidates; and add personnel to support our drug product development and future drug product launch and commercialization.
We do not expect to generate revenue from product sales unless and until we successfully complete drug development and obtain regulatory approval, which we expect will take several years and is subject to significant uncertainty. To date, we have financed our operations primarily through public offerings and private placements of our common shares, warrants and convertible debt and with the proceeds from research tax credits. Until such time that we can generate significant revenue from drug product sales, if ever, we will require additional financing, which we expect to be sourced from a combination of public or private equity offerings or debt financing's or other non-dilutive sources, which may include fees, milestone payments and royalties from collaborations with third parties. Arrangements with collaborators or others may require us to relinquish certain rights related to our technologies or drug product candidates. Adequate additional financing may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all. Our inability to raise capital as and when needed could have a negative impact on our financial condition and our ability to pursue our business strategy.
We expect to have sufficient cash resources to satisfy our objectives into the second quarter of calendar 2025, which is 21 to 24 months from the issuance date of the financial statements included elsewhere in this annual report. We require additional capital to fund our daily operating needs beyond that time. We plan to raise additional capital prior to that time in order to maintain adequate liquidity. Negative results from studies, if any, and depressed prices of our common shares could impact our ability to raise additional financing. Raising additional equity capital is subject to market conditions not within our control. If we do not raise additional funds in this time period, we may not be able to realize our assets and discharge our liabilities in the normal course of business.
In May 2023, we implemented a strategic realignment plan to enhance shareholder value that resulted in engaging a new management team and greatly reducing our research and development activities including a reduction in workforce.
Future Accounting Changes
We have considered recent accounting pronouncements and concluded that they are either not applicable to our business or that the effect is not expected to be material to our consolidated financial statements as a result of future adoption.
50
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure About Market Risk
Information relating to quantitative and qualitative disclosures about market risks is detailed in “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operation.”
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
See our consolidated financial statements beginning on page F-1 of this annual report on Form 10-K.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures Disclosure Controls and Procedures
As of the end of the period covered by this annual report, our management, with the participation of our chief executive officer (“CEO”) and chief financial officer (“CFO”), has performed an evaluation of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures within the meaning of Rules 13a-15 (e) and 15d-15(e) of the Exchange Act. Based upon this evaluation, our management has concluded that, as of March 31, 2023, our existing disclosure controls and procedures were effective. It should be noted that while the CEO and CFO believe that our disclosure controls and procedures provide a reasonable level of assurance that they are effective, they do not expect the disclosure controls and procedures to be capable of preventing all errors and fraud. A control system, no matter how well conceived or operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system are met.
Management’s Report on Internal Controls over Financial Reporting
Our management, with the participation of our CEO and CFO, is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Our internal control system was designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation and fair presentation of our financial statements. All internal control systems, no matter how well designed, have inherent limitations. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective may not prevent or detect misstatements and can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate. Our management conducted an assessment of the design and operation effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2023. In making this assessment, we used the criteria established within the Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). Based on this assessment, our management has concluded that, as of March 31, 2023, our internal control over financial reporting was effective.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
No changes were made to our internal controls over financial reporting that occurred during the year ended March 31, 2023 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal controls over financial reporting.
We are a non-accelerated filer under the Exchange Act and not required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. Therefore, this annual report does not include an attestation report of our registered public accounting firm regarding our management’s assessment of internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B. Other Information
None.
Item 9C. Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections
None.
51
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The following table sets forth information with respect to our current directors and executive officers:
Name |
|
Age |
|
Position(s) held within Acasti |
|
In Office Since |
|
Current Term to Expire |
Directors |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vimal Kavuru |
|
54 |
|
Chairman of the Board |
|
August 2021 |
|
September 2023 |
Donald Olds |
|
63 |
|
Director, Chairman of Audit Commitee and Chairman of Governance and Human Resources Committee |
|
April 2018 |
|
September 2023 |
Michael L. Derby |
|
50 |
|
Director |
|
March 2022 |
|
September 2023 |
Executive Officers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Prashant Kohli |
|
51 |
|
Chief Executive Officer |
|
April 2023 |
|
- |
Brian Ford |
|
65 |
|
Chief Financial Officer |
|
September 2020 |
|
- |
Dr. R. Loch Macdonald |
|
61 |
|
Chief Medical Officer |
|
May 2023 |
|
- |
Carrie D'Andrea |
|
51 |
|
VP Clinical Operations |
|
May 2023 |
|
- |
Amresh Kumar |
|
43 |
|
VP of Program Management |
|
May 2023 |
|
- |
The following is a brief biography of our current directors and executive officers:
Vimal Kavuru
Mr. Kavuru has created and led several pharmaceutical companies. Mr. Kavuru brings, in his vision and management, a broad-based understanding of the global pharmaceutical industry with expertise in strategic planning, product and business development, and operations. In addition to previously serving as the Chairman of the Grace Therapeutics board of directors, Mr. Kavuru is the Founder, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Rising Pharma Holdings, Inc., a U.S. generic pharmaceutical company, and Acetris Pharma Holdings, LLC, a generic pharmaceutical company serving U.S. government agencies. Previously, Mr. Kavuru founded Citron Pharma & Lucid Pharma, which were sold to Aceto Corporation in 2016, Casper Pharma LLC, an emerging specialty brand pharmaceutical company, and Gen-Source RX, a national distributor of generic pharmaceuticals that was acquired by Cardinal Health in 2014. In 2007, Mr. Kavuru also co-founded Celon Labs, a specialty oncology and critical care pharmaceutical company that was acquired by Zanzibar Pharma Limited, a portfolio company of CDC Group. He is a registered pharmacist in the state of New York, holds a B.S. in Pharmacy from HKE College of Pharmacy, Bulgarga, India, and attended Long Island University, Brooklyn, New York with specialization in industrial pharmacy. Mr. Kuvaru was elected to the Acasti board as a nominee of former shareholders of Grace Therapeutics pursuant to the terms of Acasti’s acquisition of Grace Therapeutics. Our board of directors believes that Mr. Kuvaru’s management experience in the pharmaceutical industry, as well as his operational expertise, qualify him to serve on our board of directors.
Donald Olds
Until May 2019, Mr. Olds was the President and Chief Executive Officer of the NEOMED Institute, a research and development organization dedicated to advancing Canadian research discoveries to commercial success. Prior to NEOMED, he was the Chief Operating Officer of Telesta Therapeutics Inc., a TSX-listed biotechnology company, where he was responsible for finance and investor relations, manufacturing operations, business development, human resources, and strategy. In 2016, he led the successful sale of Telesta to a larger public biotechnology company. Prior to Telesta, he was President and Chief Executive Officer of Presagia Corp., and Chief Financial Officer and Chief Operating Officer of Aegera Therapeutics Inc., where he was responsible for clinical operations, business development, finance, and mergers and acquisitions. At both Telesta and Aegera, Mr. Olds was responsible for raising equity financing and leading regional and global licensing transactions with life sciences companies. Mr. Olds is currently lead director of Goodfood Market Corp, Chair of Aifred Health, lead director of Cannara Biotech Inc, and director of Presagia Corp. He has extensive past corporate governance experience serving on the boards of private and public for-profit and not-for-profit organizations. He holds an M.B.A. (Finance & Strategy) and M..Sc. (Renewable Resources) from McGill University. Our board believes that Mr. Old’s extensive industry experience and his strong financial background, as well as his service on the board of directors of public and private companies, qualifies him to serve on our board of directors.
Michael L. Derby
Mr. Derby has more than two decades of experience and a proven track record within the biopharmaceutical industry, with particular expertise in strategic drug repurposing. Having founded or co-founded seven biopharmaceutical companies, he most recently launched TardiMed Sciences LLC, a company creation and investment firm in the life sciences. TardiMed has formed, capitalized and advanced multiple biopharmaceutical companies through development, including Timber Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (NYSE: TMBR), PaxMedica, Inc. and Visiox Pharma LLC. Mr. Derby has served as Executive Chairman of the Board of Directors for each of these companies. Prior to TardiMed, Mr. Derby co-founded Castle Creek Pharmaceuticals, which he built into a multi-product, late clinical stage company focused on treating rare and debilitating dermatologic conditions. He also founded Norphan Pharmaceuticals, a biopharmaceutical company focused on the development of drugs for orphan neurologic disease, which he led through its early stages prior to selling the company to Marathon Pharmaceuticals LLC in 2013. Prior to founding and managing life sciences companies, Mr. Derby was a private equity investor and venture capitalist, and also worked in management roles at Merck & Co. and Forest Laboratories Inc. Mr. Derby holds an M.B.A. from New York University’s Stern School of Business, a M.S. from the University of Rochester, and a B.S. from Johns Hopkins University. Mr. Derby was appointed to the Acasti board as a nominee of former shareholders of Grace Therapeutics pursuant to the terms of Acasti’s acquisition of Grace Therapeutics. Our board of directors believes that Mr. Derby’s extensive industry and management experience, including his experience in drug repositioning and his strong financial background, qualify him to serve on our board of directors.
Prashant Kohli
Prashant Kohli has over 20 years of commercialization experience leading strategy, sales, marketing, and product management. Prior to joining Acasti in August 2021, , Mr. Kohli was VP, Commercial Operations of Grace Therapeutics since December 2017. He has expertise crafting go-to-market plans for products with unique value proposition that address critical unmet needs. He has built, deployed, and led sales and marketing from the ground-up with significant experience in organization design, recruiting, performance management, incentive compensation, and P&L accountability. He has successfully implemented evidence-based, consultative-selling model that is rooted in deep understanding of the health ecosystem including patients, providers, health systems, government, and payers. He has also designed strategic marketing plans that generate leads and increase share-of-voice, augmenting the salesforce with digital tactics that increase reach and frequency. He has extensive commercial experience with specialty and small molecule drugs including in rare and orphan diseases. Prashant has worked at Archi-Tech Systems, Cardinal Health, IMS Health, Rosenbluth, and Dun & Bradstreet. He has a BA in Computer Science and Math from Augustana College and an MBA from The Wharton School.
52
Brian Ford
Mr. Ford brings over three decades of financial, project management and M&A experience within the healthcare and financial industries. Mr. Ford is an accomplished CPA-CA having served both publicly traded as well as privately owned organizations. Mr. Ford has been responsible for developing business recovery strategies, negotiating M&A transactions, as well as managing quarterly and yearly accounting reports. Most recently, Mr. Ford served as Chief Financial Officer and Senior Business Advisor at a private group of Ontario based medical clinics, including the largest chronic pain management practice in Canada. Prior to that, Mr. Ford served as Chief Financial Officer at Telesta Therapeutics Inc. At Telesta Therapeutics, Mr. Ford helped develop a new business plan and was heavily involved in all capital transactions. Previously, Mr. Ford started his own consulting firm, Petersford Consulting, where he provided clients with finance and business risk services. Mr. Ford began his career at Ernst & Young, eventually becoming a Principal, Business Risk Services, developing essential business plans that evaluated revenue and cost profiles supporting budget planning and understanding drivers of growth, specifically with healthcare companies. Additionally, at Ernst & Young, Mr. Ford participated in and often led teams in due diligence assignments in relation to M&A or the sale of a business, having extensive experience in developing financial forecasts, product and market valuation, and audits of critical accounting and processes. Mr. Ford holds a B.A. in Economics, History, and English from the University of Guelph and has a Graduate Diploma in Accounting from the University of McGill. Mr. Ford is a member of the Ontario Institute of Chartered Accountants.
Dr. R. Loch Macdonald
Dr. Macdonald is a world-renowned practicing neurosurgeon-scientist and respected authority in subarachnoid hemorrage. Dr. Macdonald acted as Professor, Department of Surgery, Division of Neurosurgery at the University of Toronto from January 2007 until December 2019, and was Head, Division of Neurosurgery, St. Michael's Hospital, University of Toronto from January 2007 until December 2015. He was Professor, Department of Neuorological Surgery, Barrow Neurological Surgery, Barrow Neurological Institute, Phoenix, Arizona, from April 2018 until August 2018; Fellow, Department of Neurosurgery, University of Illinois Hospitals in Chicago, Illinois from December 2018 until June 2019; Clinical Professor, Department of Neurological Surgery, University of California San Franciso Fresno, in Fresno, California from July 2019 until September 2021; and from October 2021 to the present has been Neurosurgeon, Community Physicians Group, Community Neurosciences Institute, Community Regional Medical Center and Medical Director of Neurosciences Research, Community Health Partners. Dr Macdonald was also a founder of Edge Therapeutics, Inc. in 2009, where he was a member of the board of directors between 2009 and 2018 and was Chief Scientific Officer between 2011 and 2018. Dr. Macdonald completed his medical degree at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, British Columbia and his PhD in Experimental Surgery at the University of Alberta in Edmonton, Alberta. He completed his Neurosurgery residency at the University of Toronto.
Carrie D’Andrea
Ms. D’Andrea is a highly experienced professional with 25 years of experience in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industry who has built and led the planning, implementation, management, and execution of global Phase 2 and Phase 3 trials for a drug candidate for subarachnoid hemorrhage. Ms. D'Andrea was the Vice President of Clinical Operations for Edge Therapeutics Inc. from October 2014 until March 2019 and for EryDel SpA from October 2020 until April 2021. Ms. D’Andrea was a clinical operations consultant at Aegle Research from July 2021-August 2022 and Praxis Precisions Medicines from September 2022-May 2023. Ms. D’Andrea was named a Healthcare Businesswomen’s Association Rising Star in 2009 and Ms. D'Andrea received her master's degree in Pharmaceutical Quality and Regulatory Affairs from Temple University and teaches Clinical Trial Design and Operations at Rutgers University in the Master of Business and Science Program.
Amresh Kumar
Mr. Kumar is an experienced drug development, CMC, and program management expert supporting investigational and marketed products for rare diseases and neurology. Mr. Kumar is the former product leader of GTX-104 while at Grace Therapeutics Inc. (which was acquired by the Company in August 2021). Mr. Kumar acted as the Sr. Director of Program Management at Foresee Pharmaceuticals Inc. from April 2022 until May 2023 and as Program Leader and Associate Director - R&D at Grace Therapeutics Inc. between March 2015 and January 2022. Mr. Kumar received a PhD in Pharmaceutical Science from Sunrise University, India, focusing on complex injectable drug delivery systems of highly soluable oncology drugs. He has published many research articles and has more than 10 granted patents and many patent applications worldwide to his credit.
Family Relationships
There are no family relationships between any directors or officers of the Company.
Code of Business Conduct and Ethics
Please see the section entitled “Code of Business Conduct and Ethics” in “Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions and Director Independence.”
Audit Committee
Our audit committee is responsible for assisting the board of directors in fulfilling its oversight responsibilities with respect to financial reporting, including:
The audit committee has direct communication channels with our management performing financial functions and our external auditor to discuss and review such issues as the audit committee may deem appropriate. The audit committee is composed of Mr. Olds, as Chairperson, Mr.Kavuru and Mr. Derby. Each of Mr. Olds, Mr. Kavuru and Mr. Derby is “financially literate” and “independent” within the meaning of the Exchange Act.
Audit Committee Financial Expert
53
Our board of directors has determined that Mr. Olds is an “audit committee financial expert”, as defined by applicable regulations of the SEC. The SEC has indicated that the designation of Mr. Olds as an audit committee financial expert does not make him an “expert” for any purpose, impose any duties, obligations or liability on Mr. Olds that are greater than those imposed on members of the audit committee and board of directors who do not carry this designation, or affect the duties, obligations or liability of any other member of the audit committee or board of directors.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
Our executive compensation program is intended to attract, motivate and retain high-performing senior executives, encourage and reward superior performance, and align the executives’ interests with ours as well as our shareholders by providing compensation that is competitive with the compensation received by executives employed by comparable companies, and ensuring that the achievement of annual objectives is rewarded through the payment of bonuses, and providing executives with long-term incentives through the grant of stock options.
Our governance and human resources committee, or GHR committee, has authority to retain the services of independent compensation consultants to advise its members on executive and board compensation and related matters, and to determine the fees and the terms and conditions of the engagement of those consultants. During our fiscal year ended March 31, 2023, the GHR committee retained compensation consulting services from FW Cook to review our executive compensation programs, including base salary, short-term and long-term incentives, total cash compensation levels and total direct compensation of certain senior positions, against those of a peer group of 20 broadly similar size, as measured by market capitalization (peer market cap all averaged less than $500M in 2021), biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies listed or headquartered in North America. The consultants also reviewed board compensation, including advisory fees and equity incentives. All of the services provided by the consultants were provided to the GHR committee. The GHR committee assessed the independence of the consultants and concluded that its engagement of the consultants did not raise any conflict of interest with us or any of our directors or executive officers.
Compensation for our CEO was below the peer company median based on FW Cook’s review during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2023.
Use of Fixed and Variable Pay Components
Compensation of our named executive officers, or NEOs, is revised each year and has been structured to encourage and reward executive officers on the basis of short-term and long-term corporate performance. In the context of its analysis of compensation for our fiscal year ended March 31, 2023, the following components were examined by the GHR committee:
For executives, more than half of their target compensation (base salary + target STIP awards + target LTIP awards) is considered “at risk”. We believe this mix results in a strong pay-for-performance relationship and alignment with shareholders and is competitive with other firms of comparable size in similar fields. The CEO (or any person acting in that capacity) makes recommendations to the GHR committee as to the compensation of our executive officers, other than the CEO for review and approval by the board of directors. The GHR committee makes recommendations to the board of directors as to the compensation of the CEO, for approval. The CEO’s salary is based on comparable market consideration, and the GHR committee’s assessment of the CEO's performance, with regard to our financial performance, and progress in achieving key strategic business goals.
Qualitative factors beyond the quantitative financial metrics are also a key consideration in determination of individual executive compensation payments. How executives achieve their financial results and demonstrate leadership consistent with our values are key to individual compensation decisions.
Base Salary
We intend to be competitive over time with comparator companies and to attract and retain top talent. The GHR committee reviews compensation matters periodically to help ensure that it meets this strategic imperative. Base salary is set to reflect an individual’s skills, experience, and contributions within a salary structure consistent with peer group data. Base salary structure is revised annually by the GHR committee as financial and market conditions evolve.
Short Term Incentive Plan (STIP)
Our Short-Term Incentive Plan, or STIP, provides for potential rewards when a threshold of corporate performance is met compared to the board of director's primary stated objectives for the fiscal year. Corporate performance is assessed against a table of weighted performance categories and sub-goals within each weighted category, which assessment of goal achievement funds the corporate bonus pool. These performance goals take into account the achievement of corporate milestones within timelines and budget and individual objectives determined annually by the board of directors according to short-term priorities. The corporate bonus pool is allocated based on achievement of personal objectives assessed through a performance grid, with pre-specified, objective performance criteria. For the most senior participants in the STIP, greater weight is assigned to corporate objectives. Target payout is expressed as a percentage of base salary, and is determined by benchmarking against peer group data. Annual salary for STIP purposes is the annual salary in effect at the end of the plan year (i.e., prior to any annual salary increases awarded for the subsequent year).
The STIP is a variable compensation plan, and all STIP payments are subject to board of directors approval. Participants must be employed by us at the end of the fiscal year to qualify.
Long Term Incentive Plan (LTIP)
The LTIP has been adopted as a reward and retention mechanism. Participation is determined annually at the discretion of the board of directors. The stock option plan is intended to align the long-term interests of participants with those of shareholders, in order to promote creation of shareholder value.
The GHR committee determines the number of stock options to be granted to a participant based on peer group data and taking into account corporate performance and the employee’s level in the organization. The LTIP calculation for NEOs is determined by both reviewing grant values and a dilution- based methodology that considers
54
the annual grant rate as a percent of shares outstanding. All fiscal 2023 grants to named executive officers had a grant value that was below the median of the peer data reviewed at the end of the year.
Our directors and executive officers are not permitted to purchase financial instruments, such as prepaid variable forward contracts, equity swaps, collars or units of exchange funds that are designed to hedge or offset a decrease in market value of equity securities granted as compensation or held, directly or indirectly, by the director or officer.
Stock Option Plan
Our stock option plan was adopted by our board of directors on October 8, 2008, and has been amended from time to time, as most recently amended on August 4, 2022, and approved by our shareholders on September 28, 2022. The grant of options is part of the long-term incentive component of executive and director compensation and an essential part of our compensation framework. Qualified directors, employees and consultants may participate in our stock option plan, which is designed to encourage option holders to link their interests with those of our shareholders, in order to promote an increase in shareholder value. Awards and the determination of any exercise price are made by our board of directors, after recommendation by the GHR committee. Awards are established, among other things, according to the role and responsibilities associated with the participant’s position and his or her influence over appreciation in shareholder value. Any award grants a participant the right to purchase a certain number of common shares during a specified term in the future, after a vesting period and/or specific performance conditions, at an exercise price equal to at least 100% of the market price (as defined below) of our common shares on the grant date. The “market price” of common shares as of a particular date generally means the highest closing price per common share on the Nasdaq, or any other exchange on which the common shares are listed from time to time, for the last preceding date on which there was a sale of common shares on that exchange (subject to certain exceptions set forth in the stock option plan in the event that our common shares are no longer traded on any stock exchange). Previous awards may sometimes be taken into account when new awards are considered.
In accordance with the stock option plan, all of an option holder’s options will immediately fully vest on the date of a Change of Control event (as defined in the stock option plan), subject to the terms of any employment agreement or other contractual arrangement between the option holder and us.
However, in no case will the grant of options under the stock option plan, together with any proposed or previously existing security-based compensation arrangement, result in (in each case, as determined on the grant date): the grant to any one consultant within any 12-month period, of options reserving for issuance a number of common shares exceeding in the aggregate 2% of our issued and outstanding common shares (on a non-diluted basis); or the grant to any one employee, director and/or consultant, which provides investor relations services, within any 12-month period, of options reserving for issuance a number of common shares exceeding in the aggregate 2% of our issued and outstanding common shares (on a non-diluted basis).
Options granted under the stock option plan are non-transferable and are subject to a minimum vesting period of 36 months for management, and 12 months for non-executive board members, in each case with gradual and equal vesting on no less than a quarterly basis in the case of management and monthly in the case of non-executive board members. They are exercisable, subject to vesting and/or performance conditions, at a price equal to the highest closing price of the common shares on the Nasdaq, or any other exchange on which the common shares are listed from time to time, on the day prior to the grant of such options. In addition, and unless otherwise provided for in the relevant agreement between us and the holder, options will also lapse upon termination of employment or the end of the business relationship with us except that they may be exercised for 90 days after termination, ceasing to hold office or the end of the business relationship (30 days for investor relations services employees), in each case to the extent that they will have vested on such date of termination of employment, end of the business relationship or ceasing to hold office, as applicable, except in the case of death, disability or retirement where this period is extended to 12 months.
Subject to the approval of relevant regulatory authorities, including the Nasdaq, if applicable, and compliance with any conditions attached to that approval (including, in certain circumstances, approval by disinterested shareholders) if applicable, the board of directors has the right to amend or terminate the stock option plan. However, unless option holders’ consent to the amendment or termination of the stock option plan in writing, any such amendment or termination of the stock option plan cannot affect the conditions of options that have already been granted and that have not been exercised under the stock option plan.
Options for common shares representing 20% of our issued and outstanding common shares as of July 28, 2022, from time to time may be granted by the board under the stock option plan, which number shall include common shares issuable pursuant to awards issued under the equity incentive. As of the date of this annual report, there were 8,898,839 common shares reserved for issuance under the stock option plan and 4,445,492 options outstanding under the stock option plan.
Equity Incentive Plan
On May 22, 2013, our equity incentive plan was adopted by the board of directors in order to, among other things, provide us with a share-related mechanism to attract, retain and motivate qualified directors, employees and consultants. The adoption of the equity incentive plan was initially approved by shareholders on June 27, 2013, and has been amended from time to time, as most recently amended on August 4, 2022, and approved by shareholders on September 28, 2022.
Eligible persons may participate in the equity incentive plan. “Eligible persons” under the equity incentive plan consist of any director, officer, employee, or consultant (as defined in the equity incentive plan) of our Company or a subsidiary. A participant is an eligible person to whom an award has been granted under the equity incentive plan. The equity incentive plan provides us with the option to grant to eligible persons bonus shares, restricted shares, restricted share units, performance share units, deferred share units and other share-based awards.
The board of directors has the discretion to determine that any unvested or unearned restricted share units, deferred share units, performance share units or other share-based awards or restricted shares subject to a restricted period outstanding immediately prior to the occurrence of a change in control will become fully vested or earned or free of restriction upon the occurrence of a change in control. The board of directors may also determine that any vested or earned restricted share units, deferred share units, performance share units or other share-based awards will be cashed out based on the market price of our common shares as of the date a change in control is deemed to have occurred, or as of such other date as the board of directors may determine prior to the change in control. Further, the board has the right to provide for the conversion or exchange of any restricted share unit, deferred share unit, performance share unit or other share-based award into or for rights or other securities in any entity participating in or resulting from the change in control.
The equity incentive plan is administered by the board of directors and the board of directors has sole and complete authority, in its discretion, to determine the type of awards under the equity incentive plan relating to the issuance of common shares (including any combination of bonus shares, restricted share units, performance share units, deferred share units, restricted shares or other share-based awards) in such amounts, to such persons and under such terms and conditions as the board of directors may determine, in accordance with the provisions of the equity incentive plan and the recommendations made by the GHR committee.
Subject to the adjustment provisions provided for in the equity incentive plan and the applicable rules and regulations of all regulatory authorities to which we are subject (including any stock exchange), the total number of common shares reserved for issuance pursuant to awards granted under the equity incentive plan will be equal to a
55
number that will not exceed 20% of the issued and outstanding common shares as of July 28, 2022, which number shall include common shares issuable pursuant to options issued under the stock option plan.
Other Forms of Compensation
Retirement Plans. We sponsor a voluntary Registered Retirement Savings Plan, or RRSP, matching program, which is open to all eligible employees, including NEOs, who reside in Canada. The RRSP matching program matches employees’ contributions up to a maximum of $1,500 per fiscal year for eligible employees who participate in the program. We have also implemented a 401K plan for US employees. Because of the small size of our current employee population in the US and to assure passage of anti-discrimination testing, the 401K plan has a “safe harbor” provision which provides a contribution of 3% of salary to the 401K accounts of all eligible US employees, including NEOs who reside in the US.
Other Benefits and Perquisites. Our executive employee benefit program also includes life, medical, dental and disability insurance. These benefits and perquisites are designed to be competitive overall with equivalent positions in comparable organizations. We do not have a pension plan for employees.
Compensation Governance
Compensation of our executive officers and directors is recommended to the board of directors by the GHR committee. In its review process, the GHR committee informally reviews executive and corporate performance on a quarterly basis, with input from management. Annually, the GHR committee conducts a more formal review and assessment of executive and corporate performance. The GHR committee is composed of the following members: Mr. Olds (Chairman), Mr. Kavuru and Mr. Derby, each of whom is independent within the meaning of applicable Nasdaq rules. The GHR committee establishes management compensation policies and oversees their general implementation. All members of the GHR committee have direct experience which is relevant to their responsibilities as GHR committee members. All GHR committee members are or have held senior executive or director roles within significant businesses in our industry, some also having public companies experience, and have a level of financial understanding which allows them to assess the costs versus benefits of compensation plans. The GHR committee’s members’ combined experience in our sector provides them with a good understanding of our success factors and risks, which are highly relevant to determining metrics for measuring success.
We do not believe that our compensation program results in unnecessary or inappropriate risk taking, including risks that are likely to have a material adverse effect on us. Payments of bonuses, if any, are not made unless performance goals are met.
Compensation Paid to Named Executive Officers
The following table sets forth the compensation information for our principal executive officer, and our two most highly compensated executive officers other than our principal executive officer (NEOs), who were serving as executive officers as of March 31, 2023, during the fiscal years ended March 31, 2023, and 2022 respectively.
Name and |
|
Year |
Salary ($) |
Bonus ($) |
Stock Awards ($) |
Option Awards ($)(1) (2) |
Nonequity Incentive Plans |
All Other Compensation ($) |
Total Compensation ($) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Jan D'Alvise (4) |
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
$ |
494,761 |
|
|
$ |
210,642 |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
426,799 |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
1,132,202 |
|
Former President and CEO |
|
March 31, |
|
$ |
445,161 |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
926,502 |
|
|
$ |
175,000 |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
1,546,663 |
|
George Kottayil (5) |
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
$ |
361,972 |
|
|
$ |
97,344 |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
38,069 |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
497,385 |
|
Former COO, US |
|
March 31, |
|
$ |
146,640 |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
701,710 |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
848,350 |
|
Prashant Kohli (6) |
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
$ |
379,370 |
|
|
$ |
75,270 |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
57,103 |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
511,743 |
|
CEO and former CCO |
|
March 31, |
|
$ |
141,000 |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
470,056 |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
- |
|
|
$ |
611,056 |
|
Notes:
Outstanding Equity Awards at March 31, 2023
The following tables provide information about the number and value of the outstanding option-based awards held by the NEOs as of March 31, 2023
56
|
|
Option awards |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
Number of securities underlying unexercised options (#) |
|
|
Number of securities underlying |
|
|
Equity incentive |
|
|
Option exercise |
|
|
Option expiration date |
||||
Jan D’Alvise, Former President and CEO |
|
|
65,625 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
9.71 |
|
|
Friday, May 12, 2023 |
|
|
|
32,250 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
10.70 |
|
|
Monday, June 14, 2027 |
|
|
|
21,500 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
10.70 |
|
|
Monday, June 14, 2027 |
|
|
|
113,281 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
4.68 |
|
|
Sunday, July 02, 2028 |
|
|
|
28,263 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
7.68 |
|
|
Sunday, April 15, 2029 |
|
|
|
96,488 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
7.68 |
|
|
Sunday, April 15, 2029 |
|
|
|
111,251 |
|
|
|
55,624 |
|
|
|
55,624 |
|
|
$ |
2.99 |
|
|
Sunday, March 31, 2030 |
|
|
|
237,566 |
|
|
|
321,155 |
|
|
|
321,155 |
|
|
$ |
1.65 |
|
|
Tuesday, November 11, 2031 |
|
|
|
140,000 |
|
|
|
420,000 |
|
|
|
420,000 |
|
|
$ |
0.89 |
|
|
Tuesday, June 22, 2032 |
George Kottayil, Former COO, US |
|
|
119,958 |
|
|
|
167,942 |
|
|
|
167,942 |
|
|
$ |
1.65 |
|
|
Tuesday, November 11, 2031 |
|
|
|
12,500 |
|
|
|
37,500 |
|
|
|
37,500 |
|
|
$ |
0.89 |
|
|
Tuesday, June 22, 2032 |
Prashant Kohli, CEO and former CCO |
|
|
51,708 |
|
|
|
72,392 |
|
|
|
72,392 |
|
|
$ |
1.65 |
|
|
Tuesday, November 11, 2031 |
|
|
|
18,750 |
|
|
|
56,250 |
|
|
|
56,250 |
|
|
$ |
0.89 |
|
|
Tuesday, June 22, 2032 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Notes:
Employment Agreements with Named Executive Officers
Jan D’Alvise, Former CEO
On June 1, 2016, we entered into an executive employment agreement with Ms. D’Alvise. Pursuant to her executive employment agreement, Ms. D’Alvise’s annual base salary was set at $330,000 and she is eligible to receive annual performance bonuses based on a target amount of 50% of her annual base salary with a maximum of up to 80% of her annual base salary. In accordance with the terms and provisions of the executive employment agreement we entered into with Ms. D’Alvise, we may terminate the executive’s employment at any time for “good and sufficient cause”, as defined in the employment agreement, without notice or severance. We may terminate the executive’s employment at any time without cause or upon a change of control, as defined in our stock option plan, by providing the executive with sixty days’ notice of termination and payment equal to twelve months’ base salary plus any bonus payable. The executive may decide to resign from employment and must provide us with at least sixty days' advance written notice. The executive may decide to terminate employment with “good reason”, as defined in the executive employment agreement, and we are required to make payment equal to twelve months’ base salary plus any bonus payable. Effective April 4, 2023, Jan D'Alvise employment was terminated as both parties mutually agreed to part ways and she is entitled to a severance payment in accordance with the terms of her executive employment agreement.
Pierre Lemieux, Former COO, Canada
On September 26, 2017, we entered into an executive employment agreement with Dr. Lemieux. Pursuant to his executive employment agreement, Dr. Lemieux’s annual base salary was set at CAD$253,700 and he was eligible to receive annual performance bonuses of up to 40% of his annual base salary. In accordance with the terms and provisions of the executive employment agreement we entered into with Dr. Lemieux, we were entitled to terminate the executive’s employment at any time for “good and sufficient cause”, as defined in the employment agreement, without notice or severance. We were entitled to terminate the executive’s employment at any time without cause or upon a change of control, as defined in our stock option plan, by providing the executive with thirty days’ notice of termination and payment equal to twelve months’ base salary plus any bonus payable. The executive was entitled to resign from employment upon providing us with at least sixty days' advance written notice. The executive was entitled to terminate employment with “good reason”, as defined in the executive employment agreement, and we were required to make payment equal to twelve months of base salary. Effective May 8, 2023, Dr. Lemieux’s employment was terminated by the Company and he is entitled to severance payment in accordance with the terms of his executive employment agreement.
57
Brian Ford, Interim CFO
On September 13, 2021, we entered into an executive employment agreement with Mr. Ford. Pursuant to his executive employment agreement, Mr. Ford’s annual base salary was set at CAD$350,000 and he was eligible to receive annual performance bonuses of up to 40% of his annual base salary. In accordance with the terms and provisions of the executive employment agreement we entered into with Mr. Ford, we were entitled to terminate his employment at any time with cause. We were entitled to terminate the executive’s employment without cause by providing the executive employee, with either a payment equal to six months of base salary, plus two months of base salary for each completed year of service, to a maximum of twelve months in total, or a payment equal to twelve months of base salary in the event that such a termination occurs within three months following a change of control, as defined in our stock option plan. The executive was entitled to resign from employment and upon providing us with at least eight weeks of advance written notice. Effective May 8, 2023, Mr. Ford employment as the Company’s Chief Financial Officer was terminated and he is entitled to severance payment in accordance with the terms of his executive employment agreement. Mr. Ford has agreed to serve as the Company’s Interim Chief Financial Officer until June 30, 2023, subject to potential extension of that term by the Company.
Dr. R. Loch Macdonald, Chief Medical Officer
On May 8, 2023 we entered into a consulting agreement with R. Loch Macdonald. The Consulting Agreement provides, among other things, that Dr.Macdonald will serve as a non-employee Chief Medical Officer on a part-time basis, in exchange for a fee of $100,000 per month. There is no arrangement or understanding between Dr. Macdonald and any other persons pursuant to which Dr. Macdonald was selected as an officer.
Carrie D’Andrea, VP Climical
On May 8, 2023 we entered into a consulting agreement with Carrie D'Andrea. The Consulting Agreement provides, among other things, that Ms. D'Andrea will serve as a non-employee vice-president of clinical operations on a full-time basis, in exchange for a fee of $18,000 per month. There is no arrangement or understanding between Ms. D’Andrea and any other persons pursuant to which Ms. D’Andrea was selected as an officer.
Non-Executive Director Compensation
Our directors’ compensation consists of an annual fixed compensation of $65,000 for the chairman of the board and $35,000 for the other non-executive board members. In addition, the chairperson of the audit committee and the chairperson of the GHR committee receive additional compensation of $15,000 and $11,000, respectively, while members of the audit committee and the GHR committee receive additional compensation of $7,500 and $6,000, respectively. The directors are also entitled to a fee of $1,000 per non-regularly scheduled board meeting as well as a reimbursement for traveling and other reasonable expenses properly incurred by them in attending meetings of the board or any committee or in otherwise serving us, in accordance with our policy on travel and expenses.
Following their first election to our board of directors, non-executive directors are eligible to receive an initial equity grant of up to 150% of their annual cash retainer worth of stock options vesting monthly in equal installments over a 12-month period, subject to the other terms and conditions set forth under the heading “Stock Option Plan”. In addition to their initial grant, non-executive directors are eligible to receive an annual equity-based award equal to 100% of their total annual cash retainer vesting monthly in equal installments over a 12-month period. These awards will be granted at the same time that we are performing our annual performance review for our employees, subject to availability of common shares and subject to the terms and conditions described under the headings “Stock Option Plan” and “Equity Incentive Plan”. The level of these awards are intended to be consistent with equivalent awards by comparable companies obtained from our benchmarking exercise and in accordance with the recommendations obtained from our independent compensation consultant.
The total compensation for our non-executive directors during fiscal year ended March 31, 2023, was as follows:
Name |
|
Fees earned or paid in cash |
|
|
Stock awards |
|
|
Option awards |
|
|
Non-equity incentive plan compensation |
|
|
Nonqualified deferred compensation earnings |
|
|
All other compensation |
|
|
Total |
|
|||||||
Vimal Kavuru |
|
|
66,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
30,189 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
96,189 |
|
Donald Olds |
|
|
60,500 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
30,189 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
90,689 |
|
Michael Derby |
|
|
44,500 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
57,024 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
101,524 |
|
Roderick N. Carter (1) |
|
|
34,400 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
34,400 |
|
|
Jean-Marie (John) Canan (2) |
|
|
59,600 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
30,189 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
89,789 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Notes:
Item 402(v) Pay Versus Performance
The disclosure included in this section is prescribed by SEC rules and does not necessarily align with how the Company or the GHR committee view the link between the Company’s performance and named executive officer pay. This disclosure is intended to comply with the requirements of Item 402(v) of Regulation S-K applicable to “smaller reporting companies.”
Required Tabular Disclosure of Pay Versus Performance
As required by Section 953(a) of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act and Item 402(v) of Regulation S-K, we are providing the following information about the relationship between executive compensation actually paid and certain financial performance of the Company. The following table sets forth information concerning Compensation Actually Paid (“CAP”) to our Principal Executive Officer (“PEO”) NEOs versus our total shareholder return (“TSR”) and net income (loss) performance results for the fiscal years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022. The amounts set forth below under the headings “Compensation Actually Paid to PEO” and “Average Compensation Actually Paid to Non-PEO NEOs” have been calculated in a manner consistent with Item 402(v) of Regulation S-K. Use of the term
58
CAP is required by the SEC’s rules and as a result of the calculation methodology required by the SEC, such amounts differ from compensation actually received by the individuals and the compensation decisions described in the “Executive Compensation Summary” section above.
The 2023 CAP to our PEO and the average CAP to our non-PEO NEOs reflects the following adjustments required by the applicable SEC rules from the total compensation reported in the Summary Compensation Table (“SCT”):
Year |
|
Summary Compensation Table Total for PEO ($) |
|
|
Compensation Actually Paid to PEO ($) |
|
|
Average Summary Compensation Table Total for Non-PEO NEOs ($) |
|
|
Average Compensation Actually Paid to non-PEO NEOs ($) |
|
|
Value of Initial Fixed $100 Investment Based On: Total Shareholder Return (TSR) ($)1 |
|
|
Net Income (Loss) ($ in 000s)2 |
|
||||||
(a) |
|
(b) |
|
|
(c) |
|
|
(d) |
|
|
(e) |
|
|
(f) |
|
|
(g) |
|
||||||
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
1,132,202 |
|
|
|
1,263,723.92 |
|
|
|
504,564 |
|
|
|
596,611 |
|
|
|
25.42 |
|
|
|
(42,429 |
) |
March 31, 2022 |
|
|
1,546,663 |
|
|
|
2,036,960.42 |
|
|
|
729,703 |
|
|
|
766,415 |
|
|
|
9.58 |
|
|
|
(9,819 |
) |
(1) Our Total Shareholder Return (“TSR”) for each of the applicable fiscal years is calculated based on a fixed investment of $100 at the applicable measurement point (March 31, 2021) on the same cumulative basis as is used in Item 201(e) of Regulation S-K.
(2) Net loss is as reported in our consolidated financial statements.
The 2023 CAP to our PEO and the average CAP to our non-PEO NEOs reflects the following adjustments required by the applicable SEC rules from the total compensation reported in the SCT:
|
|
PEO |
|
|
Average of Non-PEO NEOs |
|
||
Total Reported in 2023 SCT |
|
$ |
1,132,202.25 |
|
|
$ |
504,563.95 |
|
Less: value of equity award reported in the SCT |
|
$ |
(426,799 |
) |
|
$ |
(47,586 |
) |
Add: year-end value of equity awards granted in 2023 that are unvested and outstanding |
|
$ |
285,786 |
|
|
$ |
31,896 |
|
Add: change in fair value (from prior year-end) of prior year equity awards that are unvested and outstanding |
|
$ |
205,833 |
|
|
$ |
11,524 |
|
Add: fair market value of equity awards granted in 2023 and that vested in 2023 |
|
$ |
104,287.09 |
|
|
$ |
11,639.18 |
|
Add: change in fair value (from prior year-end) of prior year equity awards that vested in 2023 |
|
$ |
(37,584.92 |
) |
|
$ |
84,573.88 |
|
Compensation Actually Paid for 2023 |
|
$ |
1,263,723.92 |
|
|
$ |
596,610.76 |
|
The 2022 CAP to our PEO and the average CAP to our non-PEO NEOs reflects the following adjustments required by the applicable SEC rules from the total compensation reported in the SCT:
Required Disclosure of the Relationship between Compensation Actually Paid and Financial Performance Measures
|
|
PEO |
|
|
Average of Non-PEO NEOs |
|
||
Total Reported in 2022 SCT |
|
$ |
1,546,662.97 |
|
|
$ |
848,349.58 |
|
Less: value of equity award reported in the SCT |
|
$ |
(926,502 |
) |
|
$ |
(585,883 |
) |
Add: year-end value of equity awards granted in 2022 that are unvested and outstanding |
|
$ |
852,297 |
|
|
$ |
267,846 |
|
Add: change in fair value (from prior year-end) of prior year equity awards that are unvested and outstanding |
|
$ |
601,773 |
|
|
$ |
189,125 |
|
Add: fair market value of equity awards granted in 2022 and that vested in 2022 |
|
$ |
74,740.53 |
|
|
$ |
23,488.25 |
|
Add: change in fair value (from prior year-end) of prior year equity awards that vested in 2022 |
|
$ |
(112,012.07 |
) |
|
$ |
23,488.71 |
|
Compensation Actually Paid for 2022 |
|
$ |
2,036,960.42 |
|
|
$ |
766,415.30 |
|
In accordance with Item 402(v) of Regulation S-K, we are providing the following descriptions of the relationships between information presented in the Pay Versus Performance table above.
Compensation Actually Paid and Net Income (Loss)
Due to the nature of our Company’s consolidated financial's and primary focus on research and development of novel therapies, our company has not historically utilized net income (loss) as a performance measure for our executive compensation program. As a result, we do not believe there is any meaningful relationship between our net loss and compensation actually paid to our NEOs during the periods presented.
Compensation Actually Paid and TSR
The following graph sets forth the relationship between CAP to our PEO, the average of CAP to our Non-PEO NEOs, and the Company's TSR over the period covering 2023 and 2022.
59
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Shareholder Matters Equity Compensation Plan Information
The following table sets forth certain information regarding the Company’s equity compensation plans as of March 31, 2023:
|
|
(a) Number of |
|
|
(b) Weighted- |
|
|
(c) Number of |
|
|||
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders (Stock Option Plan)(1): |
|
|
4,445,492 |
|
|
$ |
2.27 |
|
|
|
4,410,152 |
|
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders (Equity Incentive Plan)(2): |
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders: |
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
Total |
|
|
4,445,492 |
|
|
|
2.27 |
|
|
|
4,410,152 |
|
Notes:
60
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners
The following table sets forth certain information regarding beneficial ownership of our common shares as of May 31, 2023 by each director and the executive officer identified above, and all directors and executive officers as a group. Beneficial ownership is determined in accordance with the rules of the SEC and generally includes voting or investment power with respect to securities. All common shares have the same voting rights.
For the purposes of calculating percentage ownership, as of May 31, 2023 , 44,612,831 common shares were issued and outstanding, and, for any individual who beneficially owns common shares represented by options exercisable within 60 days of May 31, 2023 , these shares are treated as if outstanding for that person, but not for any other person.
Name and Address |
|
Amount and Nature |
|
|
Percentage of |
|
Prashant Kohli |
|
|
198,596 |
|
|
* |
Donald Olds |
|
|
92,875 |
|
|
* |
George Kottayil |
|
|
878,522 |
|
|
1.97% |
Jan D'Alvise |
|
|
943,970 |
|
|
2.12% |
Michael Derby |
|
|
42,500 |
|
|
* |
Vimal Kavuru |
|
|
3,880,893 |
|
|
8.70% |
Directors and officers as a group (8 persons) |
|
|
4,376,072 |
|
|
9.81% |
* Less than 1%.
Notes:
To the best of our knowledge, other than as disclosed above, the only other beneficial owner of 5% or more of our outstanding common shares is Rajitha Grace Irrevocable Trust, 40 Bey Lea Road, Suite C202, Tom’s River, NJ, 08753, which beneficially owns 4,689,547 common shares, representing 10.51% of our issued and outstanding common shares.
Changes in Control
There existed no change in control arrangements at March 31, 2023
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions and Director Independence Related Transactions
Since April 1, 2022, there were no transactions or any currently proposed transactions in which the Company was or is to be a participant and the amounts exceeds $120,000, and in which any related person had or will have a direct or indirect interest.
Director Independence
Our board of directors believes that, in order to maximize its effectiveness, the board of director must be able to operate independently. A majority of directors must satisfy the applicable tests of independence, such that the board of directors complies with all independence requirements under applicable corporate and securities laws and stock exchange requirements applicable to us. No director will be independent unless the board of directors has affirmatively determined that the director has no material relationship with us or any of our affiliates, either directly or indirectly or as a partner, shareholder or officer of an organization that has a relationship with us or our affiliates. Such determinations will be made on an annual basis and, if a director joins the board of directors between annual meetings, at such time.
Independent Directors
The board of directors determined that Mr. Kavuru, Mr. Olds and Mr. Derby are independent within the meaning of Nasdaq Stock Market rules.
Chairman of the Board
Mr. Kavuru acts as chairman of the board. His duties and responsibilities consist of the oversight of the quality and integrity of the board of directors’ practices.
Board Mandate
The board of directors is responsible for overseeing management in carrying out the business and affairs of the Company. Directors are required to act and exercise their powers with reasonable prudence in the best interests of the Company. The board agrees with and confirms its responsibility for overseeing management's performance in the following particular areas:
61
In carrying out its mandate, the board relies primarily on management to provide it with regular detailed reports on the operations of the Company and its financial position. The board reviews and assesses these reports and other information provided to it at meetings of the board and/or of its committees. At least annually, the board approves a strategic plan for the Company, taking into account, among other things, the opportunities and risks of the Company’s business, its risk appetite, emerging trends, and the competitive environment in the industry.
Position Descriptions
A written position description has been approved for the chairs of each committee of the board of directors. The primary role and responsibility of the chair of each committee of the board of directors is to: (i) in general, ensure that the committee fulfills its mandate, as determined by the board of directors and in accordance with the committee’s charter; (ii) chair meetings of the committee; (iii) report to the board of directors; and (iv) act as liaison between the committee and the board of directors and our management.
The board of directors has adopted a written position description for the chairman of the board of directors. The chairman of the board of directors is responsible for leading the board to fulfill its duties under the board’s mandate as independent of management and acting as an advisor to the chief executive officer. The chairman’s duties include, but are not limited to, setting meeting agendas, approving and supervising management’s progress towards achieving strategic goals, chairing meetings and working with the respective committee and management to ensure, to the greatest extent possible, the effective functioning of the committee and the board of directors. The chairman must oversee that the relationship between the board of directors, management of the Company, the Company’s shareholders and other stakeholders are effective, efficient, and further to the best interests of the Company.
Orientation and Continuing Education
We provide orientation for new appointees to the board of directors and committees in the form of informal meetings with members of the board and senior management, complemented by presentations on the main areas of our business. The board does not formally provide continuing education to its directors, as directors are experienced members. The board of directors relies on third-party professional assistance, when judged necessary, in order to be educated/updated on a particular topic.
Code of Business Conduct and Ethics
The board of directors adopted a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, or Code of Conduct, for our directors, officers and employees on May 31, 2007, as amended from time to time. Our Code of Conduct can be found on SEDAR at www.sedar.com and on our website on www.acastipharma.com. A copy of the Code of Conduct can also be obtained by contacting our corporate secretary. We intend to disclose future amendments to or waivers from certain provisions of our Code of Conduct provisions on our website. Since its adoption by the board of directors, any breach of the Code of Conduct must be brought to the attention of the board of directors by our CEO or other senior executives. No report has ever been filed which pertains to any conduct of a director or executive officer that constitutes a breach to our Code of Conduct.
The board of directors actively monitors compliance with the Code Conduct and promotes a business environment where employees are encouraged to report malfeasance, irregularities, and other concerns. The Code of Conduct provides for specific procedures for reporting non-compliant practices in a manner which, in the opinion of the board of directors, encourages and promotes a culture of ethical business conduct.
The board of directors has also adopted a disclosure policy, insider trading policy, majority voting policy, management and board compensation policies, and a whistle blower policy.
In addition, under the Civil Code of Québec, to which we are subject as a legal person incorporated under the Business Corporations Act (Québec) (L.R.Q., c. S-31), a director must immediately disclose to the board any situation that may place him or her in a conflict of interest. Any such declaration of interest is recorded in the minutes of proceedings of the board of directors. In such instances, the director abstains, except if otherwise required, from the discussion and voting on the question. In addition, it is our policy that an interested director recuse himself or herself from the decision-making process pertaining to a contract or transaction in which he or she has an interest.
Nomination of Directors
The board of directors receives recommendations from the GHR committee, but retains responsibility for managing its own affairs by, among other things, giving its approval for the composition and size of the board of directors, and the selection of candidates nominated for election to the board of directors. The GHR committee initially evaluates candidates for nomination for election as directors, having regard to the background, diversity, employment, and qualifications of possible candidates.
The selection of the nominees for the board of directors is made by the other members of the board, based on our needs and the qualities required for the board of directors, including ethical character, integrity and maturity of judgment of the candidates; the level of experience of the candidates; their ideas regarding the material aspects of our business; the expertise of the candidates in fields relevant to us while complementing the training and experience of the other members of the board of directors; the will and ability of the candidates to devote the necessary time to their duties to the board of directors and its committees; the will of the candidates to serve on the board of directors for numerous consecutive financial periods; and the will of the candidates to refrain from engaging in activities which conflict with the responsibilities and duties of a director. The board researches the training and qualifications of potential new directors which seem to correspond to the selection criteria of the board of directors and, depending on the results of said research, organizes meetings with the potential candidates.
In the case of incumbent directors whose terms of office are set to expire, the board will review such directors’ overall service to us during their term of office, including the number of meetings attended, level of participation, quality of performance and any transactions of such directors with us during their term of office.
We may use various sources in order to identify the candidates for the board of directors, including our own contacts and the references of other directors, officers, advisors and executive placement agencies. We will consider director candidates recommended by shareholders and will evaluate those director candidates in the same manner in which we evaluate candidates recommended by other sources. In making recommendations for director nominees for the annual meeting of shareholders, we will consider any written recommendations of director candidates by shareholders received by our corporate secretary not later than 120 days before the anniversary of the previous year’s annual meeting of shareholders. Recommendations must include the candidate’s name, contact information and a statement of the candidate’s
62
background and qualifications, and must be mailed to us. Following the selection of the candidates by the board of directors, we will propose a list of candidates to the shareholders, for our annual meeting of shareholders.
The board of directors does not have a separate nominating committee and has not adopted any formal written director term limit policy. Proposed nominations of director candidates are evaluated by our GHR committee.
GHR Committee
The mandate of the GHR committee consists of the evaluation of the proposed nominations of senior executives and director candidates to our board of directors; recommending for board approval, if appropriate; revisions of our corporate governance practices and procedures; developing new charters for any new committees established by the board of directors; monitoring relationships and communication between management and the board of directors; monitoring emerging best practices in corporate governance and oversight of governance matters; and assessing the board of directors and its committees. The GHR committee is also in charge of establishing the procedures which must be followed by us to comply with applicable requirements of the Nasdaq Stock Market regarding corporate governance.
The GHR committee has the responsibility of evaluating the compensation, performance incentives as well as the benefits granted to our management in accordance with their responsibilities and performance as well as to recommend the necessary adjustments to our board of directors. The GHR committee also reviews the amount and method of compensation granted to the directors. The GHR committee may retain an external firm in order to assist it during the execution of its mandate. The GHR committee considers time commitment, comparative fees, and responsibilities in determining compensation.
Periodic Assessments
The board of directors, its committees and each director are subject to periodic evaluations of their efficacy and contribution. The evaluation procedure consists of identifying any shortcomings and implementing adjustments proposed by directors at the beginning and during meetings of the board of directors and of each of its committees. Among other things, these adjustments deal with the level of preparation of directors, management and consultants employed by us, the relevance and sufficiency of the documentation provided to directors and the time allowed to directors for discussion and debate of items on the agenda.
Director Term Limits
The board actively considers the issue of term limits from time to time. At this time, the board does not believe that it is in our best interests to establish a limit on the number of times a director may stand for election. While such a limit could help create an environment where fresh ideas and viewpoints are available to the board, a director term limit could also disadvantage us through the loss of the beneficial contribution of directors who have developed increasing knowledge of, and insight into, us and our operations over a period of time. As we operate in a unique industry, it is difficult to find qualified directors with the appropriate background and experience and the introduction of a director term limit would impose further difficulty.
Policies Regarding the Representation of Women on the Board and Among Executive Officers
We have not adopted a formal written policy regarding diversity amongst executive officers and members of the board of directors, including mechanisms for board renewal, in connection with, among other things, the identification and nomination of women directors. Nevertheless, we recognize that gender diversity is a significant aspect of diversity and acknowledge the important role that women with appropriate and relevant skills and experience can play in contributing to the diversity of perspective on the board of directors.
Rather than considering the level of representation of women for directorship and executive officer positions when making board or executive officer appointments, we consider all candidates based on their merit and qualifications relevant to the specific role. While we recognize the benefits of diversity at all levels within our organization, we do not currently have any targets, rules or formal policies that specifically require the identification, consideration, nomination, or appointment of candidates for directorship or executive management positions or that would otherwise force the composition of our board of directors and executive management team.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services Audit Fees
Our independent registered public accounting firm is Ernst & Young LLP, Montréal, Québec, Canada, “Audit fees” consist of fees for professional services for the audit of our annual financial statements and fees related to securities filings. Audit fees for Ernst & Young LLP were CAD $385,000 for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2023. Our previous independent registered public accounting firm was KPMG LLP, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, which audited our annual financial statements for our fiscal year ended March 31, 2022. Audit fees for KPMG LLP were CAD $538,400 for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2022.
Audit-Related Fees
“Audit-related fees” consist of fees for professional services that are reasonably related to the performance of the audit or review of our financial statements, and which are not reported under “Audit Fees” above. Ernst & Young LLP billed CAD nil for audit-related fees for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2023. KPMG LLP billed CAD nil for audit related fees for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2022.
Tax Fees
“Tax fees” consist of fees for professional services for tax compliance, tax advice and tax planning. Ernst & Young LLP billed CAD nil for tax fees for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2023. KPMG LLP billed CAD $28,595 for tax fees for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2022. Tax fees include, but are not limited to, preparation of tax returns.
All Other Fees
“Other fees” include all other fees billed for professional services other than those mentioned hereinabove. Ernest & Young LLP billed no fees under this category for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2023, and KPMG LLP billed no fees under this category for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2022.
Change in Accountant
KPMG LLP was previously our principal independent accountants. On February 22, 2023, the audit committee and board of directors approved the dismissal of KPMG LLP as the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm. The report of KPMG LLP on the consolidated financial statements of the Company as of and for
63
the fiscal years ended March 31, 2022 and 2021 did not contain any adverse opinion or a disclaimer of opinion, nor were they qualified or modified as to uncertainty, audit scope or accounting principles.
During the fiscal years ended March 31, 2022 and 2021 and the subsequent interim period through the date of the engagement of Ernst & Young LLP as the Company’s registered independent public accounting firm, there were no (1) disagreements between the Company and KPMG LLP on any matter of accounting principles or practices, financial statement disclosure or auditing scope or procedure, which disagreements if not resolved to the satisfaction of KPMG LLP, would have caused KPMG LLP to make reference in connection with their opinion to the subject matter of the disagreements, or (2) reportable events.
The Company provided KPMG LLP with a copy of the disclosures in the Company’s related Current Report on Form 8-K prior to its filing with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) and requested KPMG LLP furnish it a letter addressed to the SEC stating whether it agrees with the above statements. A copy of that letter, dated February 22, 2023, was filed as Exhibit 16.1 to the related Current Report on Form 8-K.
On February 22, 2023, in connection with the Company’s dismissal of KPMG LLP, the board of directors approved the engagement of Ernst & Young LLP as its new independent registered public accounting firm to audit the Company’s financial statements for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2023. The decision to retain Ernst & Young LLP was recommended by the audit committee, and approved by the board of directors, after taking into account the results of a competitive review process and other business factors.
During the fiscal years ended March 31, 2022 and 2021 and the subsequent interim period through February 22, 2023, neither the Company nor anyone on its behalf consulted with Ernst & Young LLP regarding (i) the application of accounting principles to a specific transaction, either completed or proposed, (ii) the type of audit opinion that might be rendered on the Company’s financial statements and neither a written report nor oral advice was provided to the Company that Ernst & Young LLP concluded was an important factor considered by the Company in reaching a decision as to accounting, auditing or financial reporting issues, (iii) any matter that was the subject of a disagreement (as defined in Item 304(a)(1)(iv) of Regulation S-K and the related instructions), or (iv) any reportable event (as described in Item 304(a)(1)(v) of Regulation S-K).
Pre-Approval Policies and Procedures
The audit committee approves all audit, audit-related services, tax services and other non-audit related services provided by the external auditors in advance of any engagement. Under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, audit committees are permitted to approve certain fees for non-audit related services pursuant to a de minimus exception prior to the completion of an audit engagement. Non-audit related services satisfy the de minimus exception if the following conditions are met:
None of the services described above under “Principal Accounting Fees and Services” were approved by the audit committee pursuant to the de minimus exception.
64
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules
(a)(1) Financial Statements—The financial statements included in Item 8 are filed as part of this annual report on Form 10-K.
(a)(2) Financial Statement Schedules—All schedules have been omitted because they are not applicable or required, or the information required to be set forth therein is included in the consolidated Financial Statements or notes thereto included in Item 8 of this annual report on Form 10-K.
(a)(3) Exhibits—The exhibits required by Item 601 of Regulation S-K are listed in paragraph (b) below.
(b) Exhibits—The exhibits listed on the Exhibit Index below are filed herewith or are incorporated by reference to exhibits previously filed with the SEC.
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary
None.
EXHIBITS INDEX
Exhibit No. |
|
Description |
|
|
|
2.1 |
|
Agreement and Plan of Merger dated as of May 7, 2021 among Acasti Pharma Inc., Acasti Pharma U.S., Inc. and Grace Therapeutics Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 from Form 8-K filed with the SEC on May 7, 2021) |
|
|
|
3.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
3.2 |
|
Articles of Amendment (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 from Form 8-K filed with the SEC on August 27, 2021) |
|
|
|
3.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
3.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
4.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
4.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
4.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
10.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
23.1 |
|
Consent of Ernst & Young LLP, an Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. |
|
|
|
23.2 |
|
Consent of KPMG LLP, an Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. |
|
|
|
31.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
31.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
32.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
32.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
101.INS |
|
Inline XBRL Instance Document |
|
|
|
101.SCH |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document |
|
|
|
101.CAL |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
101.DEF |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
101.LAB |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
101.PRE |
|
Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
104 |
|
Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101) |
65
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
Dated: June 23, 2023 |
|
|
|
ACASTI PHARMA INC. |
|
|
|
|
|
By: |
/s/ Prashant Kohli |
|
Name: |
Prashant Kohli |
|
|
Title: Chief Executive Officer and |
|
|
(Principal Executive Officer) |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Signature |
|
Title |
|
Date |
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Prashant Kohli |
|
Chief Executive Officer |
|
June 23, 2023 |
Prashant Kohli |
|
(Principal Executive Officer) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Brian Ford |
|
Interim Chief Financial Officer |
|
June 23, 2023 |
Brian Ford |
|
(Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Donald Olds |
|
Director |
|
June 23, 2023 |
Donald Olds |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/Vimal Kavuru |
|
Director |
|
June 23, 2023 |
Vimal Kavuru |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/Michael L.Derby |
|
Director |
|
June 23, 2023 |
Michael L.Derby |
|
|
|
|
66
ACASTI PHARMA INC.
Consolidated Financial Statements
For the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022
F-1 |
|
F-2 |
|
F-3 |
|
F-4 |
|
F-5 |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Acasti Pharma Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of Acasti Pharma Inc. (the “Corporation”) as of March 31, 2023, the related consolidated statements of loss and comprehensive loss, shareholders’ equity, and cash flows for the year ended March 31, 2023, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Corporation at March 31, 2023 and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the year ended March 31, 2023, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Corporation’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Corporation’s financial statements based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Corporation in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Corporation is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audit we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Corporation's internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audit included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audit also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective or complex judgments. The communication of the critical audit matter does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Impairment of goodwill and in-process research and development intangibles (“IPR&D”)
Description of the matter |
As discussed in Notes 2 and 5 of the consolidated financial statements, goodwill and IPR&D intangible assets are tested for impairment at least annually and more frequently when indicators of impairment exist. The Corporation recorded an impairment charge of $28.7 million and $4.8 million related to IPR&D intangible assets and goodwill, respectively, for the year ended March 31, 2023, and as of March 31, 2023 there is a remaining carrying value of $41.1 million and $8.1 million related to IPR&D intangibles and goodwill, respectively. Management estimated the fair value of the IPR&D intangible assets on an individual project basis and estimated the fair value of the reporting unit for purposes of testing goodwill.
Auditing the Corporation's impairment tests was complex and required a high degree of auditor judgment when performing procedures due to the significant estimation uncertainty in determining the fair value of the IPR&D and goodwill. Significant assumptions used in the Corporation's fair value estimate of the IPR&D assets and goodwill are the discount rates, forecasted net sales, and the probability of clinical success of research and development programs and obtaining regulatory approval.
|
How we addressed the matter in our audit |
To test the estimated fair value of the IPR&D and goodwill, our audit procedures included, among others, assessing the fair value methodologies applied and the prospective financial information used by the Corporation in its valuation analysis. We involved our valuation specialists to assist in evaluating the valuation methodologies used, and also in testing the discount rates by developing an independent range of discount rates and comparing them to the discount rates selected by management. We assessed forecasted net sales used by management by comparing to recent transactions for certain peer companies or market data. We compared management's assumptions related to probability of success with data from third party studies and the stage of product development. We performed sensitivity analyses of the significant assumptions to evaluate the change in the fair value resulting from changes in the assumptions. |
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
We have served as the Corporation’s auditor since 2023.
Montréal, Canada
June 23, 2023



Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and Board of Directors of Acasti Pharma Inc.:
Opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of Acasti Pharma Inc. (the "Company") as of March 31, 2022, the related consolidated statements of loss and comprehensive loss, shareholders’ equity, and cash flows for the year ended March 31, 2022, and the related notes (collectively, the "consolidated financial statements"). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of March 31, 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the year ended March 31, 2022, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) ("PCAOB") and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud.
Our audit included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audit also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
KPMG LLP, an Ontario limited liability partnership and member firm of the KPMG global organization of independent member firms affiliated with KPMG International Limited, a private English company limited by guarantee. KPMG Canada provides services to KPMG LLP.

Page 2
We served as the Company’s auditor from 2009 to 2023.
Montréal, Québec
June 21, 2022
ACASTI PHARMA INC.
Consolidated Balance Sheets
|
|
|
|
|
As of |
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, 2022 |
|
|||
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data) |
|
Notes |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Current assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Short-term investments |
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Receivables |
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Assets held for sale |
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Prepaid expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Total current assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Operating lease right of use asset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Equipment |
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Intangible assets |
|
4, 5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Goodwill |
|
4, 5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Total assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Liabilities and Shareholders’ equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Current liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Trade and other payables |
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Operating lease liability |
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Total current liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Derivative warrant liabilities |
|
13, 14(b) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Operating lease liability |
|
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Deferred tax liability |
|
4,19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Total liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Shareholders’ equity: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Common shares, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Additional paid-in capital |
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Accumulated deficit |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Total shareholder’s equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
ACASTI PHARMA INC.
Consolidated Statements of Loss and Comprehensive Loss
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended March 31, 2023 |
|
|
Year ended March 31, 2022 |
|
|||
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars except share and per data) |
|
Notes |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Operating Expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Research and development expenses, net of government assistance |
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
General and administrative expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Sales and marketing |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Impairment of intangible assets |
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Impairment of goodwill |
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Impairment of assets held for sale |
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
( | ) |
|
|
( | ) |
Loss from operating activities |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Other income |
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Loss before income tax recovery |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Income tax recovery |
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Net loss and total comprehensive loss |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Basic and diluted loss per share |
|
|
17 |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Weighted average number of shares outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
ACASTI PHARMA INC.
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars except share data)
|
|
Common Shares |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
Notes |
|
|
Number |
|
|
Dollar |
|
|
Additional |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Deficit |
|
|
Total |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||||||
Balance, March 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|||||
Net loss and total comprehensive loss for the period |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Cumulative translation adjustment |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Stock-based compensation |
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Net proceeds from shares issued under the at-the -market (ATM) program |
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|||
Balance at March 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
Common Shares |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
Notes |
|
|
Number |
|
|
Dollar |
|
|
Additional |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Deficit |
|
|
Total |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||||||
Balance, March 31, 2021 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|||||
Net loss and total comprehensive loss for the period |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
Cumulative translation adjustment |
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|||
Stock-based compensation |
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
||
Common shares issued in relation to merger with Grace via share-for-share, net |
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|||
Balance at March 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
F-3
ACASTI PHARMA INC.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
|
|
|
|
Year ended March 31, 2023 |
|
|
Year ended March 31, 2022 |
|
||
|
|
Notes |
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Cash flows used in operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net loss for the year |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Adjustments: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Depreciation of equipment |
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Impairment of intangible assets |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Impairment of goodwill |
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Impairment of assets held for sale |
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Stock-based compensation expense |
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Change in fair value of warrant liabilities |
|
12 |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Income tax recovery |
|
19 |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Unrealized foreign exchange loss |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Write-off of equipment |
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities |
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Net cash used in operating activities |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Cash flows from (used in) investing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Acquisition of equipment |
|
9 |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Acquisition of short-term investments |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Maturity of short-term investments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net cash from (used in) investing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Cash flows from (used in) financing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net proceeds from shares issued under the at-the-market (ATM) program |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net cash from financing activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Effect of exchange rate fluctuations on cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Translation effect on cash and cash equivalents related to reporting currency |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Net decrease in cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Cash and cash equivalents, end of year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Cash and cash equivalents are comprised of: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Cash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Cash equivalents |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Cash interest received |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for new operating lease liability |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
F-4
ACASTI PHARMA INC.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
(Expressed in thousands of U.S. dollars except share and per share data)
1. Nature of Operations
Acasti Pharma Inc. (“Acasti” or the “Corporation”) is incorporated under the Business Corporations Act (Québec) (formerly Part 1A of the Companies Act (Québec)). The Corporation is domiciled in Canada and its registered office is located at 3009 boul. de la Concorde East, Suite 102, Laval, Québec, Canada H7E 2B5.
The Corporation’s shares are listed on the Nasdaq Capital Market (the "Nasdaq"), and from April 1, 2022 through March 27, 2023 the Corporation's shares were also listed on the TSX Venture Exchange ("TSXV"), in each case, under the symbol "ACST". On March 13, 2023 the Corporation received approval to voluntarily delist from the TSXV. Effective as at the close of trading on March 27, 2023, the Corporation's common shares are no longer listed and posted for trading on the TSXV.
In August 2021, the Corporation completed the acquisition via a share-for-share merger of Grace Therapeutics, Inc. (“Grace”), a privately held emerging biopharmaceutical company focused on developing innovative drug delivery technologies for the treatment of rare and orphan diseases. The post-merger Corporation is focused on building a late-stage specialty pharmaceutical company specializing in rare and orphan diseases and developing and commercializing products that improve clinical outcomes using our novel drug delivery technologies. The Corporation seeks to apply new proprietary formulations to existing pharmaceutical compounds to achieve enhanced efficacy, faster onset of action, reduced side effects, more convenient delivery and increased patient compliance; all of which could result in improved patient outcomes. The active pharmaceutical ingredients chosen by the Corporation for further development may be already approved in the target indication or could be repurposed for use in new indications.
In May 2023, the Corporation implemented a strategic realignment plan to enhance shareholder value that resulted in the Corporation engaging a new management team and greatly reducing its research and development activities including a reduction in workforce. Moving forward part of this strategic realignment plan includes the Corporation rebuilding a smaller organization in the United States.
The Corporation has incurred operating losses and negative cash flows from operations in each year since its inception. The Corporation expects to incur significant expenses and continued operating losses for the foreseeable future. The Corporation expects its expenses will increase substantially in connection with its ongoing activities, particularly as it advances clinical development for the first three drug candidates in the Corporation’s pipeline; continues to engage contract manufacturing organizations (“CMO's”) to manufacture its clinical study materials and to ultimately develop large-scale manufacturing capabilities in preparation for commercial launch; seeks regulatory approval for its drug candidates; and adds personnel to support its drug product development and future drug product launch and commercialization.
The Corporation does not expect to generate revenue from product sales unless and until it successfully completes drug development and obtains regulatory approval, which the Corporation expects will take several years and is subject to significant uncertainty. To date, the Corporation has financed its operations primarily through public offerings and private placements of its common shares, warrants and convertible debt and the proceeds from research tax credits. Until such time that the Corporation can generate significant revenue from drug product sales, if ever, it will require additional financing, which is expected to be sourced from a combination of public or private equity or debt financing or other non-dilutive sources, which may include fees, milestone payments and royalties from collaborations with third parties. Arrangements with collaborators or others may require the Corporation to relinquish certain rights related to its technologies or drug product candidates. Adequate additional financing may not be available to the Corporation on acceptable terms, or at all. The Corporation’s inability to raise capital as and when needed could have a negative impact on its financial condition and its ability to pursue its business strategy.
Management expects the Corporation to have sufficient cash resources to satisfy its objectives into the second quarter of calendar 2025, which is 21 to 24 months from the issuance date of these Financial Statements based on current plans or forecasts. Part of the strategic realignment plan includes the decision to prioritize the development pf GTX-104 with a goal to advance to commercialization, while conserving resources as much as possible to complete development efficiently. Further development of GTX-102 and GTX-101 will occur at such time as additional funding is obtained or strategic partnerships are entered. The Corporation will require additional capital to fund our daily operating needs beyond that time. The Corporation plans to raise additional capital prior to that time in order to maintain adequate liquidity. Negative results from studies, if any, and depressed prices of the Corporation’s stock could impact the Corporation’s ability to raise additional financing. Raising additional equity capital is subject to market conditions not within the Corporation’s control. If the Corporation does not raise additional funds in this time period, the Corporation may not be able to realize our assets and discharge our liabilities in the normal course of business.
The Corporation remains subject to risks similar to other development stage companies in the biopharmaceutical industry, including compliance with government regulations, protection of proprietary technology, dependence on third-party contractors and consultants and potential product liability, among others.
Reverse stock split
On August 26, 2021, the shareholders of the Corporation approved a resolution to undertake a reverse split of the common stock within a range of 1-6 to 1-8 with such specific ratio to be approved by the Acasti Board. All references in these financial statements to number of common shares, warrants and options, price per share and weighted average number of shares outstanding prior to the reverse split have been adjusted to reflect the approved reverse stock split of 1-
2. Summary of significant accounting policies
Basis of presentation
These consolidated financial statements of Acasti Pharma Inc., which include the accounts of its subsidiaries have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles' in the United States of America ("U.S. GAAP"). All intercompany transactions and balances are eliminated on consolidation.
Smaller Reporting Company
The Corporation qualifies as a “smaller reporting company” under the Exchange Act as of March 31, 2023 because the market value of its common shares held by non-affiliates was less than $
F-5
Use of estimates
The preparation of the financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, income, and expenses. Actual results may differ from these estimates.
Estimates are based on management’s best knowledge of current events and actions that management may undertake in the future. Estimates and underlying assumptions are reviewed on an ongoing basis. Revisions to accounting estimates are recognized in the period in which the estimates are revised and in any future periods affected.
Estimates and assumptions include the measurement of derivative warrant liabilities (note 12), stock-based compensation (note 14)), assets held for sale (notes 8), the supply contract (note 19(a)) and valuation of intangibles and goodwill (note 5). Estimates and assumptions are also involved in measuring the accrual of services rendered with respect to research and developments expenditures at each reporting date, and determining which research and development expenses qualify for research and development tax credits and in what amounts. The Corporation recognizes the tax credits once it has reasonable assurance that they will be realized.
Functional and foreign currency
On April 1, 2022, the Corporation’s functional currency was changed from the Canadian dollar to the US dollar. This change is reflected prospectively in the Corporation’s financial statements.
FASB ASC Topic 830, “Functional Currency Matters,” requires a change in functional currency to be reported as of the date it is determined there has been a change, and it is generally accepted practice that the change is made at the start of the most recent period that approximates the date of the change. Management determined it would enact this change effective on April 1, 2022. While the change was based on a factual assessment, the determination of the date of the change required management’s judgment given the change in the Corporation's primary economic and business environment, which has evolved over time. As part of management’s functional currency assessment, changes in economic facts and circumstances were considered. This included analysis of changes in: impact of the merger with Grace Therapeutics, management of operations, and in the composition of cash and short term investment balances. Additionally, budgeting is in USD, whereas this was previously performed in CAD. The Corporation's cash outflows consist primarily of USD cash balances and less of CAD, as also reflected in the budget.
Transactions denominated in currencies other than the functional currency are measured and recorded in the functional currency at the exchange rate in effect on the date of the transactions. At each consolidated balance sheet date, monetary assets and liabilities denominated in currencies other than the functional currency are remeasured using the exchange rate in effect at that date. Non-monetary assets and liabilities and revenue and expense items denominated in foreign currencies are translated into the functional currency using the exchange rate prevailing at the dates of the respective transactions. Any gains or losses arising on remeasurement are included in the consolidated statement of loss.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents comprise cash balances and highly liquid investments purchased with original maturities of three months or less. Cash and cash equivalents consist of term deposits held at the bank and recorded at cost, which approximates fair value.
Investments
The Corporation’s investments consist of term deposits and are classified as held-to-maturity securities. These investments are recorded at amortized cost. Investments with original maturities exceeding three months and less than one year are categorized as short-term. The Corporation has the intent and ability to hold these securities for at least the next 12 months.
Assets held for sale
Assets that are classified as held for sale are measured at the lower of their carrying amount or fair value less expected selling costs (“estimated selling price”) with a loss recognized to the extent that the carrying amount exceeds the estimated selling price. The classification is applicable at the date upon which the sale of assets is probable, and the assets are available for immediate sale in their present condition. Assets once classified as held for sale, are not subject to depreciation or amortization and both the assets and any liabilities directly associated with the assets held for sale are classified as current in the Corporation’s Consolidated Balance Sheets. Subsequent changes to the estimated selling price of assets held for sale are recorded as gains or losses to the Consolidated Statements of Income wherein the recognition of subsequent gains is limited to the cumulative loss previously recognized.
Equipment
Equipment is measured at cost less accumulated depreciation and accumulated impairment losses, if any.
Cost includes expenditures that are directly attributable to the acquisition of the asset, including all costs incurred in bringing the asset to its present location and condition. Purchased software that is integral to the functionality of the related equipment is capitalized as part of that equipment. Gains and losses on disposal of equipment are determined by comparing the proceeds from disposal with the carrying amount of equipment and are recognized net within operating expenses in the Consolidated Statement of Loss and Comprehensive Loss.
The costs of the day-to-day servicing of equipment are recognized in profit or loss as incurred.
Depreciation is recognized in profit or loss on either a straight-line basis or a declining basis over the estimated useful lives of each part of an item of equipment, since this most closely reflects the expected pattern of consumption of the future economic benefits embodied in the asset. Items of equipment are depreciated from the date that they are available for use or, in respect of assets not yet in service, from the date they are ready for their intended use.
F-6
The estimated useful lives and rates for the current and comparative periods are as follows:
Assets |
|
Method |
|
|
|
|
Rate |
|
|
|
|
|||
Furniture and office equipment |
|
Declining balance |
|
|
% |
|
to |
|
|
|
% |
|||
Computer equipment |
|
Declining balance |
|
|
|
|
|
% |
|
|
|
|||
Laboratory equipment |
|
Declining balance |
|
|
|
|
|
% |
|
|
|
|||
Production equipment |
|
Declining balance |
|
|
% |
|
to |
|
|
|
% |
|||
Depreciation methods, useful lives and residual values are reviewed periodically and adjusted prospectively if appropriate.
Intangible assets - acquired in-process research and development
In a business combination, the fair value of in-process research and development (“IPR&D”) acquired is capitalized and accounted for as indefinite-lived intangible assets, and not amortized until the underlying project receives regulatory approval, at which point the intangible assets will be accounted for as definite-lived intangible assets and amortized over the remaining useful life or discontinued. If discontinued, the intangible asset will be written off. Research and development (“R&D”) costs incurred after the acquisition are expensed as incurred.
The estimated fair values of identifiable intangible assets were determined using the multi-period excess earnings method, which is a valuation methodology that provides an estimate of the fair value of an asset based on market participant expectations of the cash flows an asset would generate over its remaining useful life. The significant assumptions used in the valuation are the discount rate, the probability of clinical success of research and development programs, obtaining regulatory approval and forecasted net sales, including milestone payments and royalty revenues.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
The Corporation reviews the recoverability of its finite long-lived assets whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that it is carrying amount may not be recoverable. The carrying amount is first compared with the undiscounted cash flows. If the carrying amount is higher than the sum of undiscounted cash flows, then the Corporation determines the fair value of the underlying asset group. Any impairment loss to be recognized is measured as the difference by which the carrying amount of the asset group exceeds the estimated fair value of the asset group.
Goodwill and indefinite-lived assets are not amortized but are subject to an impairment review annually and more frequently when indicators of impairment exist. An impairment of goodwill could occur if the carrying amount of a reporting unit exceeds the fair value of that reporting unit. An impairment of indefinite-lived intangible assets would occur if the fair value of the intangible asset is less than the carrying value.
The Corporation tests its goodwill for impairment by first assessing qualitative factors to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value is less than its carrying amount. If the Corporation concludes it is more likely than not that fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, a quantitative impairment test is performed.
The Corporation tests indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment by first assessing qualitative factors to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value is less than its carrying amount. If the Corporation concludes it is more likely than not that the fair value is less than it's carrying amount, a quantitative impairment test is performed. The Corporation's annual impairment test is performed in the fourth quarter of the fiscal year.
Research and Development Costs
Research and developments expenditures are expensed as incurred. These costs primarily consist of employees’ salaries and benefits related to research and development activities, contractors and consultants that conduct the Corporation’s clinical trials, independent auditors and consultants to perform investigation activities on behalf of the Corporation, laboratory material and small equipment, clinical trial materials, stock-based compensation expense, and other non-clinical costs and regulatory fees. Advance payments for goods and services that will be used in future research and development are recognized in prepaids or other assets and are expensed when the services are performed, or the goods are used.
Stock - based compensation
The Corporation has in place a stock option plan for directors, officers, employees, and consultants of the Corporation, with grants under the stock option plan approved by the Corporation’s Board of Directors. The plan provides for the granting of options to purchase Common Shares and the exercise price of each option equals the closing trading price of Common Shares on the day prior to the grant. The terms and conditions for acquiring and exercising options are set by the Corporation’s Board of Directors in accordance with and subject to the terms and conditions of the stock option plan. The Corporation measures the cost of such awards based on the fair value of the award at grant date, net of estimated forfeiture, and recognizes stock-based compensation expense in the Consolidated Statements of Loss and Comprehensive Loss on a graded vesting basis over the requisite service period. The requisite service period equals the vesting periods of the awards. The fair value of options is estimated for each tranche of an award that vests on a graded basis. The fair value of options is estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model, which uses various inputs including fair value of the Common Shares at the grant date, expected term, estimated volatility, risk-free interest rate and expected dividend yields of the Common Shares. The Corporation applies an estimated forfeiture rate derived from historical employee termination behaviour. If the actual forfeitures differ from those estimated by management, adjustment to compensation expense may be required in future periods.
Non-employee stock-based compensation transactions in which the Corporation receives goods or services as consideration for its own equity instruments are accounted for as stock-based compensation transactions. The Corporation establishes the fair value at the grant date for non-employee awards and measures the fair value based on the fair value of equity instruments issued. The fair value of a non-employee award is estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model, which uses various inputs including fair value of the Common Shares at the grant date, contractual term, estimated volatility, risk-free interest rate and expected dividend yields of the Common Shares.
Government grants
Government grants are recorded as a reduction of the related expense or cost of the asset acquired. Government grants are recognized when there is reasonable assurance that the Corporation has met the requirements of the approved grant program and there is reasonable assurance that the grant will be received.
F-7
Grants that compensate the Corporation for expenses incurred are recognized in profit or loss in reduction thereof on a systematic basis in the same years in which the expenses are recognized. Grants that compensate the Corporation for the cost of an asset are recognized in profit or loss on a systematic basis over the useful life of the asset.
Leases
At the inception of an arrangement, the Corporation determines whether the arrangement is or contains a lease based on the unique facts and circumstances present in the arrangement. Operating lease liabilities and their corresponding right-of-use assets are initially recorded based on the present value of lease payments over the expected remaining lease term. Certain adjustments to the right-of-use asset may be required for items such as incentives received. The interest rate implicit in lease contracts is typically not readily determinable. As a result, the Corporation utilizes its incremental borrowing rate to discount lease payments, which reflects the fixed rate at which the Corporation could borrow on a collateralized basis the amount of the lease payments in the same currency, for a similar term, in a similar economic environment. . The Corporation has elected not to recognize leases with an original term of one year or less on the balance sheet. The Corporation typically only includes an initial lease term in its assessment of a lease arrangement. Options to renew a lease are not included in the Corporation’s assessment unless there is reasonable certainty that the Corporation will renew. The Corporation’s lease expense is recognized in research and development expenses. The Corporation does not have financing leases.
In accordance with ASC 842, components of a lease should be split into three categories: lease components, non-lease components and non-components. The fixed and in-substance fixed contract consideration (including any consideration related to non-components) must be allocated based on the respective relative fair values to the lease components and non-lease components. Entities may elect not to separate lease and non-lease components. The Corporation has elected to account for lease and non-lease components together as a single lease component for all underlying assets and allocate all of the contract consideration to the lease component only.
Income tax
Income tax expense comprises current and deferred taxes. Current and deferred taxes are recognized in profit or loss except to the extent that they relate to items recognized directly in equity or in other comprehensive income.
Current tax is the expected tax payable or receivable on the taxable income or loss for the year, using tax rates enacted at the reporting date, and any adjustment to tax payable in respect of previous years.
Deferred tax is recognized in respect of temporary differences between the carrying amounts (tax base) of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for taxation purposes. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured at the tax rate expected to apply when the underlying asset or liability is realised (settled) based on the rates that are enacted at the reporting date. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are offset if the Corporation has the right to set off the amount owed by with the amount owed by the other party, the Corporation intends to set off and the offset right is enforceable at law. A deferred tax asset is recognized for unused tax losses and tax credits, reduced by a valuation allowance to the extent that it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax asset will not be realized.
Earnings per share
The Corporation presents basic and diluted earnings per share (EPS) data for its Common Shares. Basic EPS is calculated by dividing the profit or loss attributable to the holders of Common Shares by the weighted average number of Common Shares outstanding during the year. Diluted EPS is determined by adjusting the profit or loss attributable to the holders of Common Shares and the weighted average number of Common Shares outstanding adjusted for the effects of all dilutive potential Common Shares, which comprise warrants and share options granted to employees.
Segment reporting
An operating segment is a component of the Corporation that engages in business activities from which it may earn revenues and incur expenses. The Corporation has
Derivative financial instruments
The Corporation has issued warrants of which some are accounted for as liability-classified derivatives over its own equity. Derivatives are recognized initially at fair value; attributable transaction costs are recognized in profit and loss as incurred. Subsequent to initial recognition, derivatives are measured at fair value, and all changes in their fair value are recognized immediately in profit or loss as a component of financial expenses.
Other equity instruments
Warrants that do not meet the definition of a liability instrument are recognized in equity as additional paid in capital.
Fair Value Measurements
Certain of the Corporation’s accounting policies and disclosures require the determination of fair value, for both financial assets and liabilities.
In establishing fair value, the Corporation uses a fair value hierarchy based on levels as defined below:
The Corporation has determined that the carrying values of its short-term financial assets and liabilities (cash and cash equivalents, short-term investments and trade and other payables) approximate their fair value given the short-term nature of these instruments. The Corporation measured its derivative warrant liabilities at fair value on a recurring basis using level 3 inputs.
F-8
3. Recent Accounting Pronouncements
The Corporation has considered recent accounting pronouncements and concluded that they are either not applicable to the business or that the effect is not expected to be material to the consolidated financial statements as a result of future adoption.
4. Acquisition of Grace
On August 27, 2021, the Corporation completed its acquisition of all outstanding equity interests in Grace Therapeutics Inc, via a merger. Grace, based in New Jersey and organized under the laws of Delaware, was a rare and orphan disease specialty pharmaceutical company.
In connection with the share-for-share noncash transaction, Grace was merged with a new wholly owned subsidiary of Acasti and became a subsidiary of Acasti. As a result, Acasti acquired Grace’s entire therapeutic pipeline consisting of three unique clinical stage and multiple pre-clinical stage assets supported by an intellectual property portfolio consisting of various granted and pending patents in various jurisdictions worldwide. Under the terms of the acquisition, each issued and outstanding share of Grace common stock was automatically converted into the right to receive Acasti common shares equal to the equity exchange ratio set forth in the merger agreement.
Consideration for acquisition
A total of
|
|
|
|
|
Total common shares issued |
|
|
|
|
Acasti share price (closing share price on August 27, 2021) |
|
$ |
|
|
Fair value of common shares issued |
|
$ |
|
|
The acquisition of Grace has been accounted for as a business combination using the acquisition method of accounting. The fair value of the purchase price was allocated to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed at their respective fair values. This acquisition method requires, among other things, that assets acquired, and liabilities assumed in a business combination be recognized at their fair values as of the acquisition date. The valuation of assets acquired, and liabilities assumed has been finalized during the fourth quarter of 2022.
Measurement period adjustments to the preliminary purchase price allocation during 2022 included (i) an increase to intangible assets of $
The following table summarizes the final fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the acquisition date:
|
|
$ |
|
|
Assets acquired and liabilities assumed |
|
|
|
|
Cash and equivalents |
|
|
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
|
|
Intangible assets – in-process research and development |
|
|
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
|
( |
) |
Deferred tax liability |
|
|
( |
) |
Total assets acquired and liabilities assumed |
|
|
|
|
Intangible assets of $
Acquisition-related expenses, which were comprised primarily of regulatory, financial advisory and legal fees, totalled $
Pro forma financial information
The following table presents the unaudited pro forma combined results of Acasti and Grace for the year ended March 31, 2022, as if the acquisition of Grace had occurred on April 1, 2020:
|
|
|
|
Year ended March 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
Net loss |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
The unaudited pro forma condensed combined financial information was prepared using the acquisition method of accounting and was based on the historical financial information of Acasti and Grace. The unaudited pro forma financial information is not necessarily indicative of what the consolidated results of operations would have been had the acquisition been completed on April 1, 2020. In addition, the unaudited pro forma financial information is not a projection of future results of operations of the combined company, nor does it reflect the realization of any synergies or cost savings associated with the acquisition.
5. Intangible assets and Goodwill
F-9
Intangible assets and goodwill resulted from the acquisition of Grace (note 4), related to Grace’s therapeutic pipeline, consisting of three unique clinical stage programs/assets supported by intellectual property. Individual IPR&D projects and goodwill is tested for impairment on an annual basis in the fourth quarter, and in between annual tests if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of each technology or our reporting unit below its carrying value. The Corporation has one reporting unit which we have determined to be the Company. The strategic realignment plan announced April 4, 2023, to prioritize resources to GTX-104, from GTX-101 and GTX-102 triggered a comprehensive review and have been considered in our annual impairment test. The estimated fair values of identifiable intangible assets were determined using the multi-period excess earnings method.
|
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
$ |
|
||||
|
|
GTX 104 |
|
GTX 102 |
|
GTX 101 |
|
Total |
|
||||
Intangible assets – in-process research and development |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Balance, beginning of the year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Impairment |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
( |
) |
|
Balance, end of the year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
The impairment of $
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
|
|
Balance, beginning of the year |
|
|
|
|
Impairment |
|
|
( | ) |
Balance, end of the year |
|
|
|
|
The multi-period excess earnings method models used to estimate the fair value of assets of our IPR&D reflect significant assumptions and are level 3 un-observable data regarding the estimates a market participant would make in order to evaluate a drug development asset, including the following:
Our IPR&D projects, consistent with others in our industry, have risks and uncertainties associated with the timely and successful completion of the development and commercialization of product candidates, including our ability to confirm safety and efficacy based on data from clinical trials, our ability to obtain necessary regulatory approvals and our ability to successfully complete these tasks within budgeted costs. It is not permitted to market a human therapeutic without obtaining regulatory approvals, and such approvals require the completion of clinical trials that demonstrate that a product candidate is safe and effective. In addition, the availability and extent of coverage and reimbursement from third-party payers, including government healthcare programs and private insurance plans as well as competitive product launches, affect the revenues a product can generate. Consequently, the eventual realized values, if any, of acquired IPR&D projects may vary from their estimated fair values.
6. Receivables
|
|
|
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, 2022 |
|
|||
|
|
Notes |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Sales tax receivables |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Government assistance |
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Interest receivable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Total receivables |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
7. Short-term Investments
The Corporation holds various short term investments with maturities greater than 3 months at the time of purchase as follows:
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, 2022 |
|
||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Term deposits issued in CAD currency earning interest at |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Term deposits issued in USD currency earning interest at |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Term deposits issued in CAD currency earning interest at ranges between |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total short-term investments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
8. Assets held for sale
In January 2020 and August 2020, the Corporation released Phase 3 TRILOGY clinical study results for the Corporation’s lead drug candidate, CaPre. The TRILOGY
studies did not meet the primary endpoint which resulted in the Corporation’s Board of Directors deciding not to proceed with a filing of an NDA with the FDA. With
the completion of the TRILOGY studies beginning in the second half of fiscal 2021,
F-10
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, 2022 |
|
||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Reclassed as explained in note 9 |
|
||
Other assets (a) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Production equipment (b) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
a. Other assets
Other assets represent krill oil (RKO) held by the Corporation that was expected to be used in the conduct of R&D activities and commercial inventory scale up related to the development and commercialization of the CaPre drug. Given that the development of CaPre will no longer be pursued, the Corporation expected to sell this reserve. The other asset is being recorded at the fair value less costs to sell, which has resulted in an impairment loss of $
b. Production equipment
Similarly, to the Other assets, the announcement of the outcomes of the TRILOGY clinical trials resulted in an impairment trigger for the production equipment. The impairment loss is based on management’s estimate of the fair value of the equipment less cost -to sell, which is based primarily on estimated market conditions for selling used equipment and the inability to sell. These projections are based on Level 3 inputs of the fair value hierarchy and reflect the Corporations best estimate of market participants’ pricing of the assets as well as the general condition of the assets. This resulted in an impairment loss of $
March 31, 2022 |
|
Cost, net of previous impairment |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Net book |
|
|||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Production equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
9. Equipment
In
|
|
Cost, net of |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Net |
|
|||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Furniture and office equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
( | ) |
|
|
|
||
Computer equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
( | ) |
|
|
|
||
Laboratory equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Furthermore, depreciation expense of $
March 31, 2023 |
|
Cost, net of impairment |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Write off |
|
|
Net book |
|
||||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
||||
Furniture and office equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
( | ) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Computer equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
( | ) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
Laboratory equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
March 31, 2022 |
|
Cost, net of impairment |
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
Net book |
|
|||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Furniture and office equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
( | ) |
|
|
|
||
Computer equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
( | ) |
|
|
|
||
Laboratory equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
||
10. Government assistance
F-11
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, 2022 |
|
||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Investment tax credit |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Government assistance is comprised of research and development investment tax credits receivable from the Quebec provincial government which relate to qualifiable research and development expenditures under the applicable tax laws. The amounts recorded as receivables are subject to a government tax audit and the final amounts received may differ from those recorded. For the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022, the Corporation recorded $
Unrecognized Canadian federal tax credits may be used to reduce future Canadian federal income tax and expire as follows:
|
|
$ |
|
|
2029 |
|
|
||
2030 |
|
|
|
|
2031 |
|
|
|
|
2032 |
|
|
|
|
2033 |
|
|
|
|
2034 |
|
|
|
|
2035 |
|
|
|
|
2036 |
|
|
|
|
2037 |
|
|
|
|
2038 |
|
|
|
|
2039 |
|
|
|
|
2040 |
|
|
|
|
2041 |
|
|
|
|
2042 |
|
|
|
|
2043 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
11. Trade and other payables
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, 2022 |
|
||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Trade payables |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Accrued liabilities and other payables |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Employee salaries and benefits payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Total trade and other payables |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
12. Leases
The Corporation has historically entered into lease arrangements for its research and development and quality control laboratory facility located in Sherbrooke, Québec. As of March 31, 2023, the Corporation had one operating lease with required future minimum payments.
The following tables contains a summary of the lease costs recognized under ASC 842 and other information pertaining to the Corporation’s operating leases for the year ended March 31, 2023:
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
Operating cash flows for operating leases |
|
$ |
|
|
Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for lease obligations |
|
$ |
|
|
Weighted-average remaining lease term (in years) |
|
|
|
|
Weighted-average discount rate |
|
|
% |
|
As the Corporation's leases do not provide an implicit rate, the Corporation utilized its incremental borrowing rate to discount lease payments, which reflects the fixed rate at which the Corporation could borrow on a collateralized basis the amount of the lease payments in the same currency, for a similar term, in a similar economic environment.
Future minimum lease payments under the Corporation’s operating leases as of March 31, 2023 were as follows:
F-12
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
2024 |
|
|
|
|
2025 |
|
|
|
|
2026 |
|
|
|
|
2027 |
|
|
|
|
2028 |
|
|
|
|
Total lease payments |
|
|
|
|
Less: interest |
|
|
( |
) |
Total lease liabilities |
|
|
|
|
13. Derivative warrant liabilities
In connection with the Canadian public offering of units consisting of common shares and warrants that closed on May 9, 2018, the Corporation issued a total of
In connection with the U.S. public offering units consisting of common shares and warrants that closed on December 27, 2017, the Corporation issued a total of
The derivative warrant liabilities are measured at fair value at each reporting period and the reconciliation of changes in fair value is presented in the following tables:
|
|
Warrants issued May 2018 |
|
|
Warrants issued December 27, 2017 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, |
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, |
|
||||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||||
Balance – beginning of year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Change in fair value |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Translation effect |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Balance – end of year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Fair value per warrant issuable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
As at March 31, 2022, the fair value of the derivative warrant liabilities was estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model and based on the following assumptions:
|
|
Warrant liabilities issued |
|
|
Warrant liabilities issued |
|
||
|
|
March 31, |
|
|
March 31, |
|
||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Exercise price |
|
CAD $ |
|
|
USD $ |
|
||
Share price |
|
CAD $ |
|
|
USD $ |
|
||
Risk-free interest |
|
|
% |
|
|
% |
||
Contractual life (years) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Expected volatility |
|
|
% |
|
|
% |
||
The Corporation measured its derivative warrant liabilities at fair value on a recurring basis. These financial liabilities were measured using level 3 inputs (see Note 19). As at March 31, 2023, the effect of an increase or a decrease of
14. Capital and other components of equity
a. Common Shares
Authorized capital stock
Unlimited number of shares
F-13
“At-the-market” sales agreement
On June 29, 2020, the Corporation entered into an amended and restated sales agreement (the Sales Agreement) with B. Riley, Oppenheimer& Co. Inc. and H.C. Wainwright & Co., LLC (collectively, the “Agents”) to amend the existing ATM program. Under the terms of the Sales Agreement, which has a three-year term, the Corporation may issue and sell from time to time its common shares (the Shares) having an aggregate offering price of up to US $
On November 10, 2021, the Corporation filed a prospectus supplement relating to its at-the-market program, expiring July 7, 2023, with B. Riley, Oppenheimer& Co. Inc. and H.C. Wainwright & Co., LLC acting as agents. Under the terms of the ATM Sales Agreement and the prospectus supplement, the Corporation may issue and sell from time-to-time common shares having an aggregate offering price of up to $
During the year ended March 31, 2023,
b. Warrants
The warrants of the Corporation are composed of the following:
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, 2022 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
Number |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Number |
|
|
Amount |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
||||
Liability |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
May 2018 public offering warrants 2018 (i) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
December 2017 U.S. public offering warrants (ii) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Public offering warrants |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Public offering U.S. broker warrants December 2017 (iii) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
During the years ended March 31, 2023 and 2022
15. Other income (expenses)
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, 2022 |
|
||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Foreign exchange gain (loss) |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Interest income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Other income |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Change in fair value of warrant liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Other income (expenses) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
16. Stock-based compensation
At March 31, 2021, the Corporation has the following stock-based compensation arrangement:
a. Corporation stock option plan
The Corporation has in place a stock option plan for directors, officers, employees, and consultants of the Corporation. An amendment of the stock option plan was approved by shareholders on September 28, 2022. The amendment provides for a change to the existing limits for Common Shares reserved for issuance under the Stock Option Plan.
The Stock Option Plan continues to provide for the granting of options to purchase common shares. The exercise price of the stock options granted under this amended plan is not lower than the closing price of the common shares on the Nasdaq at the close of markets the day preceding the grant. The maximum number of common shares that may be issued upon exercise of options granted under the amended Stock Option Plan shall not exceed 20% of the aggregate number of issued and outstanding shares of the Corporation as of July 28, 2022. The terms and conditions for acquiring and exercising options are set by the Corporation’s Board of Directors, subject among others, to the following limitations: the term of the options cannot exceed
F-14
thirty-six (36) months.
The total number of shares issued to any one consultant within any twelve-month period cannot exceed
In connection to the voluntary delisting from the TSXV, and as permissible under the stock option plan the Corporation communicated to each holder of stock options, that the exercise price of all existing option grants will be redesignated in US dollars on the basis of the equivalent price in US dollar at the applicable date of grant. This does not constitute a repricing of the existing exercise price of stock options and has no impact on the compensation expense recognized under the stock option plan.
The following tables summarize information about activities within the stock option plan:
|
|
Number of |
|
|
Weighted average |
|
|
Weighted average |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
USD $ |
|
|
USD $ |
|
|||
Outstanding, March 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Granted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Forfeited |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Expired |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Outstanding, March 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Exercisable at end of year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Number of |
|
|
Weighted average |
|
|
Weighted average |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
CAD $ |
|
|
CAD $ |
|
|||
Outstanding, March 31, 2021 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Granted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Exercised |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Forfeited |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Outstanding, March 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
USD $ |
Weighted average fair value of the options granted to employees and directors of the Corporation- |
|
$ |
|
|
Year ended March 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
CAD $ |
|
|
Weighted average fair value of the options granted to employees and directors of the Corporation- |
|
|
|
|
Compensation expense recognized under the stock option plan is summarized as follows:
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, 2022 |
|
||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Research and development expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
General and administrative expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Sales and marketing expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
As of March 31, 2023, there was USD $
A summary of the non-vested stock option activity and related information for the Corporation’s stock options granted is as follows:
|
|
Number of |
|
|
Weighted average |
|
||
Non- vested, March 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Options granted |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Options vested |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Non- vested, March 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
The fair value of options granted was estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model, resulting in the following weighted average assumptions for options granted during the periods ended:
F-15
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
|
|
Weighted average |
|
|
Exercise price |
|
$ |
|
|
Share price |
|
$ |
|
|
Dividend |
|
|
|
|
Risk-free interest |
|
|
% |
|
Estimated life (years) |
|
|
|
|
Expected volatility |
|
|
% |
|
|
|
March 31, 2022 |
|
|
|
|
Weighted average- CAD |
|
|
Exercise price |
|
$ |
|
|
Share price |
|
$ |
|
|
Dividend |
|
|
|
|
Risk-free interest |
|
|
% |
|
Estimated life (years) |
|
|
% |
|
Expected volatility |
|
|
% |
|
The following tables summarize information about activities within the stock option plan:
March 31, 2023 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average |
|
|
Number of options |
|
|
Number of options |
|
||||||
$ |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
$ |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
$ |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
$ |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
$ |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
Stock-based compensation payment transactions
The fair value of stock-based compensation transactions is measured using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. Measurement inputs include share price on measurement date, exercise price of the instrument, expected volatility (based on weighted average historic volatility for a duration equal to the weighted average life of the instruments, life based on the average of the vesting and contractual periods for employee awards as minimal prior exercises of options in which to establish historical exercise experience), and the risk-free interest rate (based on government bonds). Service and performance conditions attached to the transactions, if any, are not considered in determining fair value. The expected life of the stock options is not necessarily indicative of exercise patterns that may occur. The expected volatility reflects the assumption that the historical volatility over a period similar to the life of the options is indicative of future trends, which may also not necessarily be the actual outcome.
b. Corporation equity incentive plan
The Corporation established an equity incentive plan for employees, directors and consultants. The plan provides for the issuance of restricted share units (RSUs), performance share units, restricted shares, deferred share units and other stock-based awards, subject to restricted conditions as may be determined by the Board of Directors. There were
17. Loss per share
Diluted loss per share was the same amount as basic loss per share, as the effect of options, and warrants would have been anti-dilutive, as the Corporation has incurred losses in each of the periods presented. All outstanding options, and warrants could potentially be dilutive in the future.
18. Supplemental cash flow disclosure
Changes in operating assets and liabilities:
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, 2022 |
|
||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Receivables |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Prepaid expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Trade and other payables |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
Total changes in working capital items |
|
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
F-16
19. Income taxes
Income tax (recovery) expense:
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, 2022 |
|
||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Current tax (recovery) expense |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Deferred tax (recovery) expense |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Income tax (recovery) expense |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Reconciliation of effective tax rate:
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, 2022 |
|
||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Loss before income taxes |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Basic combined Canadian statutory income tax rate 1 |
|
|
% |
|
|
% |
||
Computed income tax recovery |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Increase resulting from: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Difference in foreign tax rates |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Non-deductible stock-based compensation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Non-deductible change in fair value of warrants |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Non-deductible transaction costs |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Non-deductible goodwill impairment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Non-refundable federal ITC |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Change in valuation allowance |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Other – foreign exchange |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Other |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Total tax (recovery) expense |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net deferred income tax assets as of March 31, 2023, and 2022 were comprised of the following:
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|
March 31, 2022 |
|
||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
||
Deferred tax assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Tax losses carried forward |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Research and development expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Financing expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Licenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Tax credit carry forwards |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Operating lease right of use asset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Other temporary differences |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Deferred tax assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Deferred tax liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Equipment and intangible assets |
|
|
( | ) |
|
|
( | ) |
Operating lease liability |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Other taxable temporary differences |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
|
|
Deferred tax liabilities |
|
|
( | ) |
|
|
( | ) |
Valuation allowance |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
Net deferred tax liabilities |
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
As at March 31, 2023, the amounts and expiry dates of tax attributes and temporary differences, which are available to reduce future years’ taxable income, were as
F-17
follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
March 31, 2023 |
|
|||
|
|
Federal |
|
|
Provincial |
|
|
United States |
|
|||
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|
$ |
|
|||
Tax losses carried forward |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2028 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2029 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2030 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2031 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2032 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2033 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2034 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2035 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2036 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2037 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2038 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2039 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2040 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2041 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2042 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
2043 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
No expiry |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Research and development expenses, without time limitation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Unrecognized tax benefits
The Corporation does not expect a significant change to the amount of unrecognized tax benefits over the next 12 months. However, any adjustments arising from certain ongoing examinations by tax authorities could alter the timing or amount of taxable income or deductions, of the allocation of income among tax jurisdictions, and these adjustments could differ from the amount accrued. The Corporation’s federal and provincial income tax returns filed for all years remain subject to examination by the taxation authorities.
20. Financial instruments
a. Concentration of credit risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Corporation to a concentration of credit risk consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents and investments. Cash and cash equivalents and investments are all invested in accordance with the Corporation’s Investment Policy with the primary objective being the preservation of capital and the maintenance of liquidity, which is managed by dealing only with highly rated Canadian institutions. The carrying amount of financial assets, as disclosed in the consolidated balance sheets, represents the Corporation’s credit exposure at the reporting date.
b. Foreign currency risk
The Corporation is exposed to the financial risk related to the fluctuation of foreign exchange rates and the degrees of volatility of those rates. Foreign currency risk is limited to the portion of the Corporation's business transactions denominated in currencies other than the Corporation's functional currency of the U.S. dollar. Fluctuations related to foreign exchange rates could cause unforeseen fluctuations in the Corporation's operating results. The Corporation does not use derivative instruments to hedge exposure to foreign exchange risk. The fluctuation of the Canadian dollar in relation to the U.S. dollar and other foreign currencies will consequently have an impact upon the Corporation’s net loss.
c. Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk is the risk that the Corporation will encounter difficulty in meeting the obligations associated with its financial liabilities that are settled by delivering cash or another financial asset. The Corporation manages liquidity risk through the management of its capital structure and financial leverage. It also manages liquidity risk by continuously monitoring actual and projected cash flows. The Board of Directors reviews and approves the Corporation's operating budgets, and reviews material transactions outside the normal course of business. The Corporation currently does not have long-term debt nor arranged committed sources of financing and is operating via use of existing cash and short-term investment balances. Refer to Note 1 – Nature of Operations.
The Corporation’s financial liabilities obligations include trade and other payables, which fall due within the next 12 months.
F-18
21
Research and development contracts and contract research organizations agreements
We utilize contract manufacturing organizations, for the development and production of clinical materials and contract research organizations to perform services related to our clinical trials. Pursuant to the agreements with these contract manufacturing organizations and contract research organizations, we have either the right to terminate the agreements without penalties or under certain penalty conditions.
Supply contract
On October 25, 2019, the Corporation signed a supply agreement with Aker Biomarine Antarctic. (“Aker”) to purchase raw krill oil product for a committed volume of commercial starting material for CaPre for a total fixed value of $
Legal proceedings and disputes
In the ordinary course of business, the Corporation is at times subject to various legal proceedings and disputes. The Corporation assesses its liabilities and contingencies in connection with outstanding legal proceedings utilizing the latest information available. Where it is probable that the Corporation will incur a loss and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated, the Corporation records a liability in its consolidated financial statements. These legal contingencies may be adjusted to reflect any relevant developments. Where a loss is not probable or the amount of loss is not estimable, the Corporation does not accrue legal contingencies. While the outcome of legal proceedings is inherently uncertain, based on information currently available, management believes that it has established appropriate legal reserves. Any incremental liabilities arising from pending legal proceedings are not expected to have a material adverse effect on the Corporation’s financial position, results of operations, or cash flows. However, it is possible that the ultimate resolution of these matters, if unfavorable, may be material to the Corporation’s financial position, results of operations, or cash flows. reserves or liabilities have been accrued as at March 31, 2023.
22. Subsequent events
In May 2023, the Corporation communicated the decision to terminate its Canadian employees as part of discontinuing its operations in Canada and the rebuilding of a leaner organization in the United States, which resulted in $
F-19